Shader Properties
If Shadows is set to Color, the Shadow gradient influences the color of shadows.
The Diffuse gradient controls the diffuse color of the objects, from areas in total darkness (left end of gradient) to areas which are fully lit (right end of gradient).
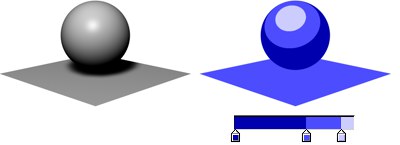 The Diffuse gradient controls the diffuse color of objects.
The Diffuse gradient controls the diffuse color of objects.If you want the lights to generate specular highlights, enable this option.
To use the illumination of each light (not just its direction), enable the Illumination option.
To apply a bump map to the shader, enable this option and define the bump mapping on the material’s Bump tab as you would for a normal material.
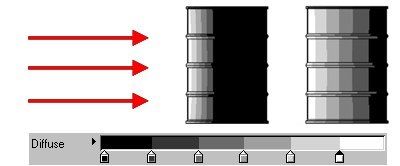 Two oil drums, both lit from the left. Enable Backfacing if you want the gradient to span frontfaces and backfaces, not just frontfaces.
Two oil drums, both lit from the left. Enable Backfacing if you want the gradient to span frontfaces and backfaces, not just frontfaces.Usually the Diffuse gradient controls the color of all frontfaces (i.e. faces which point towards the light), but backfaces simply take the darkest color (i.e. the color at the left edge of the gradient).
If instead you want the gradient to fully control the color of frontfaces and backfaces, enable the Backfacing option. The left edge of the gradient then corresponds to surfaces facing directly away from the light, the right edge corresponds to surfaces facing directly towards the light. Among other things, Backfacing gives you a quick way to create rim light effects.
Enable the Camera option to use the camera as a light source.
To use the lights in the scene as light sources, enable the Lights option. Usually the color of the objects is controlled by the Diffuse gradient. To color the objects using the color of the lights instead, enable the Use Light Color option. The Diffuse gradient then controls the brightness values for the objects.
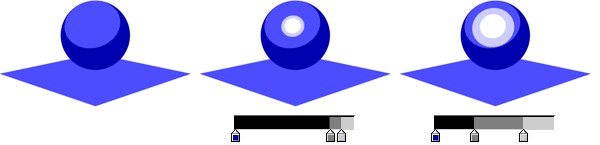
The Specular gradient controls the color, width, height and falloff of the highlights, from areas of no specular (left end of gradient) to areas of full specular (right end of gradient).
Activates the Illumination Gradient.
See Lights.
See Cel shader shadows below.
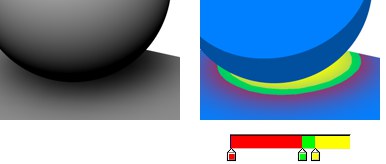
To include shadows, enable the Shadows option and set the Shadows to Multiply, Color or Light Shadow.
If Light Shadow is enabled, the shadow will use the color defined on the light object’s Shadow tab in the Attribute Manager.
When Shadows is set to Multiply, you have a choice of four modes: Normal, Hue, Saturation or Value.
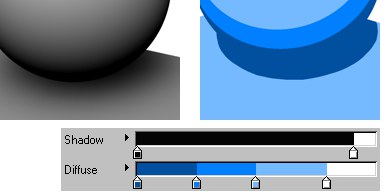 Shadow under a sphere.
Shadow under a sphere.In Normal mode, the Shadow gradient affects the brightness of shadows, from areas of full shadow (left end of gradient) to areas of no shadow (right end of gradient). Note that the color of the shadows is restricted to the colors defined by the Diffuse gradient.
These three modes enable you to adjust the hue, saturation or value (H, S, V) based on the shadow. They take either the hue, saturation or value of the resulting cell shader color and multiply it by the shadow. The Invert option swaps the multiply so the shadow either moves the H, S or V down or up.
By default, all lights in the scene will be used as light sources when Lights is enabled. To include or exclude specific lights, set Use Lights to Include or Exclude and Drag & drop the lights into the Lights box.