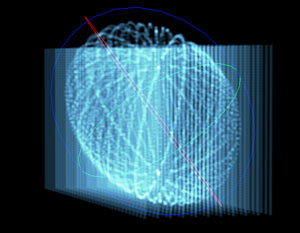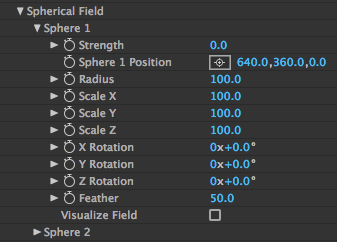
Form
Spherical Field pushes particles toward or away from a spherical volume. This group of controls helps shape the form and integrate it with other graphic elements. For example, Spherical Field can push particles away from an area where a logo is placed. There are two Sphere fields, and they process in order: Sphere 1 first, then Sphere 2.

Strength: Defines the field's power. Strength is the directional displacement amount with which the sphere pushes particles around, making it an important control.
When set to a positive value, Strength creates a field that pushes particles outward and away from the spherical form. When set to a negative value, Strength pulls particles toward the center. Negative attracts, positive repels.
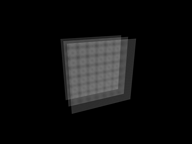
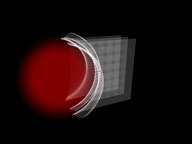
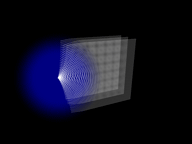
Strength at 0 (left), a positive value (center), and a negative value (right).
Sphere Position: Positions the center of the sphere in 3D space along the x, y, and z axes.
Radius: Defines the size of the Spherical Field for the x, y, and z planes together. Higher values make a larger field.
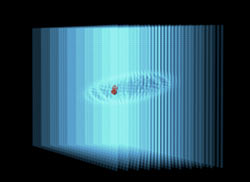
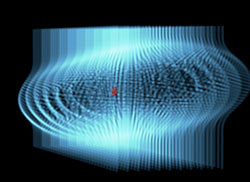
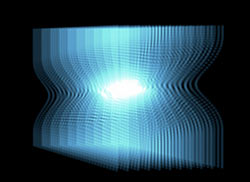
Radius at 30, Strength at 30 (left); Radius at 160, Strength at 30 (center); and Radius at 160, Strength at -30 (right).
Scale X/Y/Z: Scales the diameter of the field on the x, y, or z plane. Higher values make the plane larger.
By default, all Scale values are set to 100, which creates a sphere. By setting different values for Scale X, Scale Y, and Scale Z, you can push a spherical field into any kind of elliptical shape.
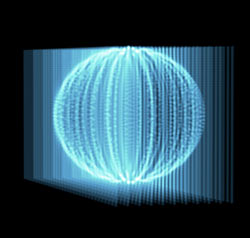
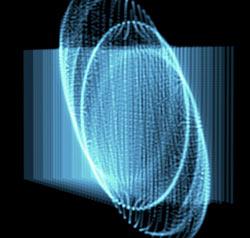
Scale X at 100, Scale Y at 100, Scale Z at 100 (left) and Scale X at 230, Scale Y at 200, Scale Z at 50 (right).
X/Y/Z Rotation: Rotates the elliptical shape in the x, y, and z directions.
Feather: Defines the softness of the edges of the Spherical Field. This feathers the strength of how far the field gets pushed out (or in). Higher values make a softer field.
Visualize Field checkbox: With this checkbox enabled, a visual representation of the field displays. The x plane is in red, y plane is in blue, and z plane is in green. This is turned off by default.