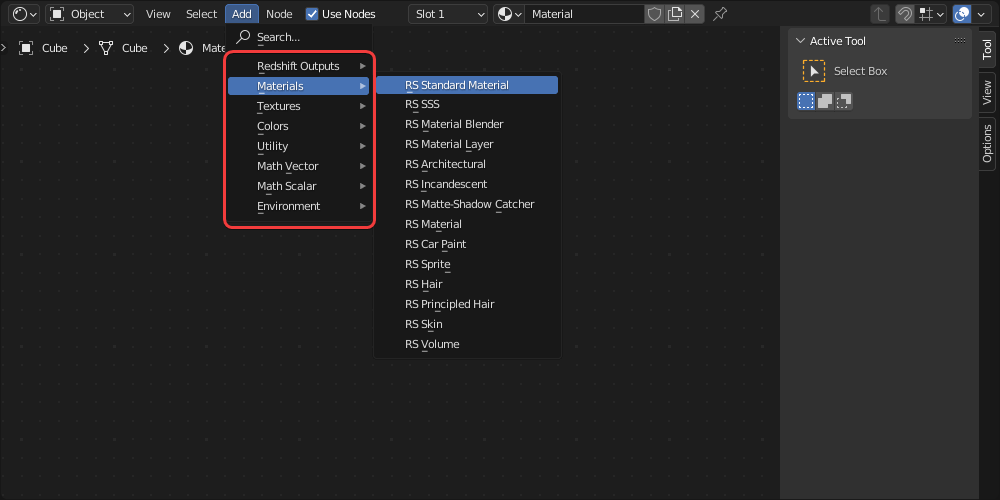
Blender Materials
Redshift for Blender is compatible with all core Redshift materials and textures.
For more information on these node please see the Shaders section.

|
| List of available Redshift shaders |
Redshift for Blender is also compatible with two Blender shading nodes:
BL Color Ramp
BL Vector Curves
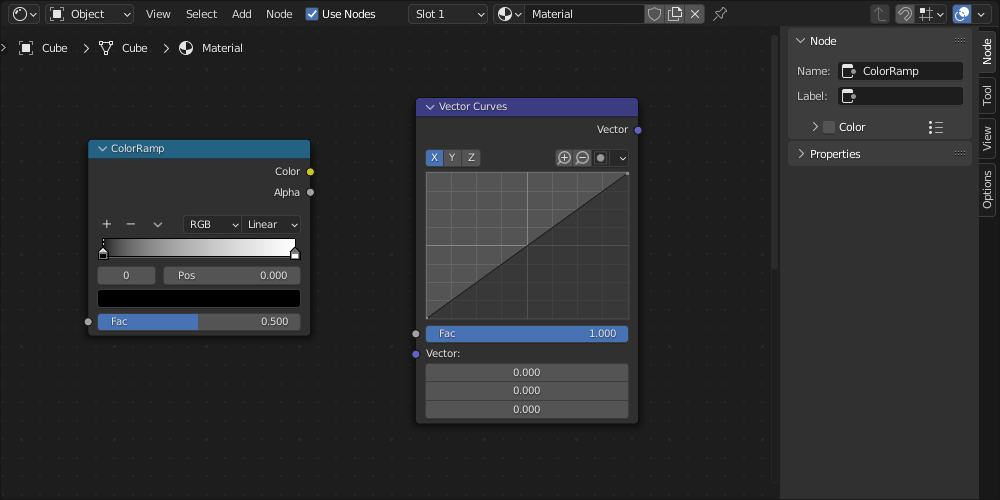
|
| Compatible Blender shading nodes |
With an object selected create a new Blender material by clicking on the "New" button in the Materials Properties panel outlined below.

|
| Creating a new Blender material |
Now a Blender material has been created and linked to the selected object but it is not yet ready for rendering a Redshift material.
To set it up for a Redshift material click on the "Add RS Nodetree" button.
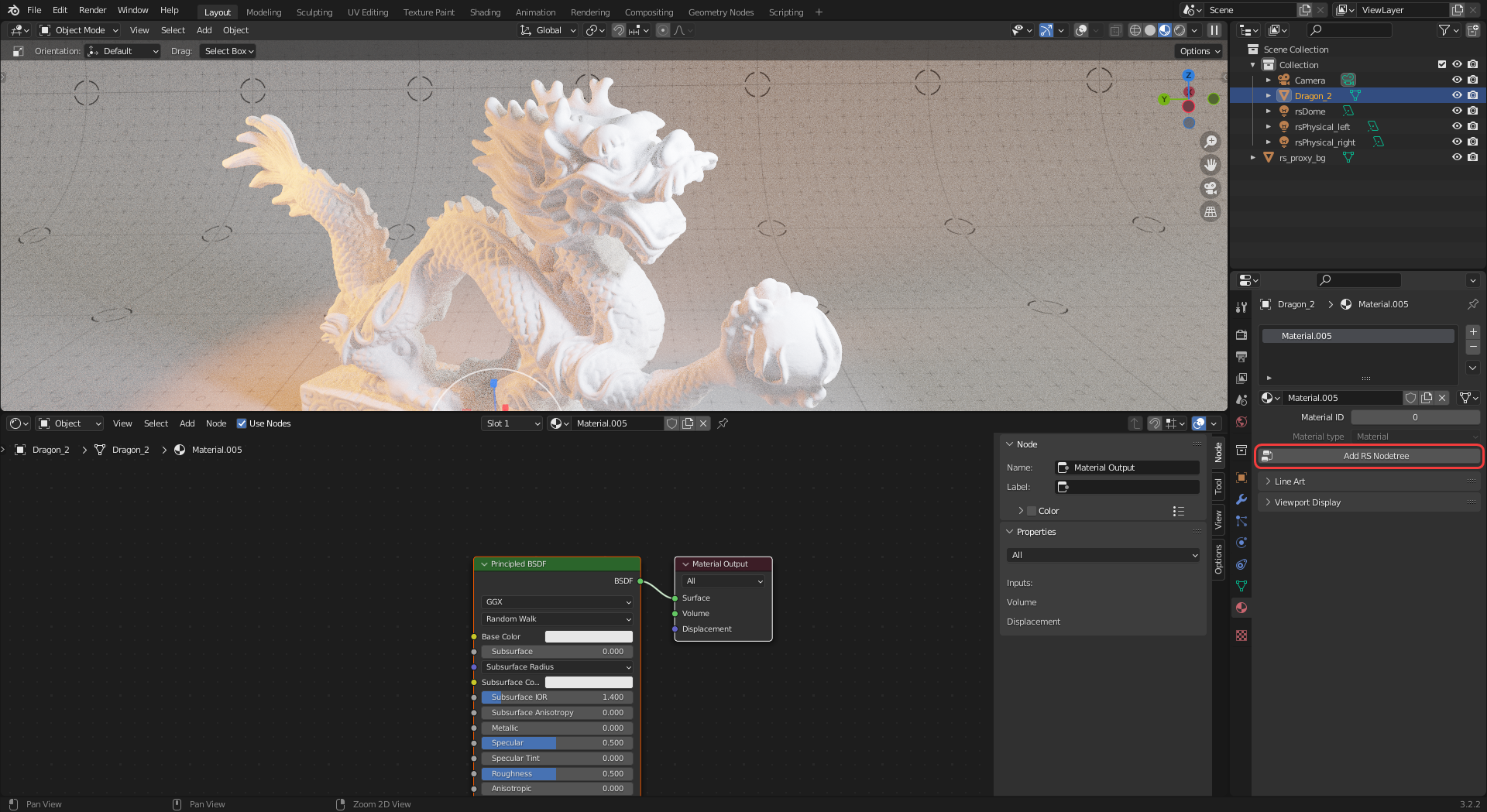
|
| Add RS Nodetree button |
This will create a simple Redshift shader network with a Redshift Material connected to a Redshift Material Output node.

|
| Default Redshift shader network |
From this point a custom Redshift shader network can be created using any of the available Redshift shading nodes.
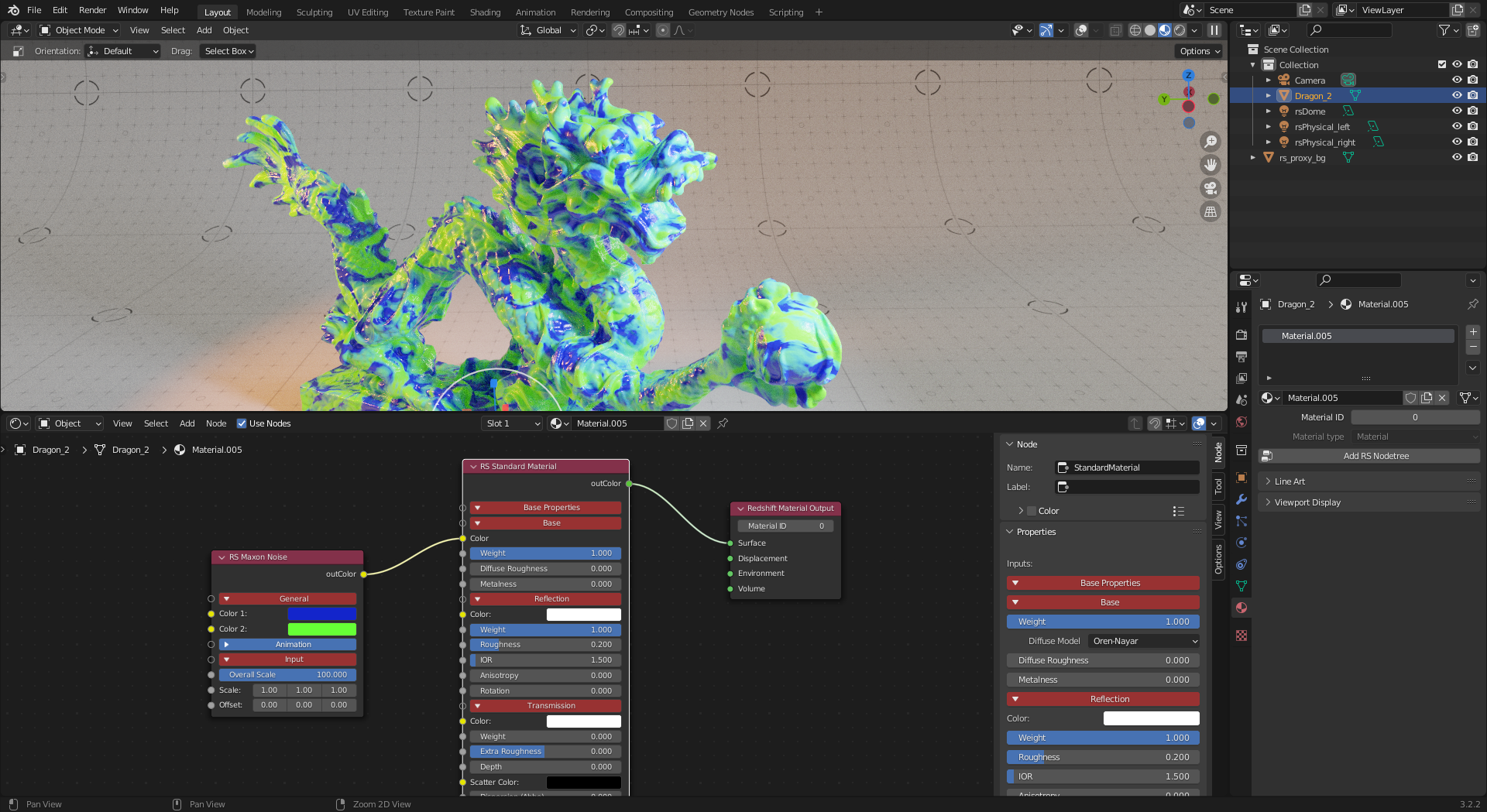
|
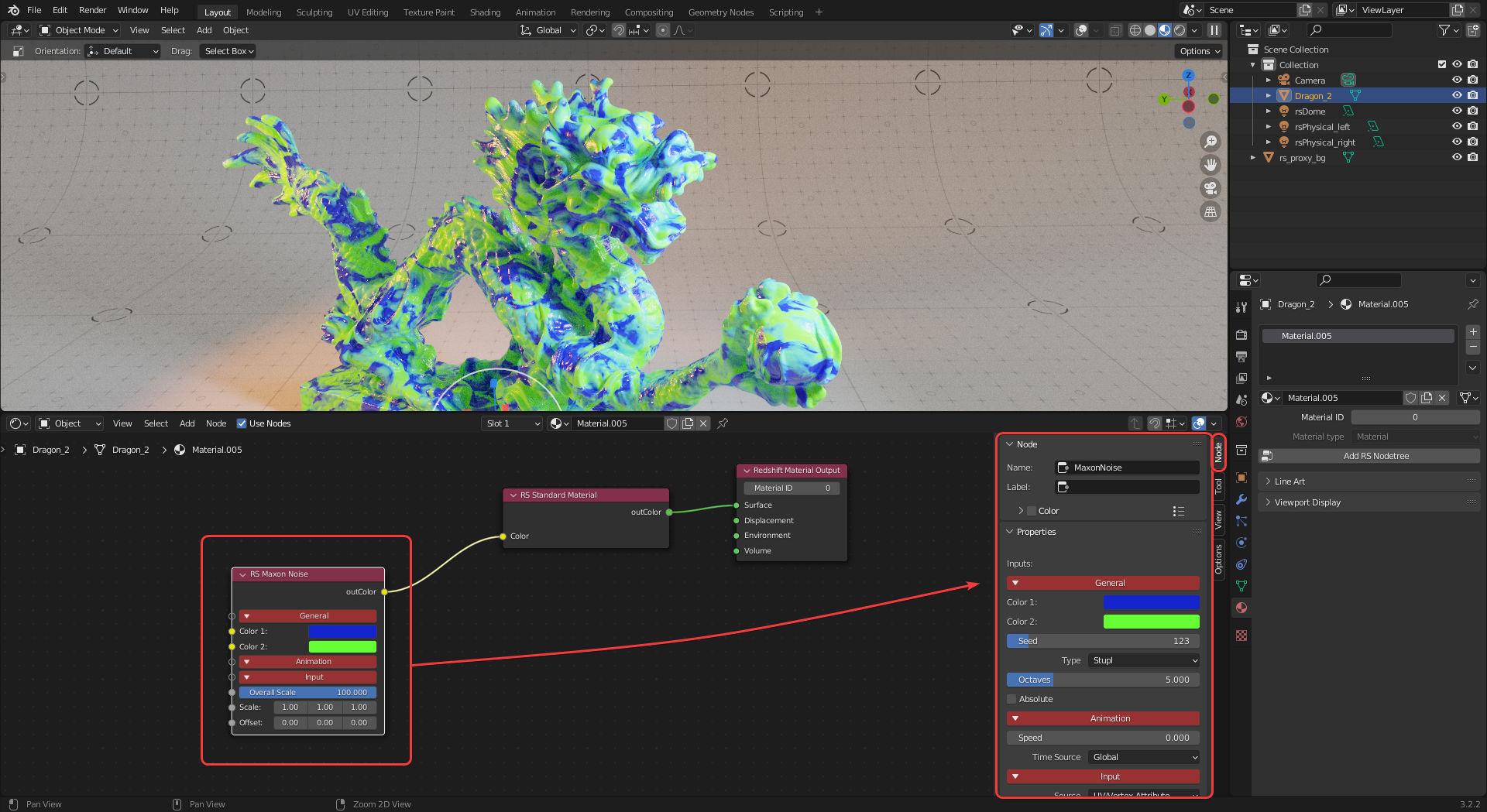
| Maxon Noise texture driving the base color of a Redshift Standard Material |
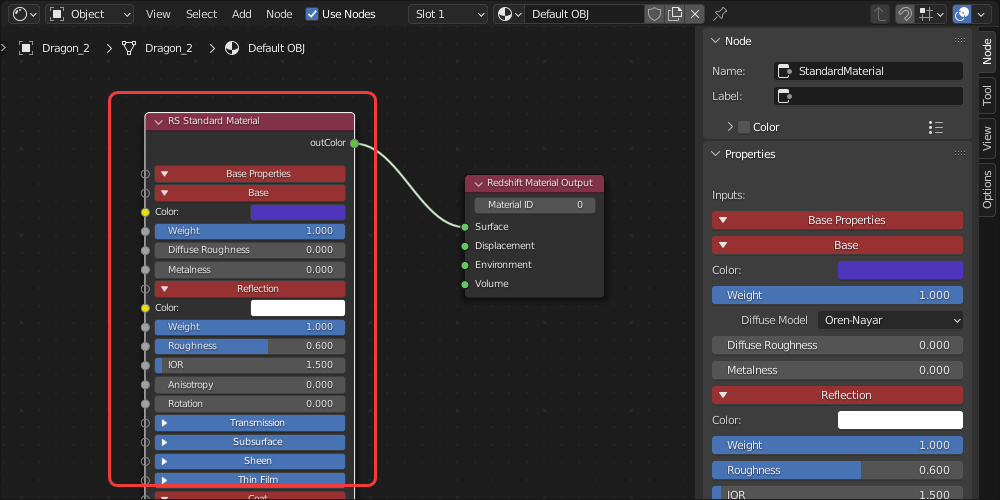
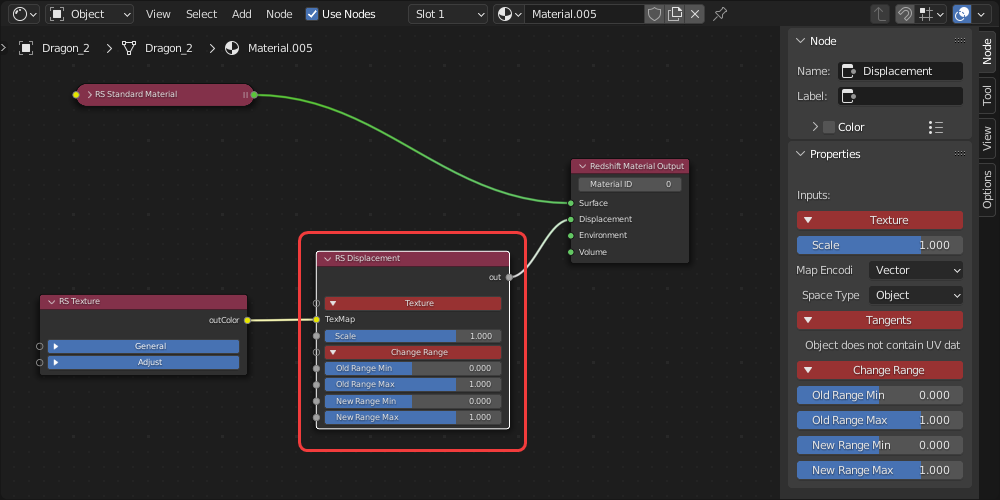
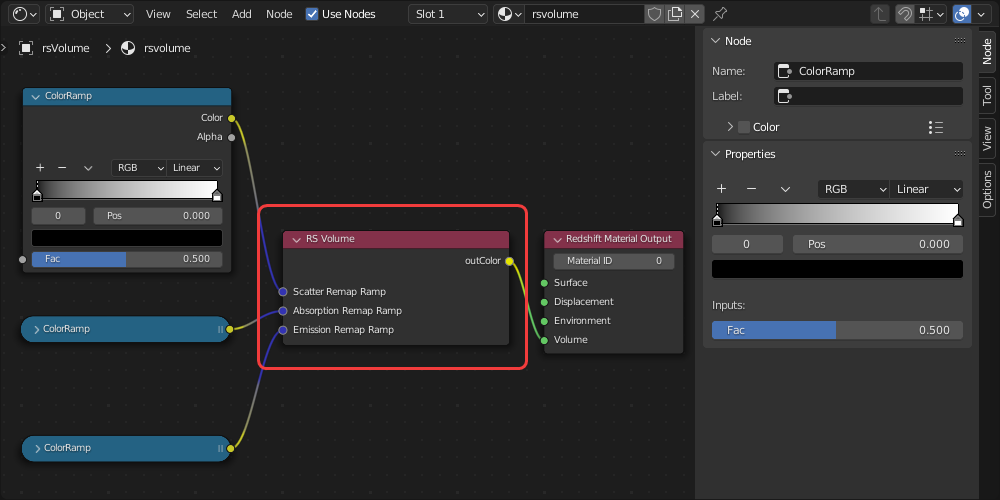
The Redshift Material Output node is required for materials in Redshift, its inputs control the final output.
Surface input - Controls which material is rendered on the object.
Displacement input - Used with a displacement or displacement blender node.
Environment input - Used with an environment shader for use with that specific material.
Note: Any dome light in a scene will override an environment shader.
Volume input - Used for connecting a volume shader for volumetric rendering
|
|

|
|
| Surface input example | Displacement input example | Environment input example | Volume input example |
Most material adjustments should be done in the Shader Editor. Individual nodes frequently have more parameters to tweak in the Node panel on the right side of the shader editor as seen in the image below. For example, the Maxon noise node's "noise type" must be changed from the node panel rather than in the working area of the shader editor.
|
| Maxon Noise texture driving the base color of a Redshift Standard Material |
Normal Maps in Blender
Calculating and exporting an object's tangents is a costly operation but it is necessary when using a normal map. Due to this performance cost all objects in Blender have the option 'Skip Tangents' enabled by default. This means that in order for normal maps to render correctly you must first disable the Skip Tangents option. Height field bump mapping will render correctly even when skip tangents is enabled.
Skip Tangents is an object level option that can be found in multiple places like the Object Data Properties panel under the UV Maps section and a Redshift shading node inside a UV relevant section. All of these areas are linked to one another per-object, changing the Skip Tangents option in any location affects the others.
|
|
| Skip Tangents option in Object Data Properties |