 Shader
Shader
Shader
Note also the Shader Field, which works similarly within the Field functionality.
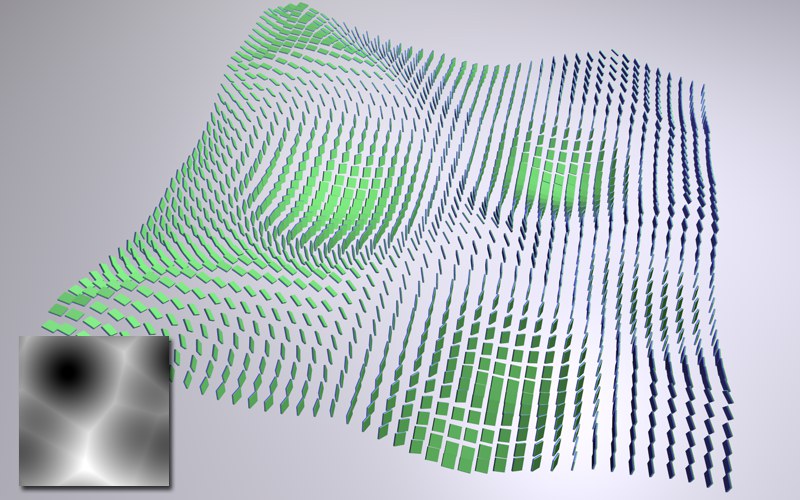 Above, a noise (Voronoi) is used to define position
and rotation of the clones via its gray scale values.
Above, a noise (Voronoi) is used to define position
and rotation of the clones via its gray scale values.
The Shader Effector primarily uses a texture’s gray scale values to transform clones. To do this, the texture somehow needs to be projected onto the clones. UV-mapping is used in place of Material tags.
The Shader Texture can also be used to color clones (as well a Lights!) directly. Simply define the following:
- A texture in the Shading tab (faster method) or
- Drag a material containing a texture in a texture channel onto the Shader Effector and select the corresponding texture channel in the Shading tab’s Channel menu. In case you have several Material tags, simply drag the corresponding tag into the Material tag field. (offers better projection control).
When using linear or radial clone modes, we recommend using the 2D-UColor Gradient shader.
The Shader Effector serves well as a basic Effector if, for example, you only want to influence the clones based only on their position, scale and angle falloff settings. Make sure no shader or Material tag has been loaded in the Shader tab.
The Shader Effector is also effective for creating attractive, random, discreet values. So, what exactly does that mean?
 From left to right: Cloned surface; Shader Effector
with noise; Shader Effector with noise and additional Colorizer.
From left to right: Cloned surface; Shader Effector
with noise; Shader Effector with noise and additional Colorizer.
Let’s say you want to clone a surface in a grid array and the clones should be randomly rotated in 90-degree steps. The Shader Effector (Parameters tab: W.H = 360°) can be used to create a random grayscale dispersion that will reduce the colorizer to 4 discrete gray tones:
- Create a Layer Shader in the Shading tab.
- Create a Noise Shader (Cell Noise; lower the Global Scale value) in the Layer Shader and subsequently an Effector Colorizer (Effect button).
- Adjust the Colorizer to match the gradient shown above (all tags white, intensity set to: 100, 75, 50 and 25 percent, respectively).
Since the levels of intensity are defined in steps of 25% the Shader Effector can only rotate the clones randomly by 0, 90, 180 or 270 degrees. Using this method, any random discrete value can be generated. All you have to do is match the colorizer gradient to the number of steps involved.