
|
| Custom Depth Pass |
Table Of Contents
This shader allows you access different aspects of the shading state for various shading effects, debugging, or AOV output.

|
| Custom Depth Pass |
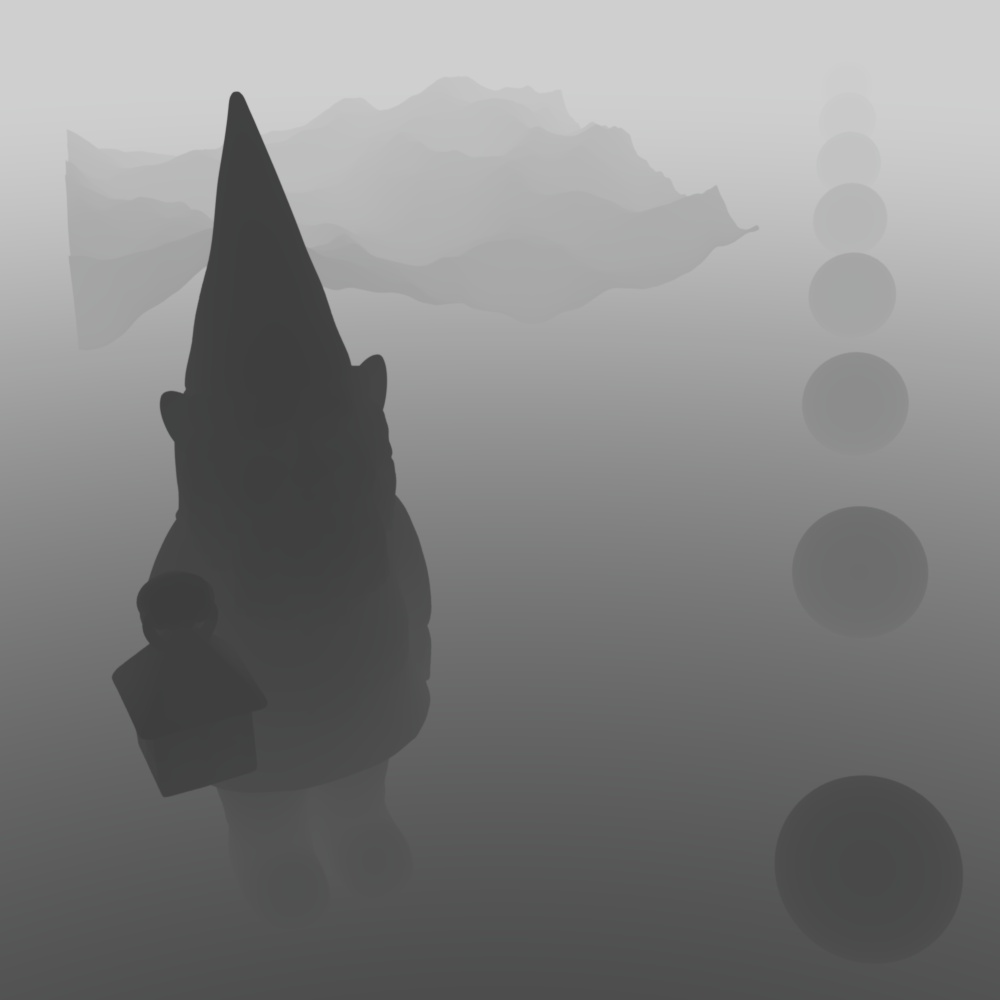
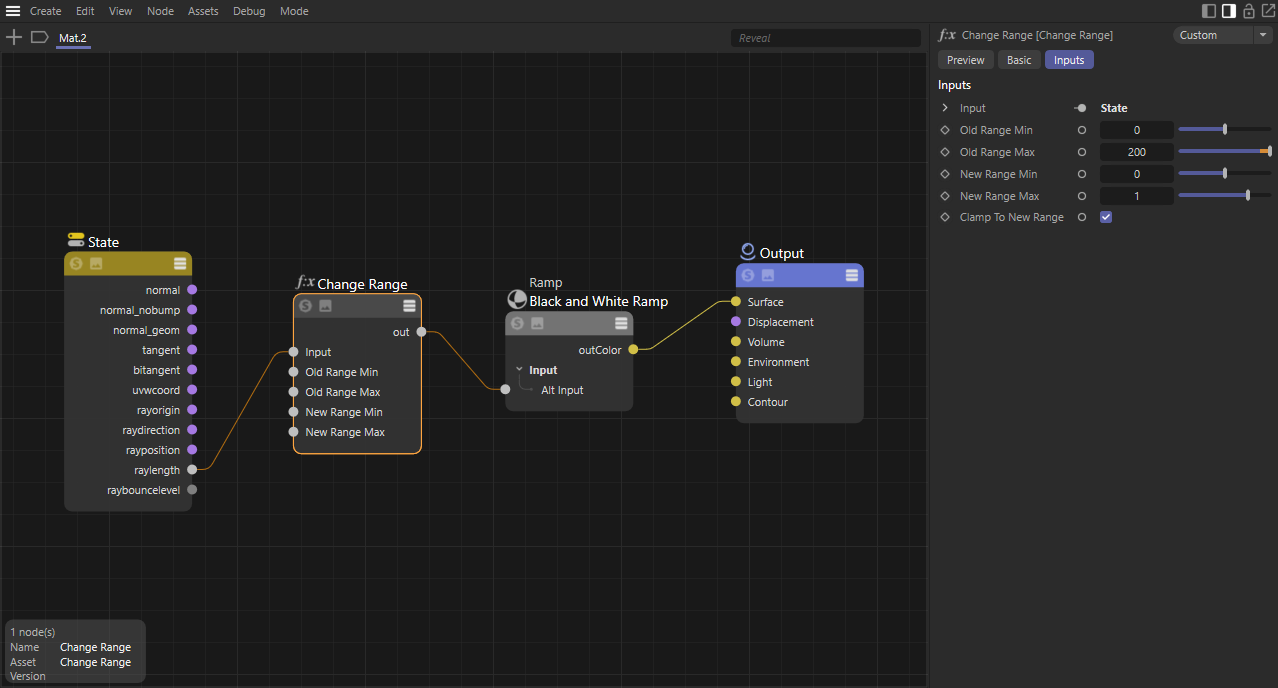
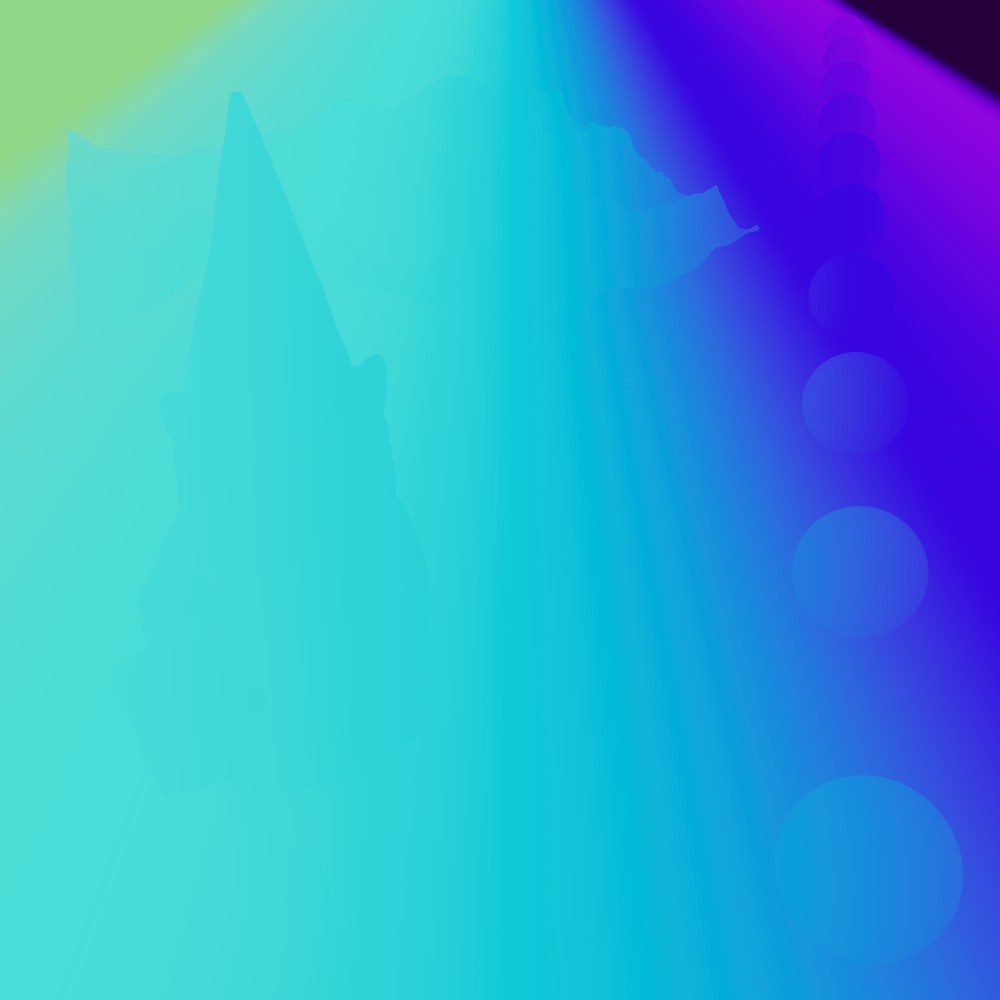
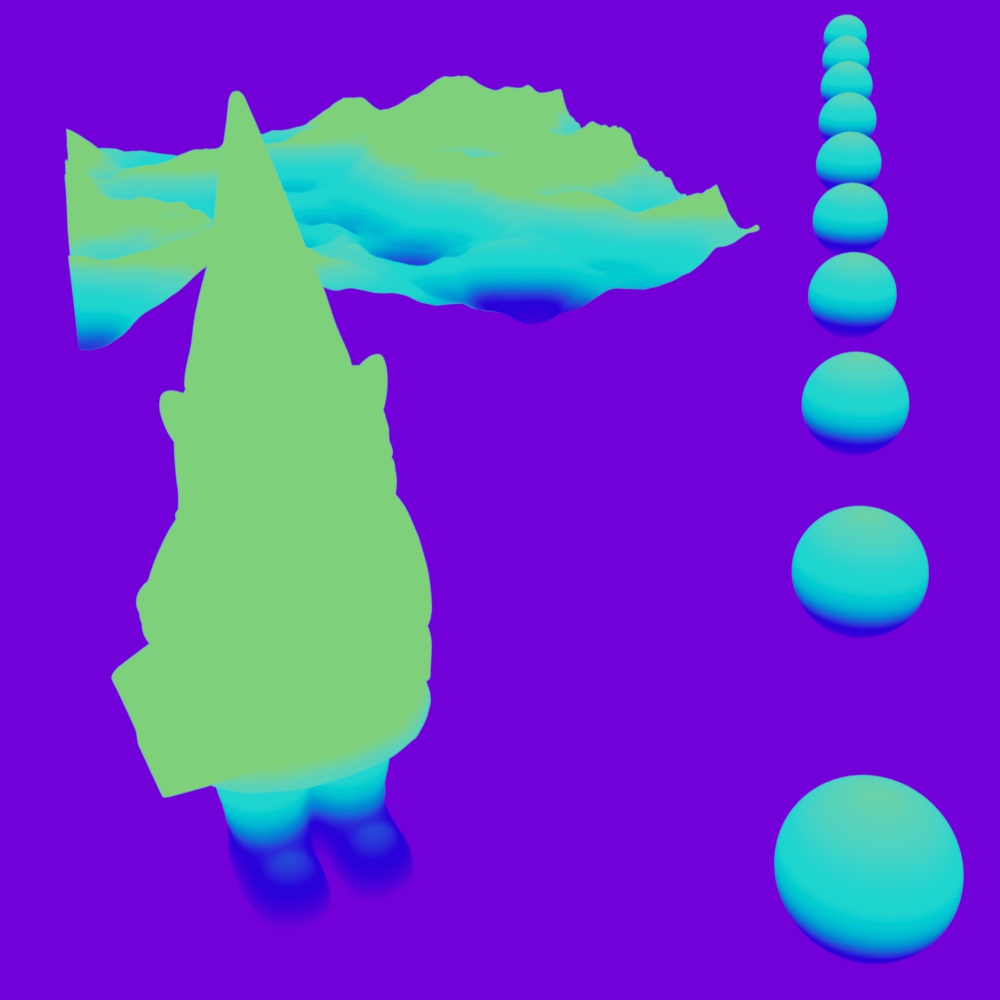
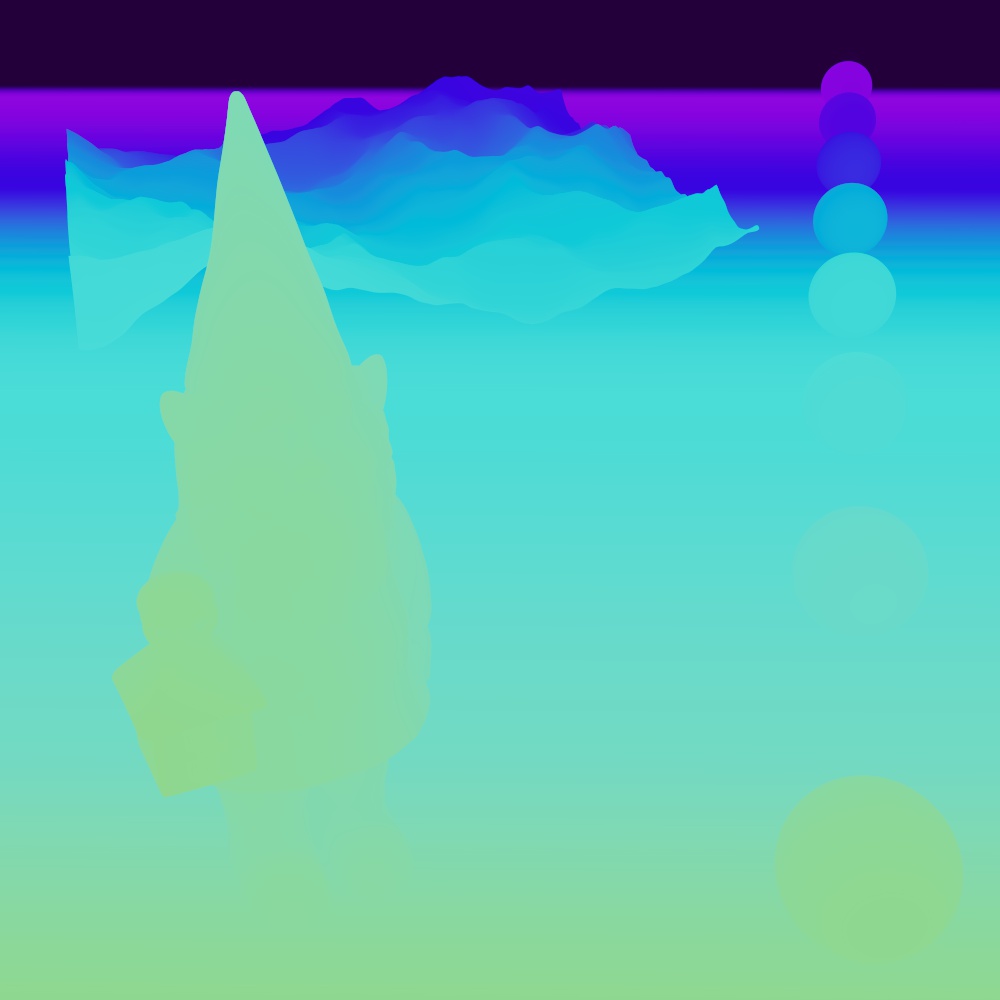
A custom depth pass can be created by using the ray length output into a Change Range node which is used to drive a black and white ramp. The ray length produces the distance an object is from the camera so the change range input should be set to the maximum depth in scene units to the minimum distance to control the farther and nearest points of the depth pass. The output range should be set to 0 to 1 which is fed into the ramp in order to color the depth from white to black. This same process can be used for other camera distance effects, like changing the thickness of contour lines based on distance.
|
|
|
|
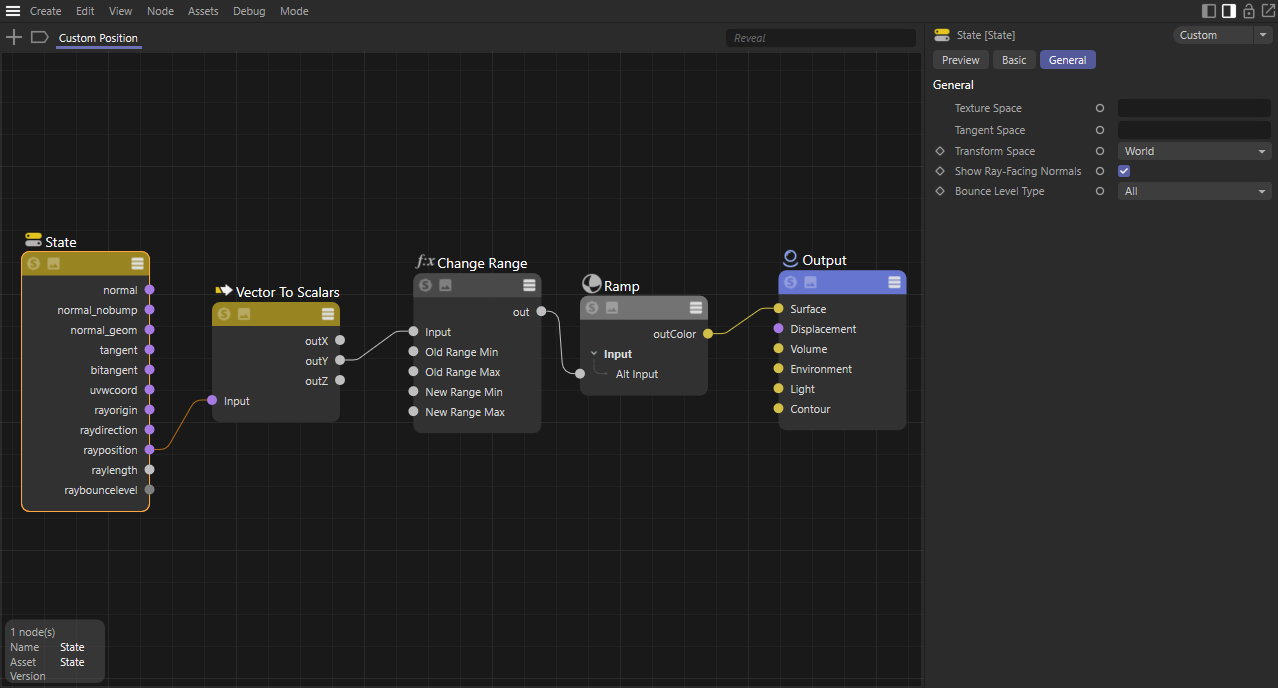
| Custom World Position Axis: X Color Channel: Red |
Y Green |
Z Blue |
A custom axis gradient can be created by using the ray position output with the State node in Transform Space: World mode. The ray position produces a vector so it should be split in order to isolate an axis to drive a change range node. The change range input controls the range of the gradient in scene units and the output should be set from 0 to 1 which is used to drive a color ramp.
|

|
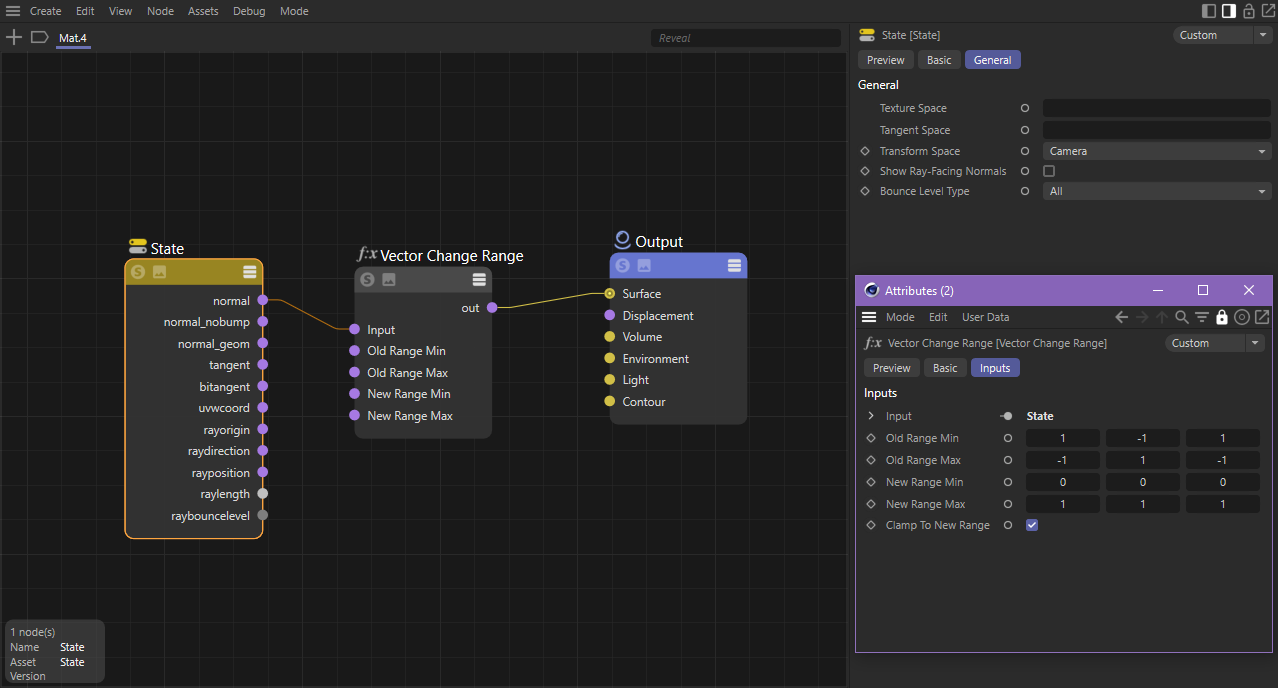
| Camera Space Normals |
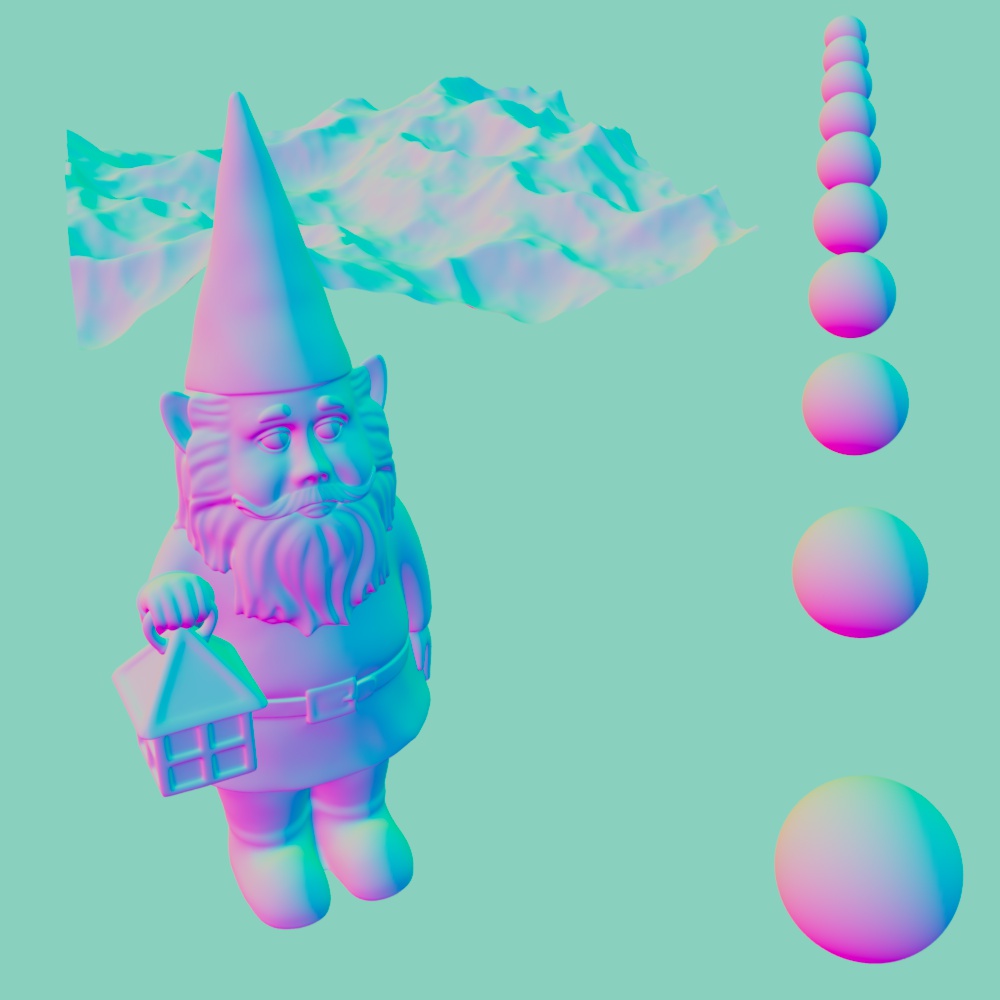
A camera space normal pass can be created by using the normal output with the State node in Transform Space: Camera mode. The normal output should be remapped using a vector change range with the following values:
| Old Min | Old Max | New Min | New Max | |
| X | 1 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| Y | -1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Z | 1 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
|
|
|
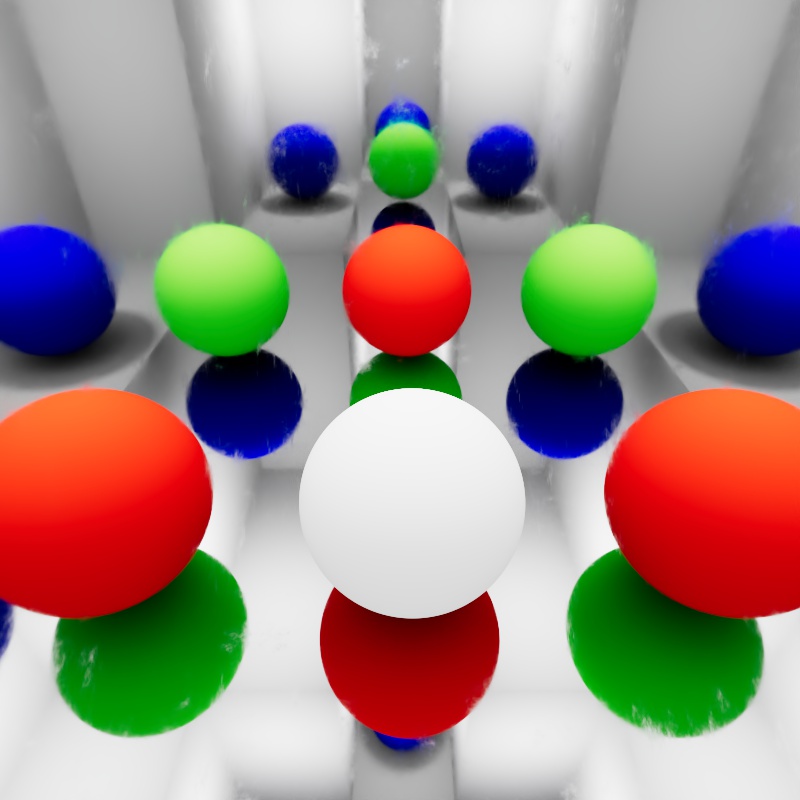
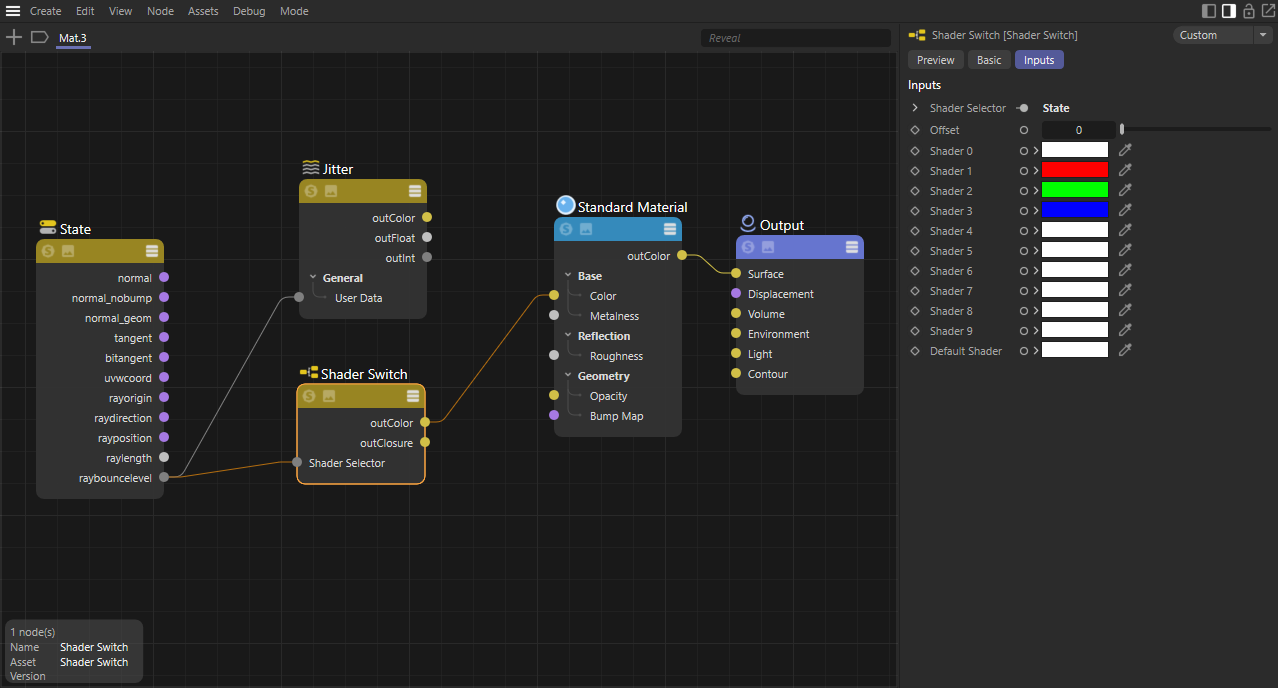
| Reflection Bounce Level with RGB Shader Selector Reflection Trace Depth: 3 |
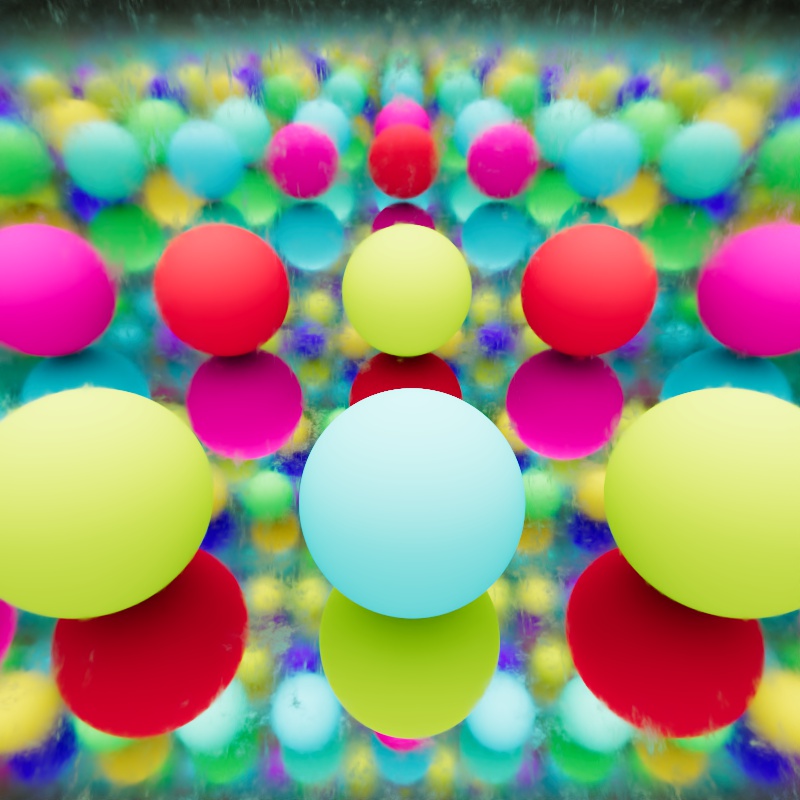
Reflection Bounce Level with Color Jitter Reflection Trace Depth: 63 |
The Ray Bounce Level output gives you control over what happens on each bounce of a certain ray type. In the above example, a single sphere sits in a mirrored room and the example shader is only applied to the sphere. The Bounce Level Type is set to Reflection and the ray bounce level output is used to drive a shader selector which colors the Base Color. Slot 0 is left white and slots 1 through 3 are red, green, and blue resulting in a different color for each reflection that shares the same number of bounces. In the RGB example the trace depth is limited to 3, the white sphere is the original sphere and it is left white because it is seen directly with a primary ray — however, the first reflection of that sphere is red, the reflection of the red reflections are green, and the third and final reflections of those reflections are blue.
In the color jitter example, the reflection trace depth has been increased to 63 and the ray bounce level output is now used to drive a jitter node set to User Data mode. This results in a random color value for each reflection bounce and it also randomly colors the primary ray used for the original sphere which is seen here as light blue.
|
|
The name of the uv map channel to read the uvw state from.
The name of the uv map channel to read the tangent/bitangent state from.
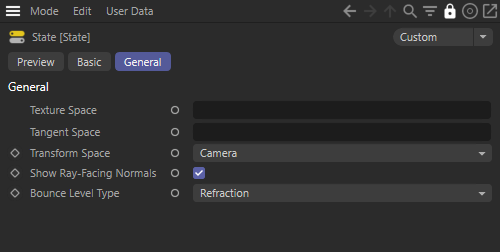
This option ensures that normals are always corrected to be ray-facing, which is how lighting on back-facing surfaces is computed internally in Redshift. When this option is disabled, the normals will not be corrected and will represent the true orientation of the surface. Disabling this option is useful for debugging.
Controls which ray type is used for the "raybouncelevel" output state from the following options.
|
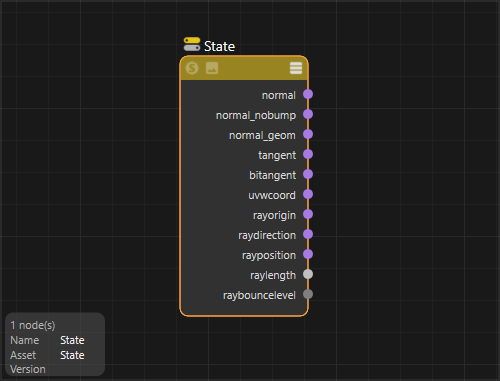
The shading normal, with bump mapping.
The shading normal, without bump mapping.
The geometric normal.
The tangent as read from the UV Set / Tangent Space channel, if available.
The bitangent as read from the UV Set / Tangent Space channel, if available.
The uvw coordinate as read from the UV Set / Texture Space channel, if available.
The origin of the ray that has intersected this surface.
The direction of the ray that has intersected this surface. This vector has been normalized.
The position of the ray intersection on this surface. Helpful for positioning effects within the scene.
The length of the ray that has intersected this surface. Helpful for distance based outputs, like scene depth.
Outputs the number of ray bounces for the specified ray type. This can be used to control how each shading bounce looks.