Table OF Contents
Introduction
IES stands for Illuminating Engineering Society. The IES data format describes the distribution of light from a point source. Most major manufacturers of lights provide IES profiles which can be downloaded for free on the internet.
Redshift IES lights use IES profiles to define the light's intensity and distribution.
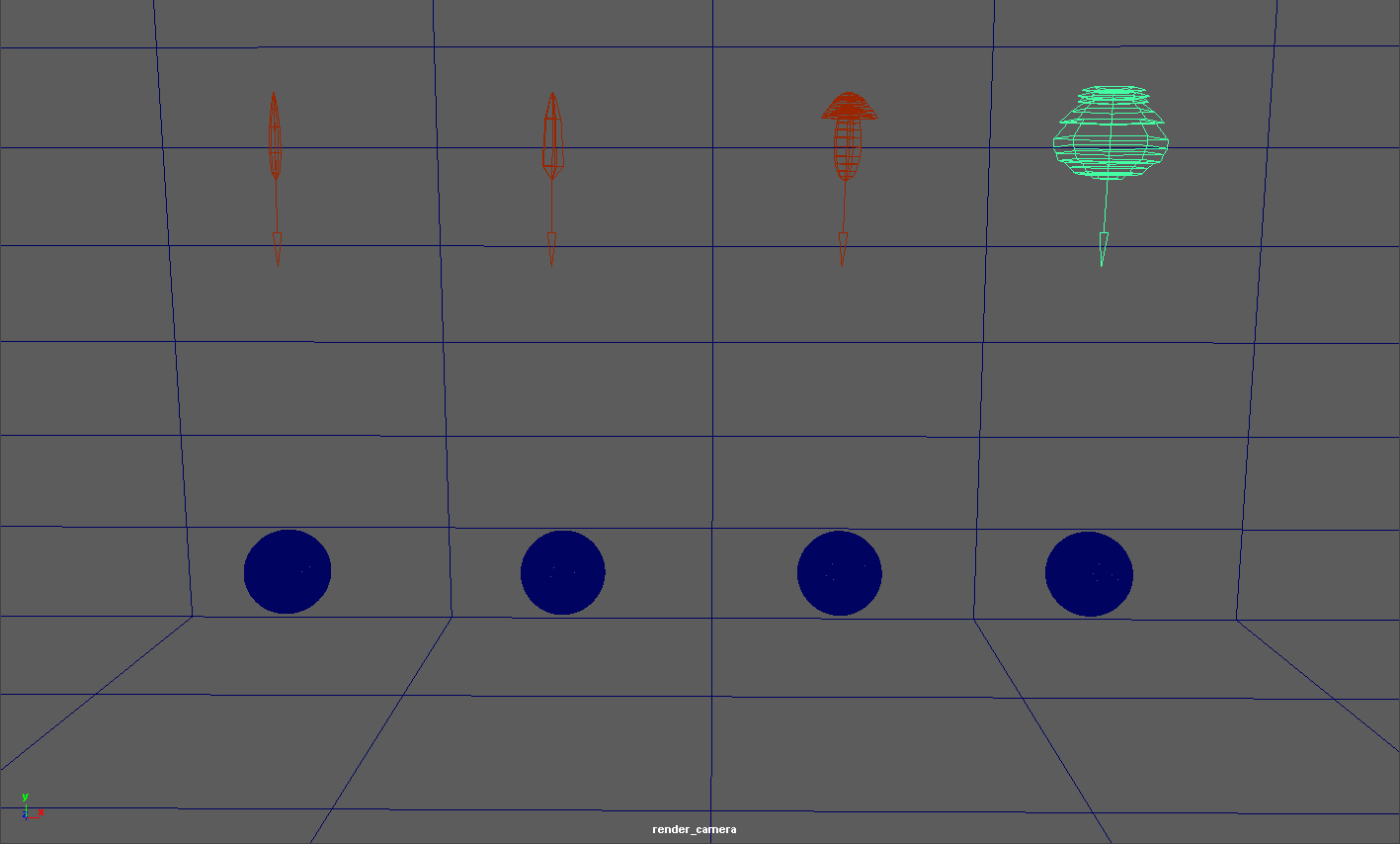
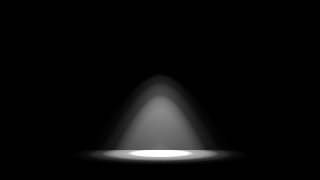
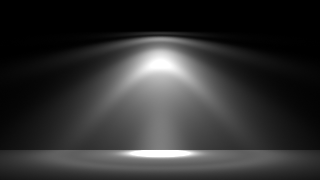
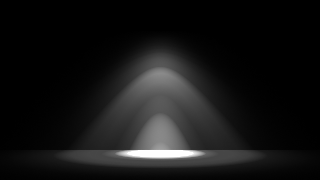
Below are some examples of different IES light profiles, note their drastically different light distribution patterns.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General
On
Turns the light on or off.
IES Profile
Specifies the IES profile to use for the light.
Intensity
Mode
Specifies the color mode.
- Color: Light color is specified by the Color parameter below.
- Temperature: Light color is specified by the Temperature parameter below.
Color
Specifies the color of the light using (R,G,B) values when mode is set to Color.
Temperature
Specifies the color of the light using a color temperature value (in Kelvin) when mode is set to Temperature. Redshift supports color temperatures between 1667K and 25000K. Lower values are 'warmer' or more red, while higher values are 'cooler' or more blue.
Intensity Multiplier
Specifies a multiplier for the light intensities described in the IES profile. This parameter allows you to scale the IES intensity up or down.
Ray Contribution
See Common Redshift Light Parameters.
Shadow
See Common Redshift Light Parameters.
Volume
See Common Redshift Light Parameters.
Photon
See Common Redshift Light Parameters.
IES Light Examples
The example below illustrates some sample IES profiles and their respective light distribution patterns.
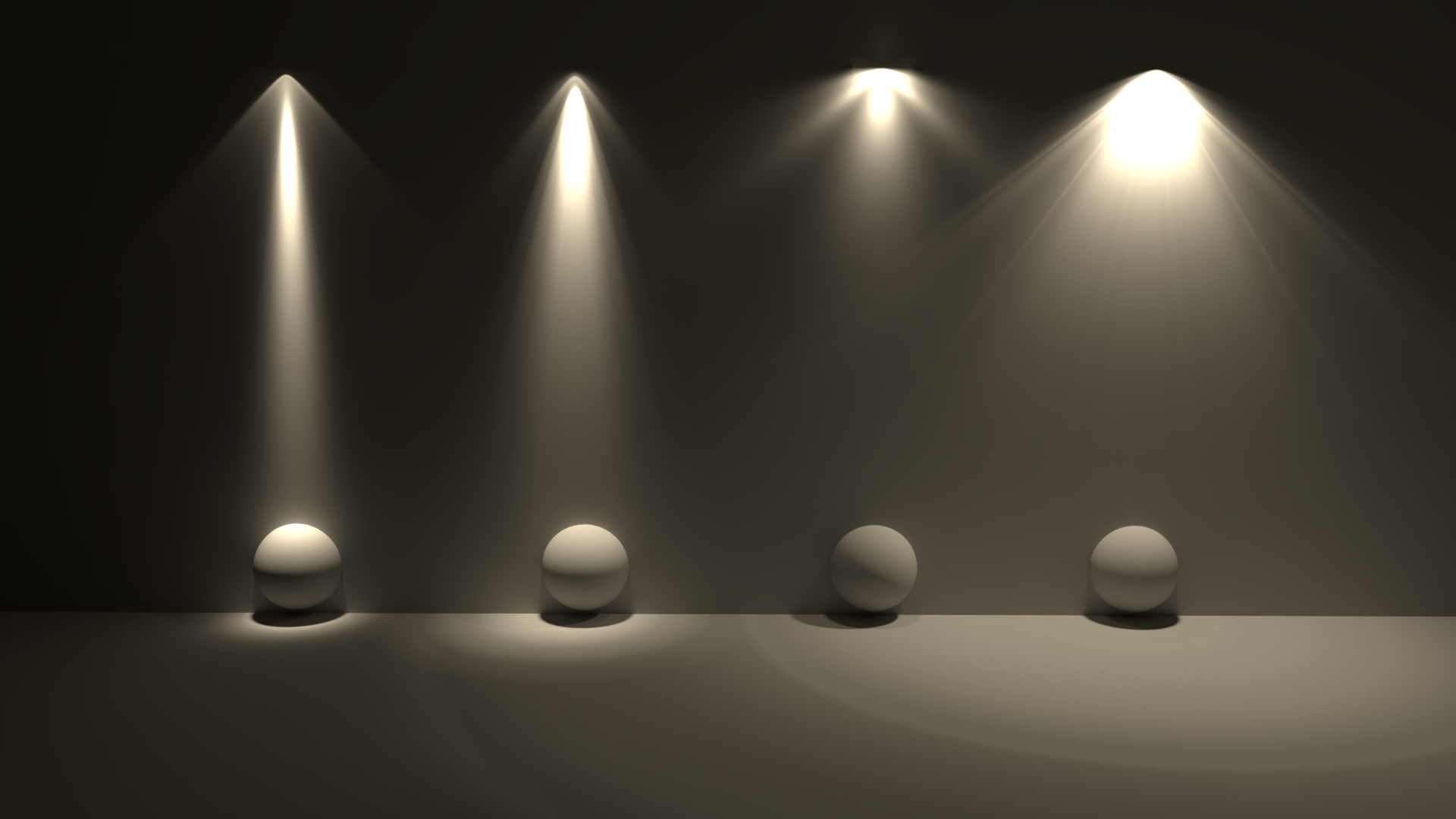
Four different IES lights
Redshift automatically creates a simple geometric shape in the viewport to better that roughly illustrates the IES lights distribution pattern.
Below you can see the viewport of the same scene from above. Note how the shape below mimics the light cast in the example above.