Detailing
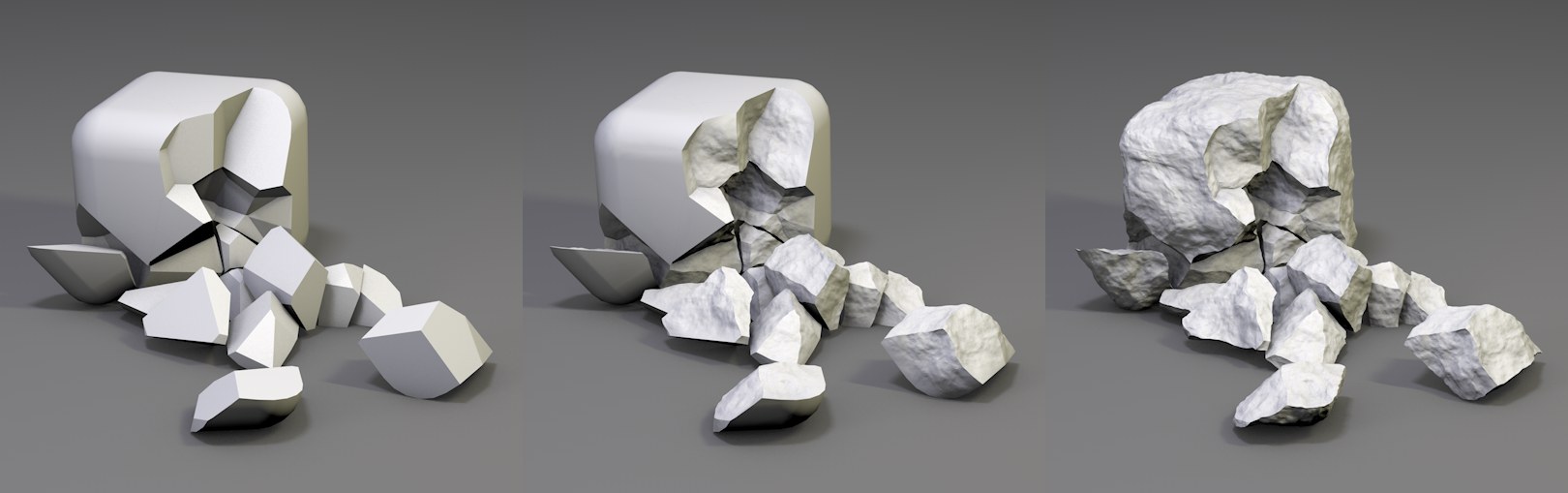 From left to right: without Detailing; with Detailing; with Keep Original Surface disenabled.
From left to right: without Detailing; with Detailing; with Keep Original Surface disenabled.Fragments that are too smooth look unrealistic. These settings can be used to offset the fragment points using an internal noise. The fragments will be subdivided and a Displace object (with a Vertex Map shader) will be used along with a Vertex Color tag that is assigned to each fragment (if you make the Voronoi Fracture object editable, these will be made visible)
Enables or disables the Detailing function (the Displace object will be disabled internally).
Enables or disables the internal Deformer. If disabled, the speed with which the animation is played in the Viewport will increase dramatically (the subdivision will be maintained). The rendered result will not be affected.
Maximum Edge Length [0.1..+∞m]
Each fragment must first be subdivided so the deformation has a sufficient number of points. This is done via triangulation, i.e., triangles are generated. The Maximum Edge Length defines how long an edge length can be. Smaller values will subdivide the fragment increasingly. If very small values are used, the process will be come correspondingly more arduous because very many points will be created for each Deformer.
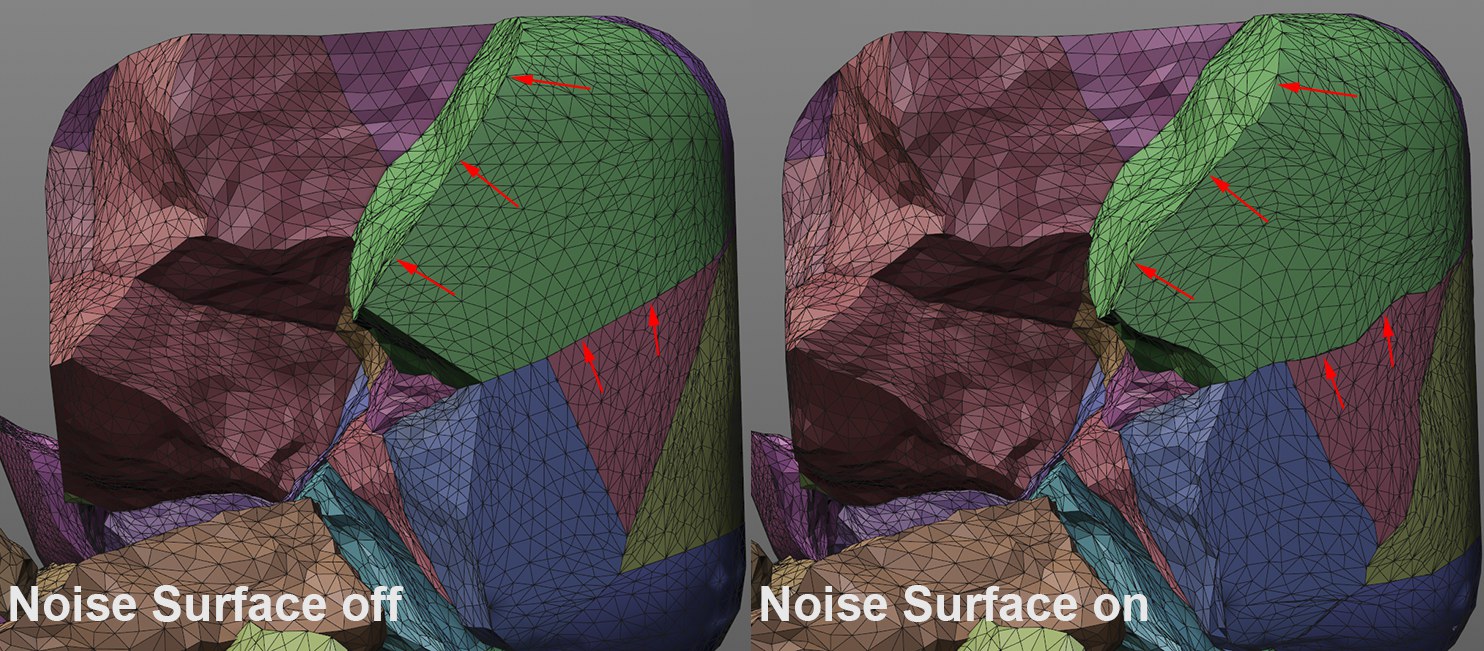 This option can be used to distort the outer edges.
This option can be used to distort the outer edges.Enable this option if you also want the outer surface of the edge fragments to be distorted with regard to their detailing (this will create a jagged outer edge; see marking in the image above). If this option is disabled, only the edges of the inner-lying surfaces (originating from the original object) will be distorted.
Note that the distortion along Phong edges (as well as each angle greater than 90°) of the original object will be stopped and remain unchanged.
Artefact Prevention Strength [1..+∞]
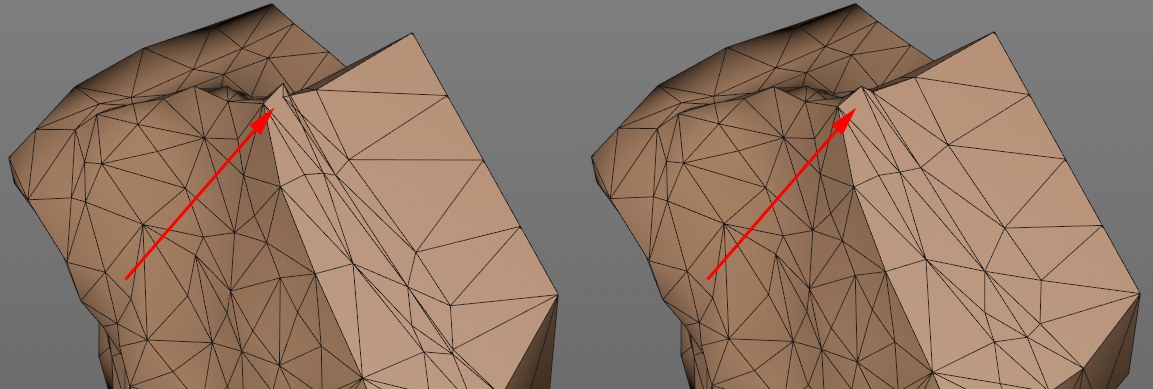
If Noise Surface is enabled, the mesh on the surface of the original outer shape (and beyond) will be distorted. Shading errors can occur if polygons intersect. If larger values are used, the points will be brought correspondingly closer to the original (Phong)fracture edge in the region of the fractured edges, which helps reduce such shading errors.
Note that Phong smoothing plays an important role. The mesh distortion ends, as described above, at Phong edges, i.e., if there are no Phong edges on the outer surfaces (of the original object), this setting has no function.
Internally, Normal tags will be used - these are made visible if the Voronoi Fracture object is made editable - in order to ensure an accurate smoothing of the surfaces (a point’s vertex normals point in the identical direction). If this option is disabled, no smoothing will take place (which can indeed be desired since fractured elements are generally not smooth). If this option is enabled, smoothing will be done in accordance with the following two settings.
If this option is enabled, fractured edges (i.e., edges with Enable Detailing disabled) will never be smoothed and will be maintained. If this option is disabled, smoothing will take place according to the following Phong Angle setting.
If Use Original Edges is disabled, smoothing will take place according to the angle defined here (fracture edges will also be smoothed).
Relax Inside Edges [0..2147483647]
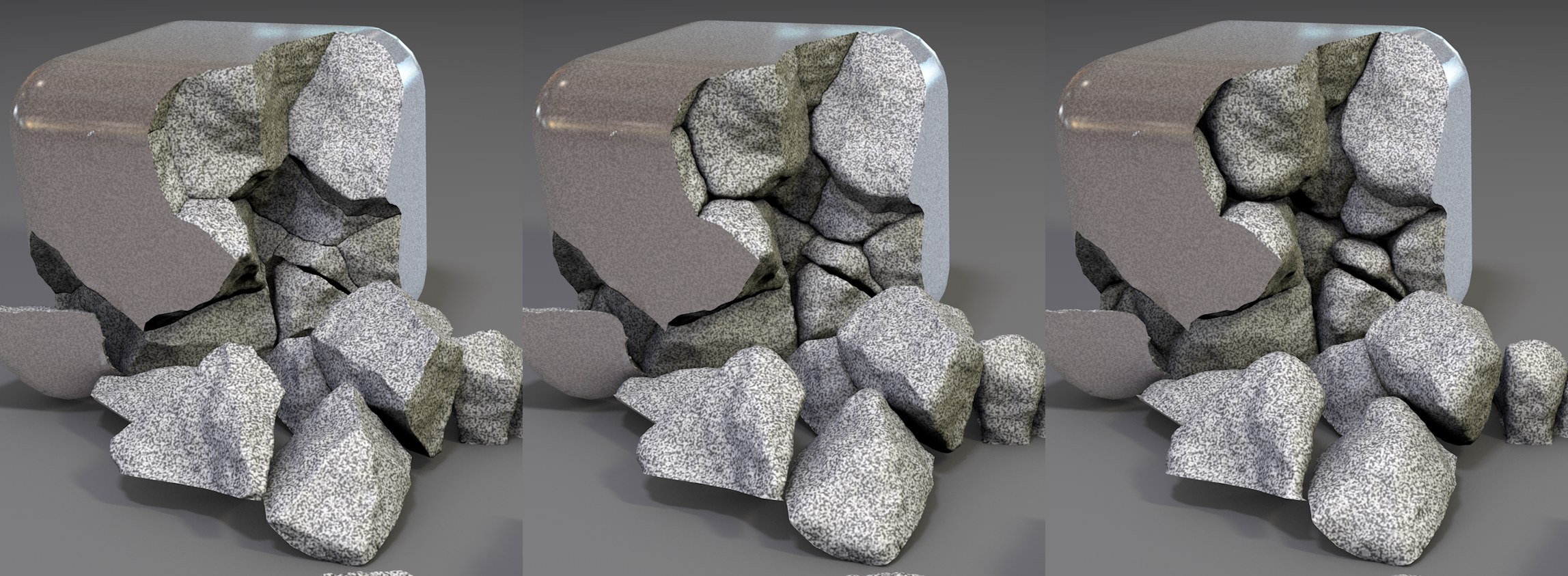 Increasing Relax Inside Edges values from left to right.
Increasing Relax Inside Edges values from left to right.This setting can be used to round inside edges. The larger the value, the more rounded the fragment will be. The fragment’s volume will be correspondingly smaller (without outer edges until it disappears) and the fragments will no longer fit perfectly together.
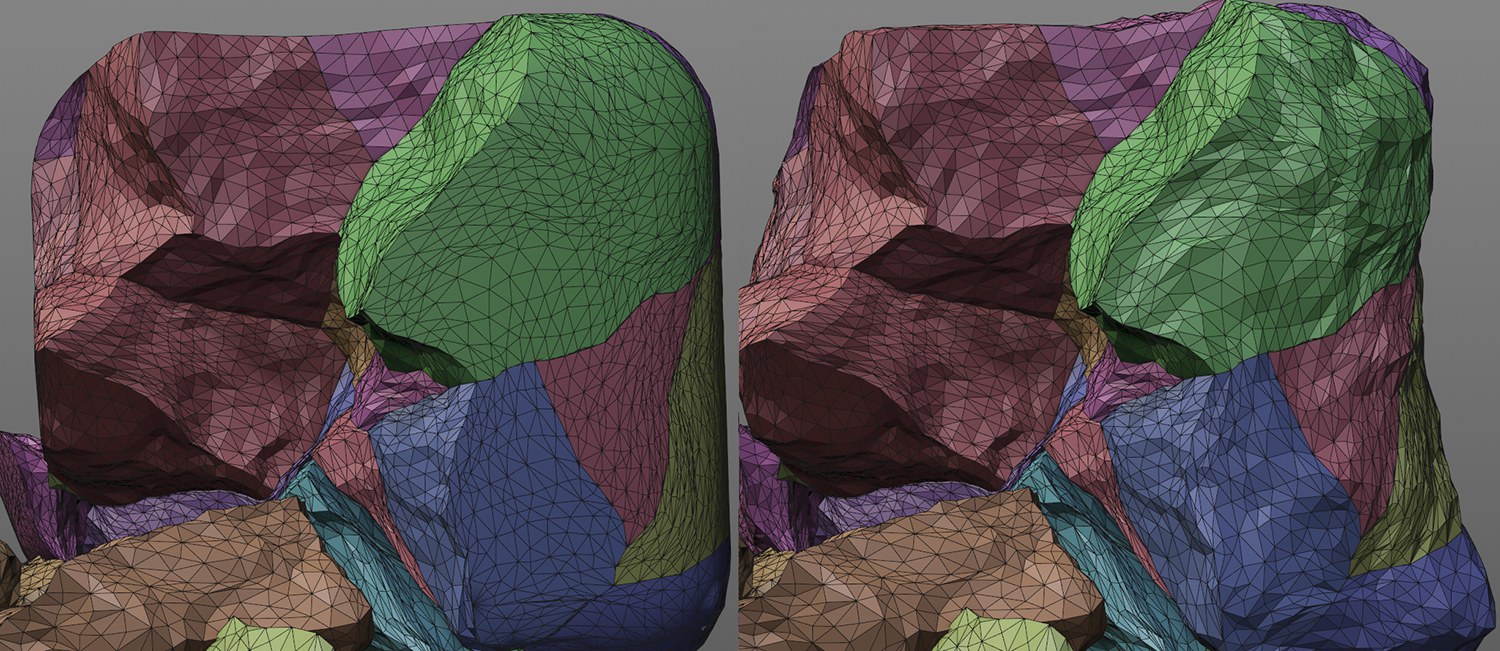 Keep Original Surface enabled on left, disabled on right.
Keep Original Surface enabled on left, disabled on right.Enable this option if you want to maintain the original outer edge shape. Disable this option if the noise should affect all fragment surfaces.
![]() Noise Settings
Noise Settings
Most of the following settings should be familiar to you from the shader noises. Imagine a 3D noise placed over fragments: the fragments’ points will be offset to different degrees according to the grayscale and other settings.
Select a noise noise type the drop-down menu.
This setting defines the strength of the deformation. Negative values can also be used, which will invert the effect accordingly.
This setting defines the random dispersion of noise. Details can be found under Seed.
Generally speaking, this value defines the entangledness of the noise structures. larger values create increasingly detailed fragments (as long as the subdivision allows this).
Global Scale [0..+∞%]
Relative Scale [%]
Use these settings to scale the noise in all directions. Global Scale works evenly in all directions; Relative Scale scales along axes.
This setting can be used to make the noise "billow" internally. The fragments will have an almost organic behavior.
Low Clip [0..100%]
High Clip [0..100%]
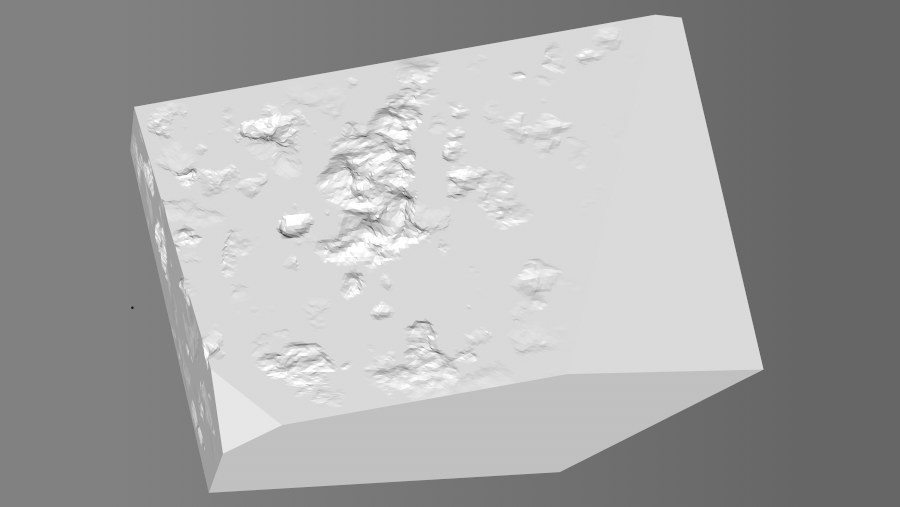
These settings can be used to create plateaus. Grayscale values beneath or above these clip values will be cut off and colored black or white (with no or maximum effect, respectively).
The best results are achieved if you leave these values unchanged.
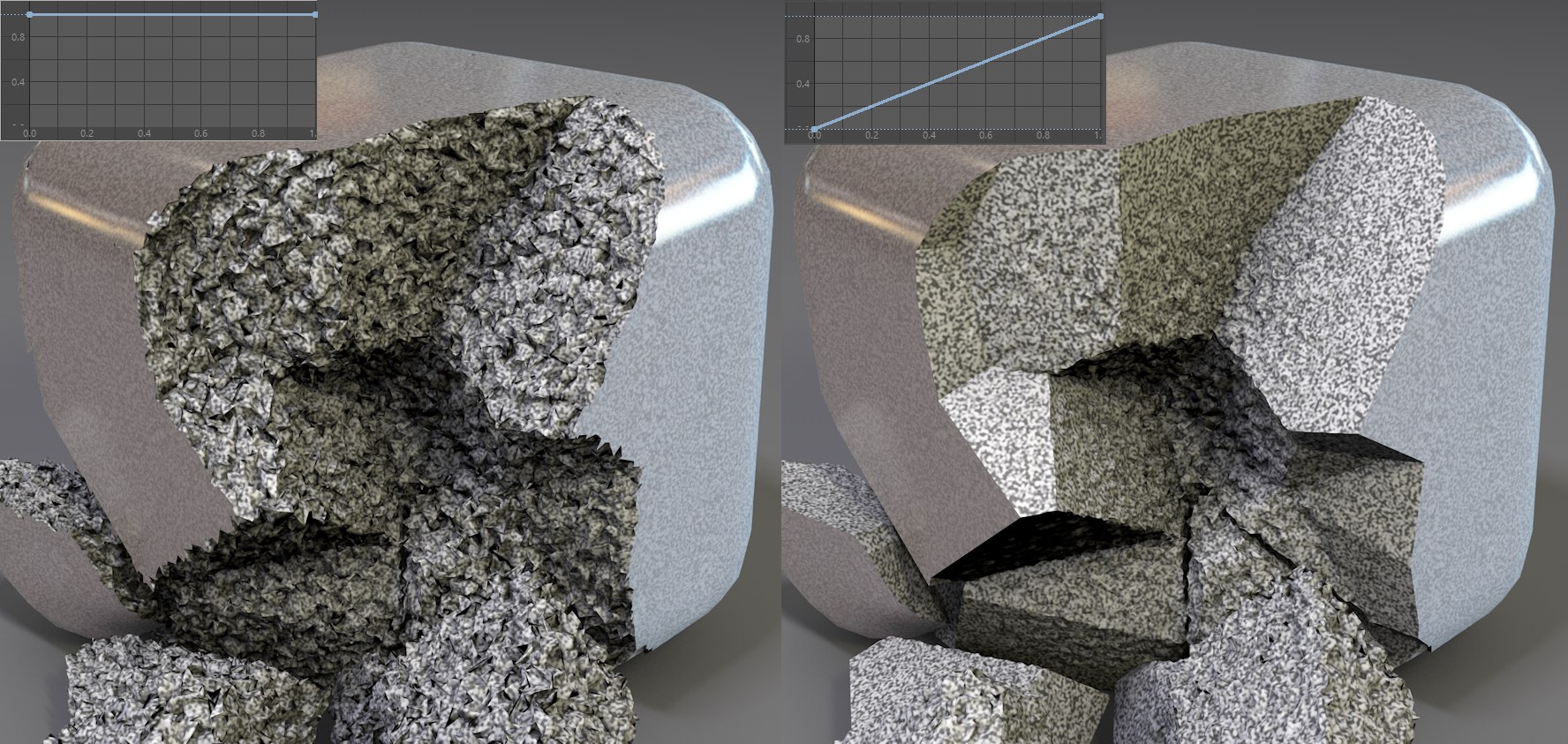 The spline defines the strength of the deformation of the outer surface to the inside.
The spline defines the strength of the deformation of the outer surface to the inside.Normally the deformation affects all fragment regions equally. This spline can be used to define the deformation strength originating from the surface of the original object.