Table Of Contents
- Common Light Parameters
Introduction
The Redshift Physical Sun light is a physically accurate representation of real sun-light based on the paper 'A Practical Analytic Model for Daylight', by A.J. Preetham, Peter Shirley and Brian Smits. Physical Sun is generally used in conjunction with the Physical Sky environment shader.
For additional information about the Redshift Physical Sun & Sky system, please refer to the Physical Sky topic.
Physical Sun emits light at an extremely high intensity (to model the physical intensity of sunlight that hits the Earth's surface) and you should therefore always use a Photographic Exposure lens shader to achieve useful results when using Physical Sun. Without a Photographic Exposure lens shader, the scene will likely render completely white.
|
Intensity
On
Turns the sun light on or off.
Intensity Multiplier
Specifies an intensity multiplier for the sun light. This parameter can be used to scale the intensity of the sun up or down.
Non-Physical Intensity
When enabled reduces the intensity of the sun light to a range that can be used without a Photographic Exposure lens shader.

|

|

|

|
| Use Non-Physical Intensity: Enabled | Disabled | Enabled | Disabled |
Sun Disk Scale
Use this value to scale the size of the sun disc. Smaller values result in harder the shadows while larger values result in softer shadows.
S
Color
Red-Blue Shift
Specifies a hue shift for the color of the sun light. The default value of 0 will yield physically accurate sun light color. Negative values will shift the sun light color towards blue, while positive values will shift it towards red.

|

|

|
| Red-Blue Shift: -0.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
Saturation
Specifies the color saturation of the sun light. The default value of 1 will yield physically accurate sun light color. Smaller values will reduce the color saturation of the sun light, with a value of 0 producing pure white light. Values above 1 will exaggerate the color of the sun light.
Atmosphere
Turbidity
Specifies the haziness of the air – a measure of dust particle pollution. A value of 2.0 represents a very clear, blue sky, while larger values will make the sky an orange color.

|

|

|

|

|
| Turbidity example demonstrating lower values on the left to higher values on the right . | ||||
Ozone
Specifies the amount of ozone in the atmosphere, with values ranging from 0.0 to 1.0. The default is 0.35, which is commonly used for the Earth's atmosphere. Smaller values will increase the amount of orange in the sunlight, while larger values will make it more blue.

|

|

|

|

|
| Ozone example demonstrating (warmer) lower values on the left to (cooler) higher values on the right . | ||||
Horizon Height
Specifies the position of the horizon. Values below 0 will push the horizon down, while values above 0 will raise the horizon.

|

|

|

|

|
| Horizon Height: -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 1.75 |
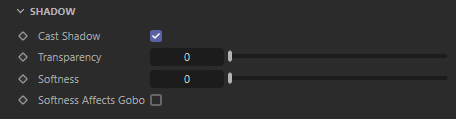
Shadow
|
Enable
Enable or disable shadow casting.
Transparency
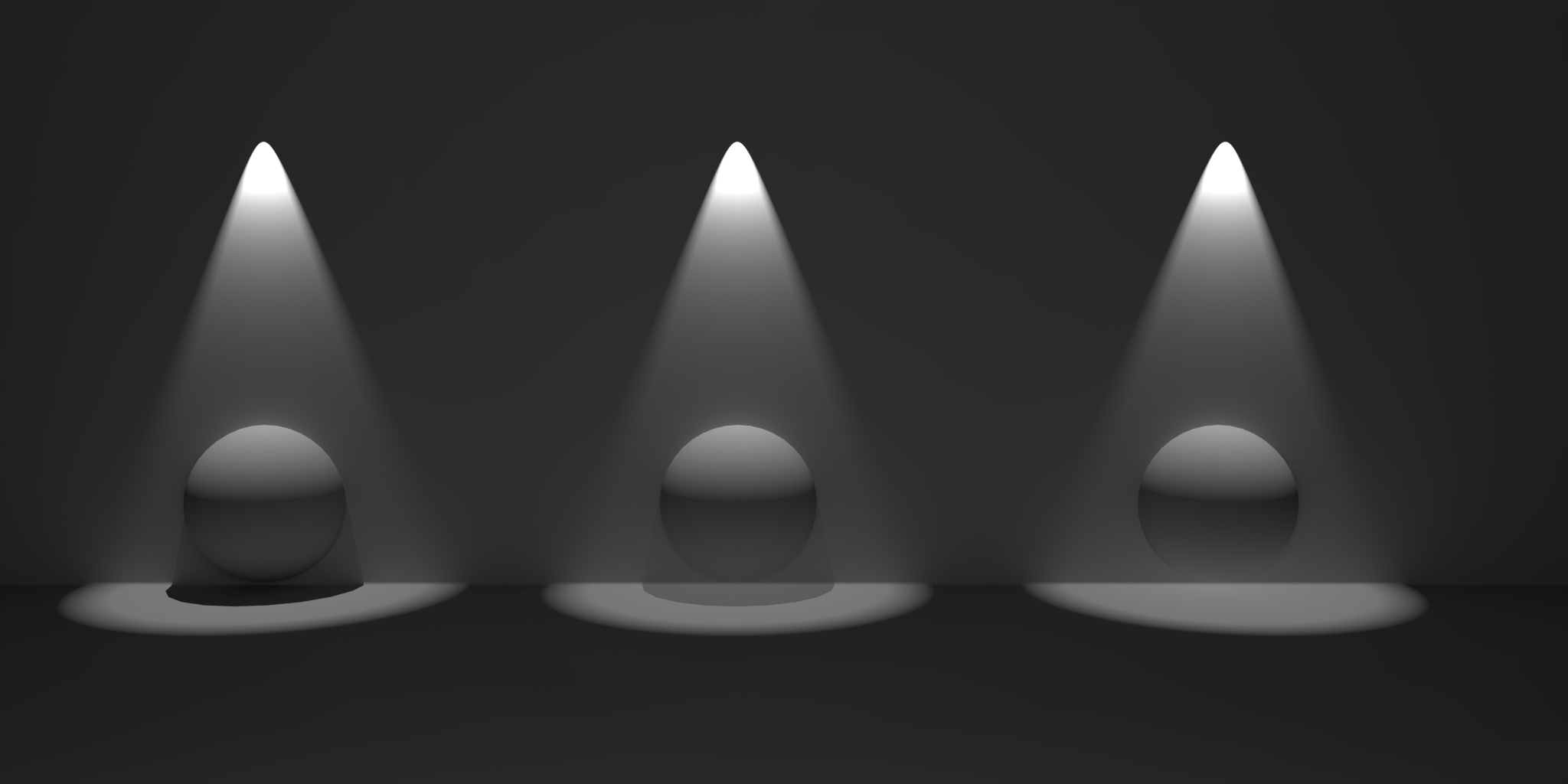
Specifies the transparency of the shadows cast by the light. Smaller values yield darker shadows. The default value of 0 will produce a completely black shadow. A value of 1 will produce no shadow at all.
The example below shows how a completely opaque sphere's shadow transparency can be controlled by this light setting.
|
|
| Transparency 0 to 1 |
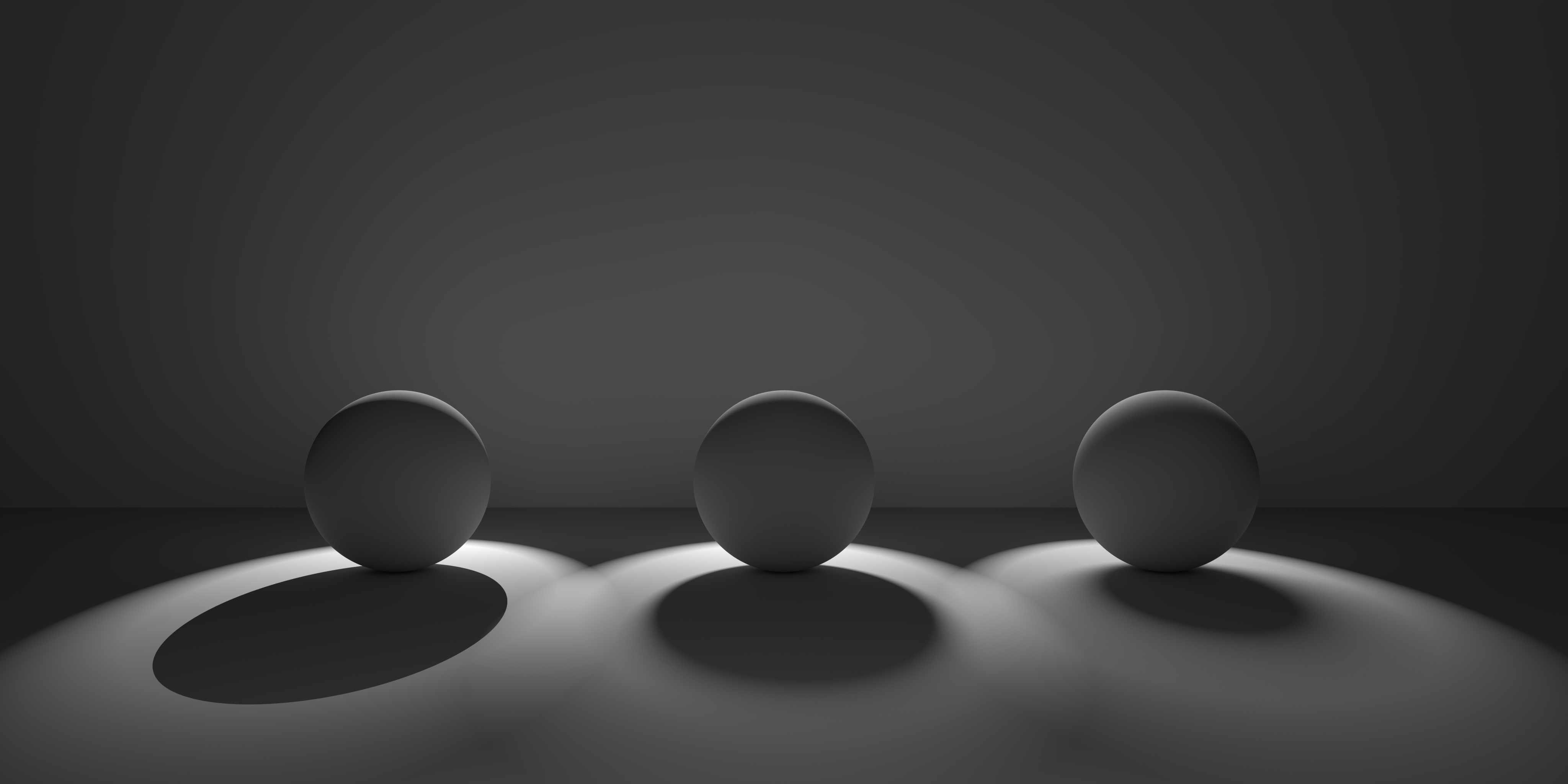
Softness
Specifies edge softness for non-area light shadows. A value of 0 means no softness and will yield sharp shadows. Values above 0 will produce softer shadow edges.
Softness is not available for Physical lights when set to Area. The softness of an Area light is controlled by the light's size itself.
|
|
| Softness 0 to higher values |
Softness Affects Gobo
Enables soft gobo texture projection, to match the softness of the shadows, giving the same appearance as if the light was an area light.
Softness Affects Gobo is only available for non-Area Physical lights and IES lights.
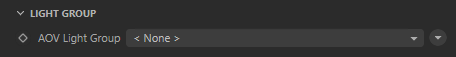
Light Group
|
AOV Light Group
This is the name of the AOV light group this light is associated with.
For more information on Light Groups and how to set them up and use them please see here.
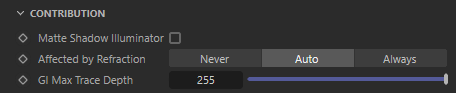
Contribution
|
Matte Shadow Illuminator
Specifies whether the light can illuminate 'Matte Shadow' surfaces (see Matte Shadow Catcher shader).
Matte Shadow Illuminator is only available for Redshift Physical and Redshift IES lights.
Affected by Refraction
This option allows you to control how specular reflections are affected by rough/refractive objects that block the light and whether or not the light rays bend as they pass through. Prior to 2.6.10 this option was not available and the light rays would never bend. Specular ray bending is an important effect for rendering realistic-looking glass and lenses.
- Never - Specular rays do not bend. This is the legacy lighting behavior.
- Auto - Specular rays bend through refractions if they are not too rough and bias towards not bending if they are rough.
- Always - Specular rays bend through refractions regardless of ray roughness.
This effect is available only for area lights and dome lights. Spot and IES lights can not be seen through bent rays because their source is infinitesimally small.
Care must be taken when using 'Always', as this can disable Multiple Importance Sampling, which is a crucial technique for getting clean renders for rough surfaces.
Light/Shadow linking is not available for specular rays that have been bent.
GI Max Trace Depth
This option lets you override the maximum trace depth for GI rays on a per-light basis.
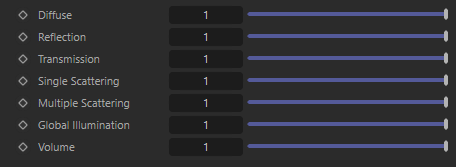
Contribution Scale Parameters
|
The light contribution parameters covered below modify the scale of individual light shading elements. These parameters offer full creative control in adjusting how much a light impacts a scenes, they can even bet set above 1.
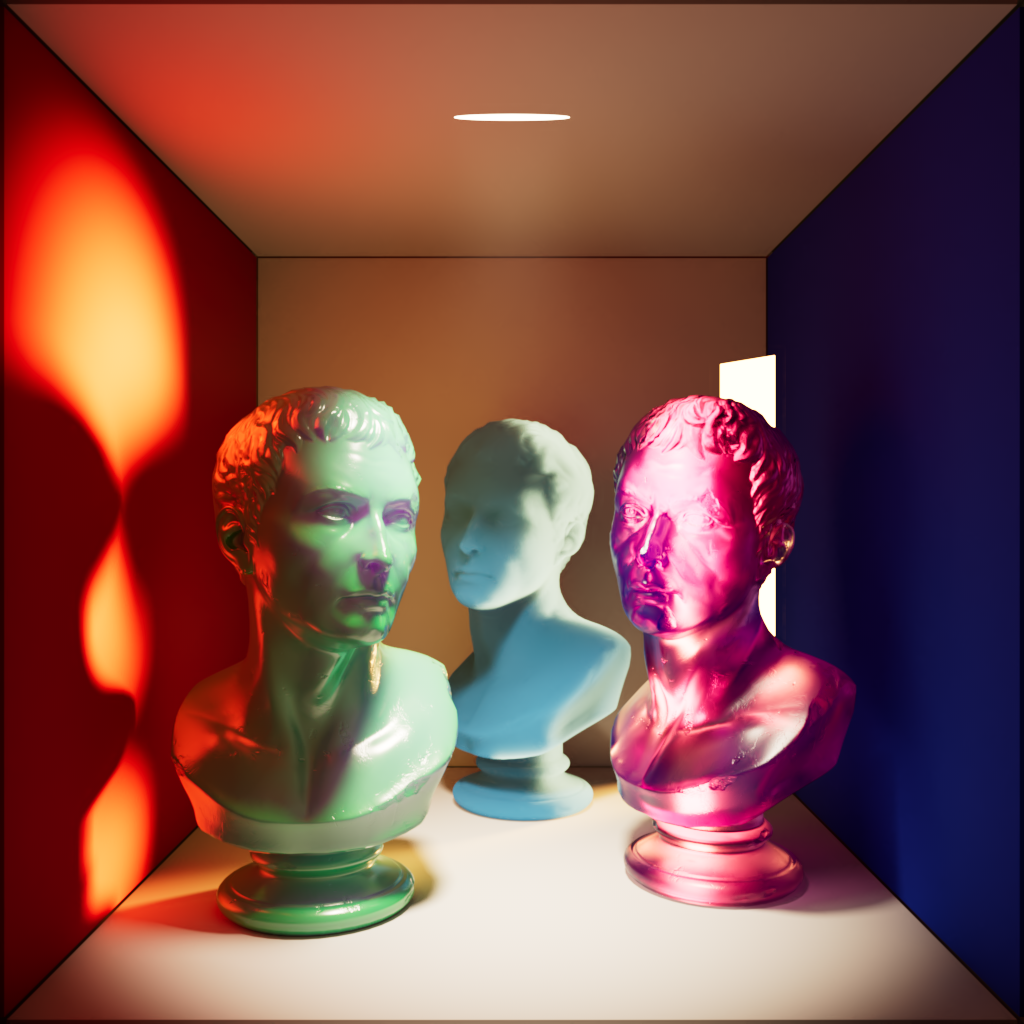
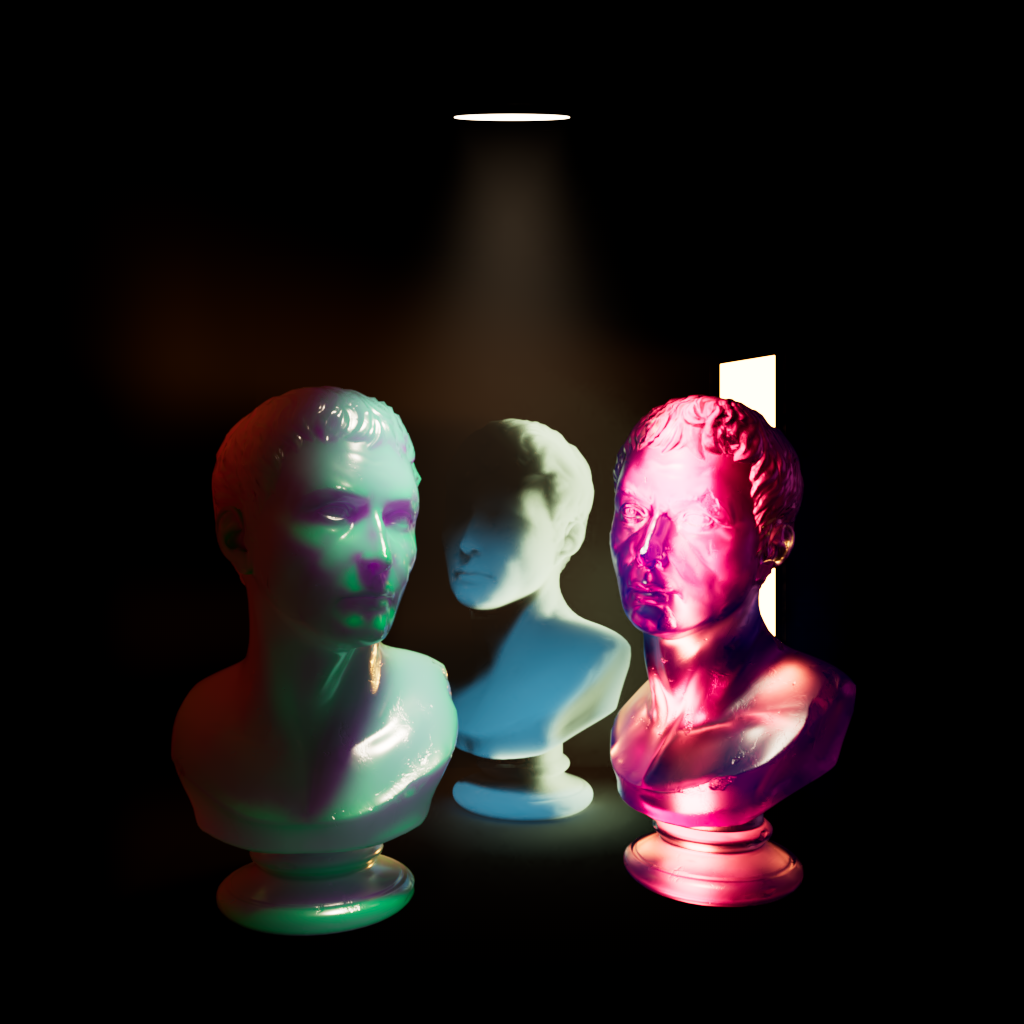
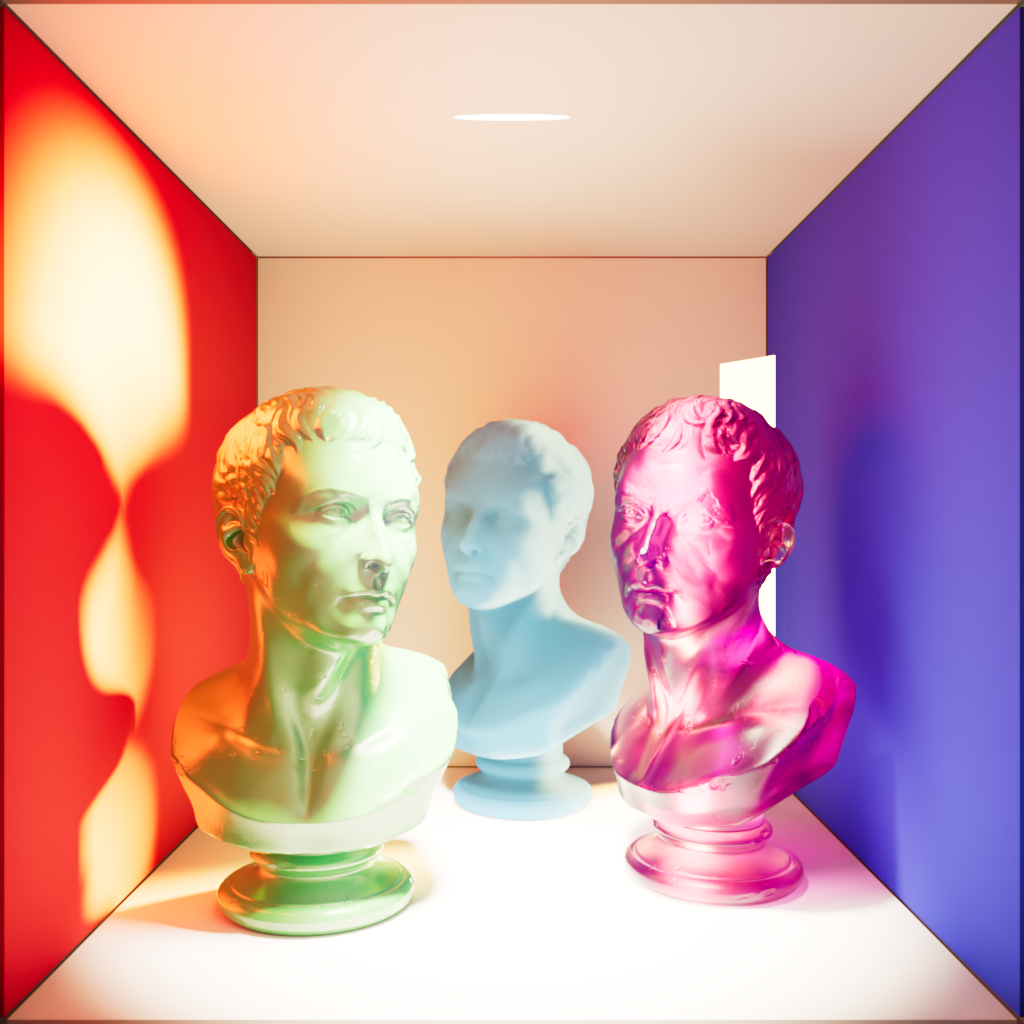
The example scene used below contains three of PolyHaven's marble bust model, the model on the left has a standard shader with diffuse, reflection, and multiple scattering components, the model on the right has a fully transmission shader with single scattering, and the model in the back has been turned into a volume object in order to demonstrate volume contribution. There are two area lights in the scene, a disc area light in the top center and a rectangular area light in the back right. Each light has a contribution value of 1 for each shading type but when a parameter is modified for the example images both lights are adjusted equally.
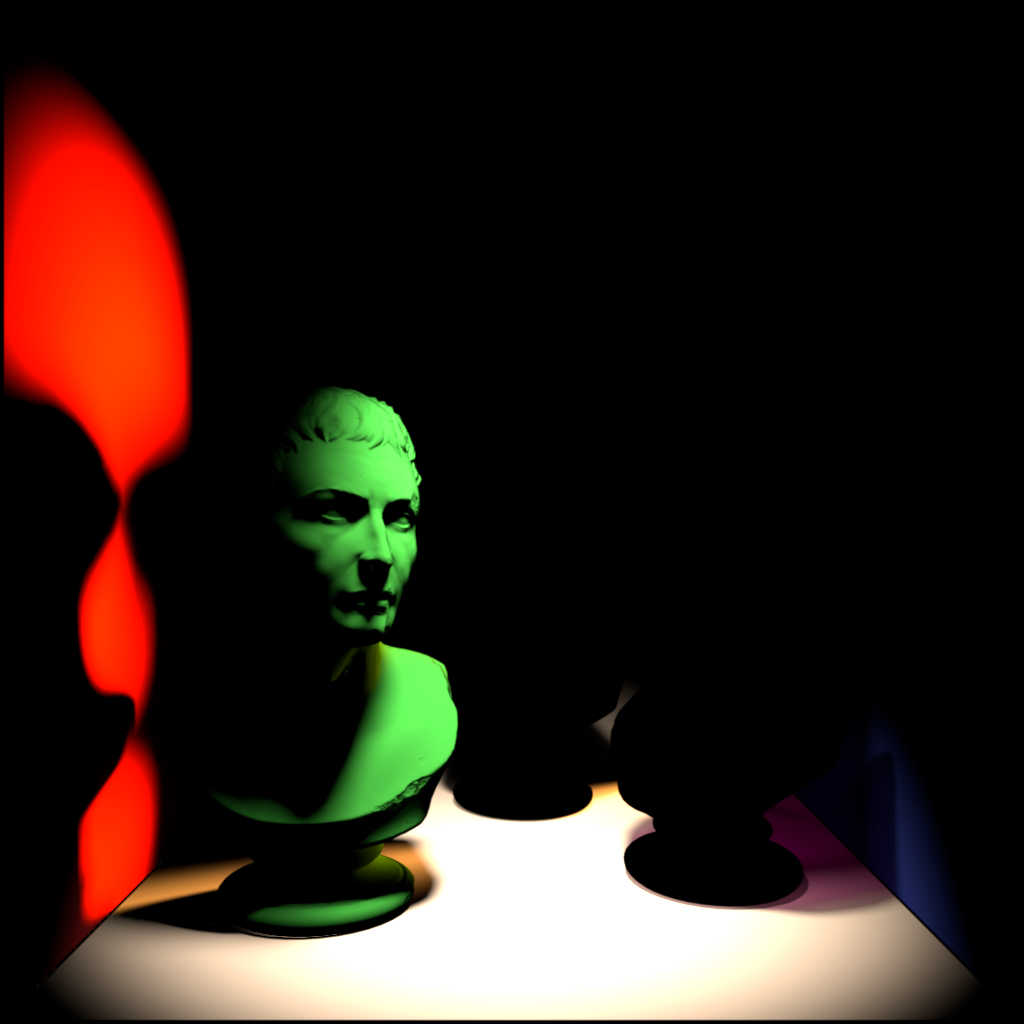

|
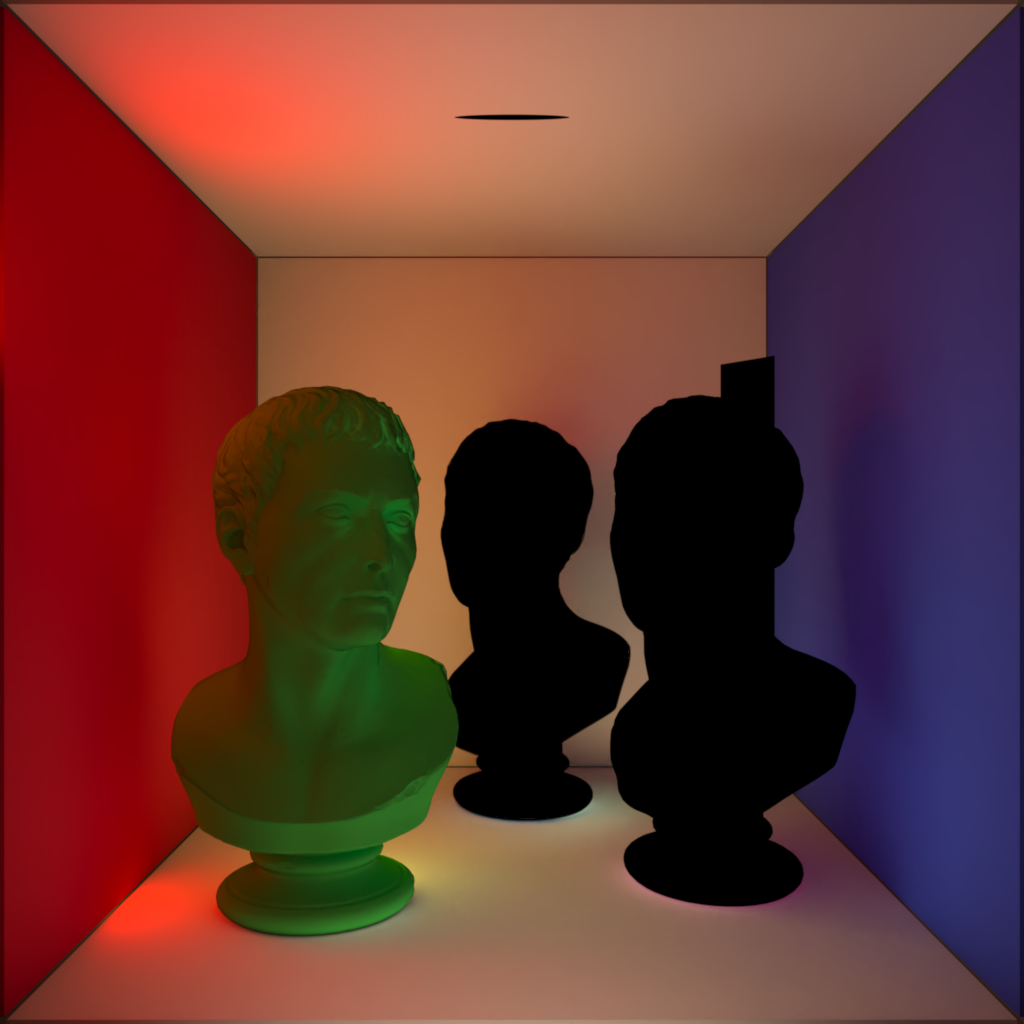
|

|
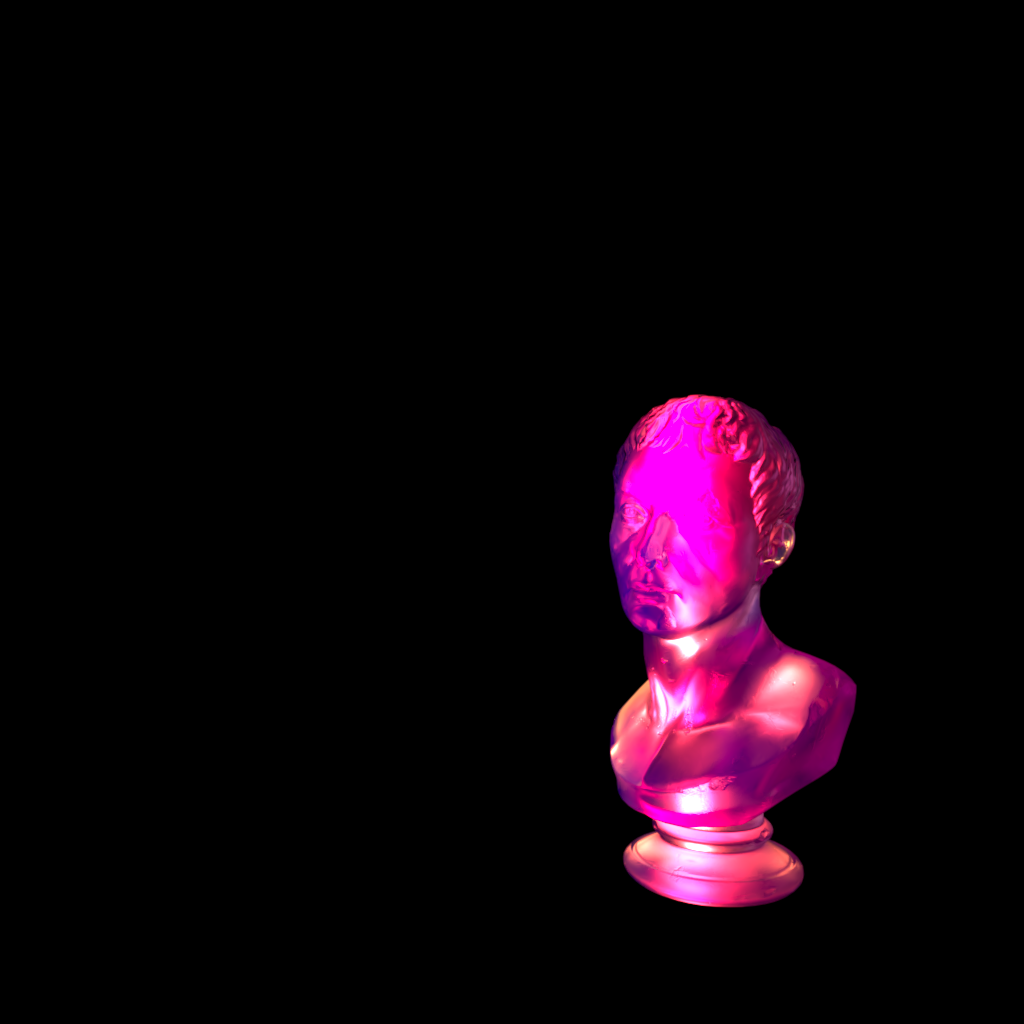

|
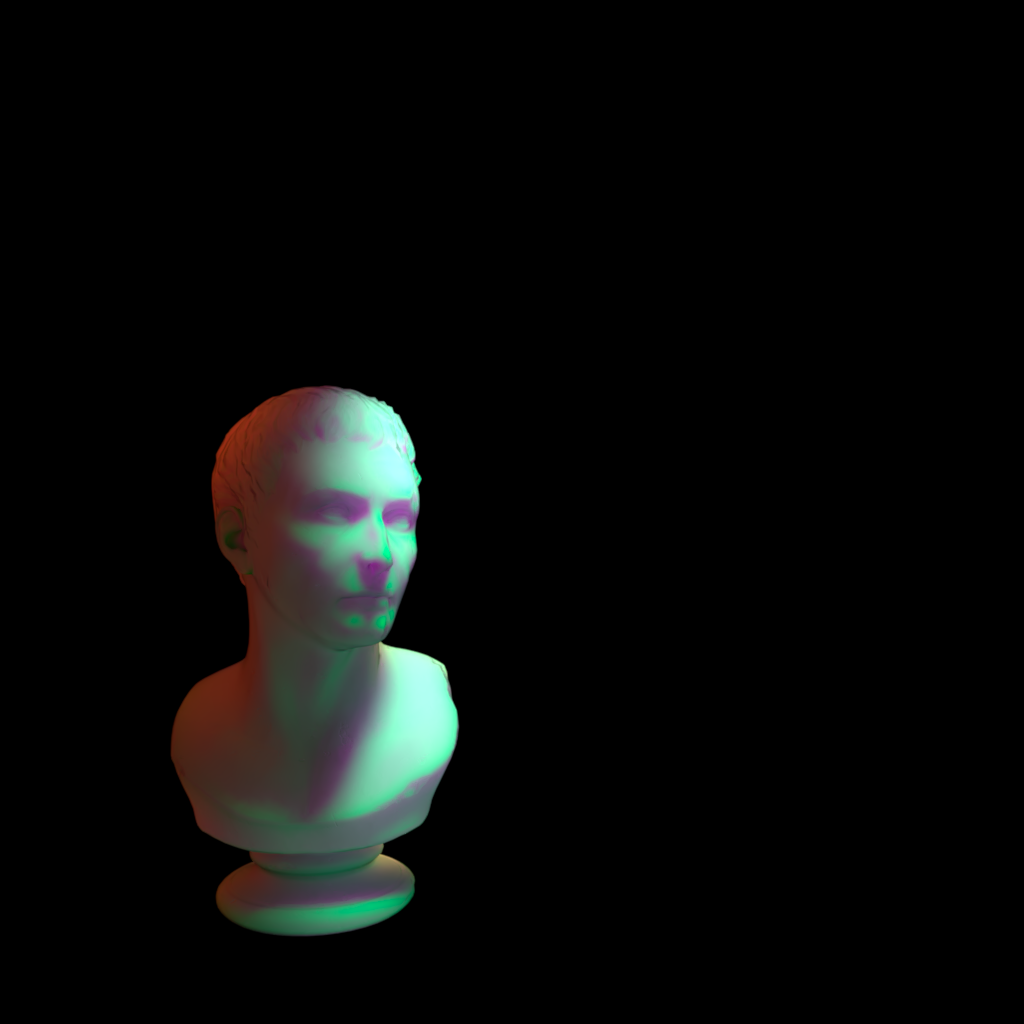

|

|
| Diffuse | Global Illumination | Reflection |
Transmission & |
Multiple Scattering | Volume |
 |
|||||
| Beauty | |||||
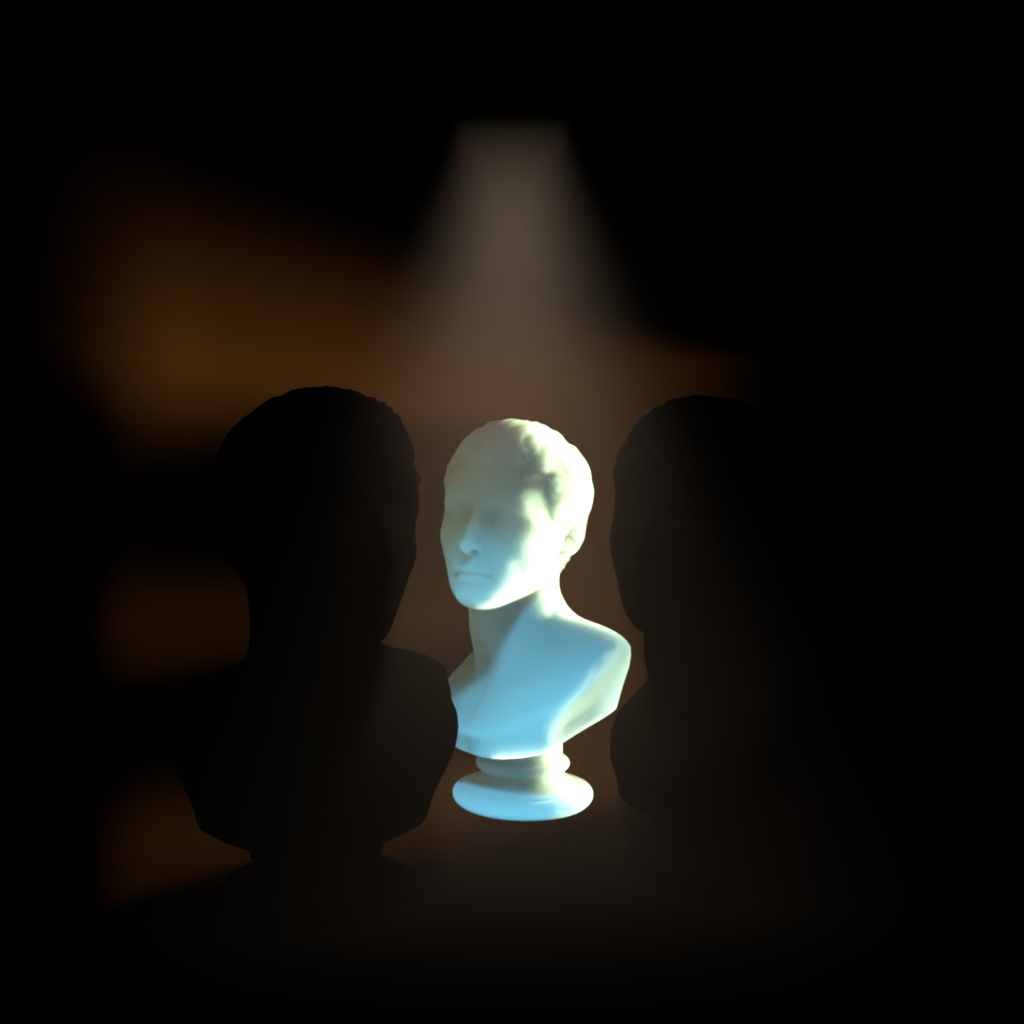
Diffuse
Scales the intensity a light has on diffuse shading.

|

|

|
| Diffuse: 0 | 1 | 10 |
| Observe in the first image that when there is no diffuse contribution there is also no global illumination bounce lighting. | ||
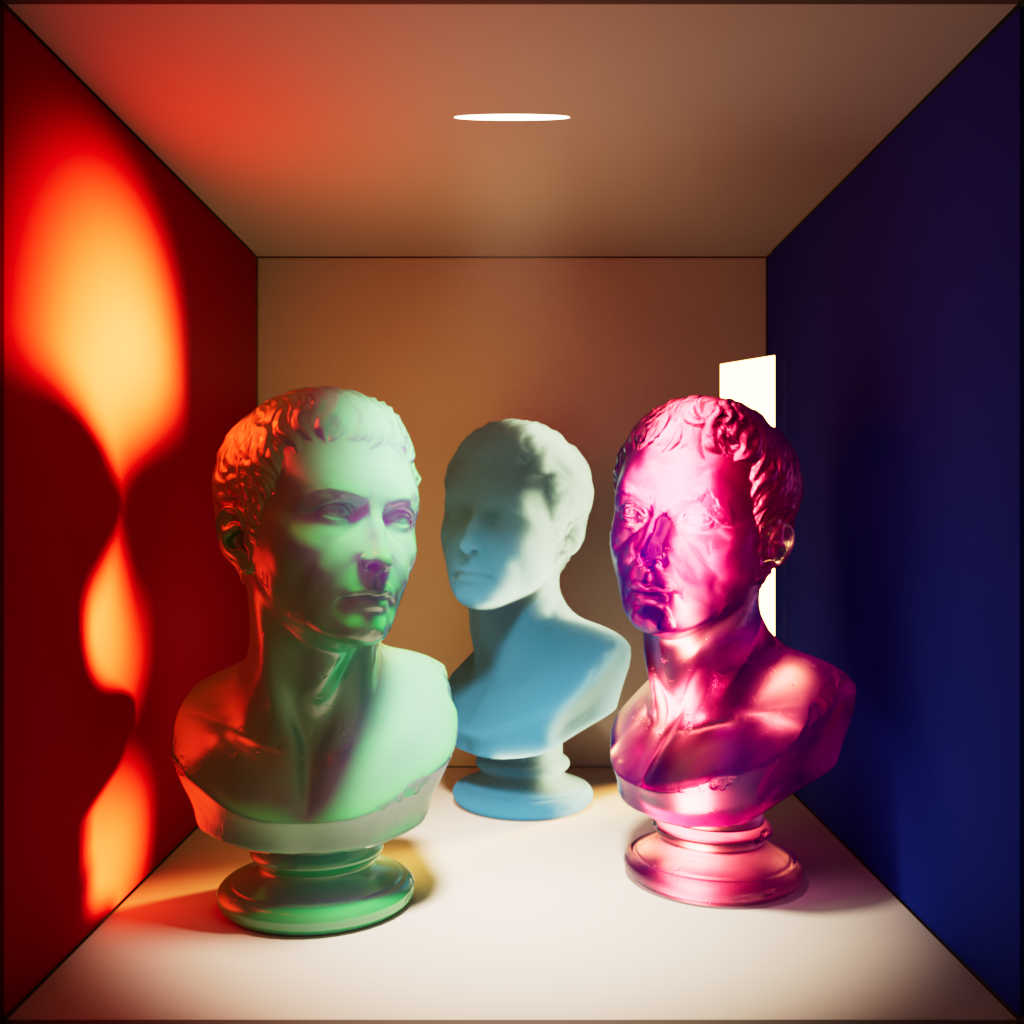
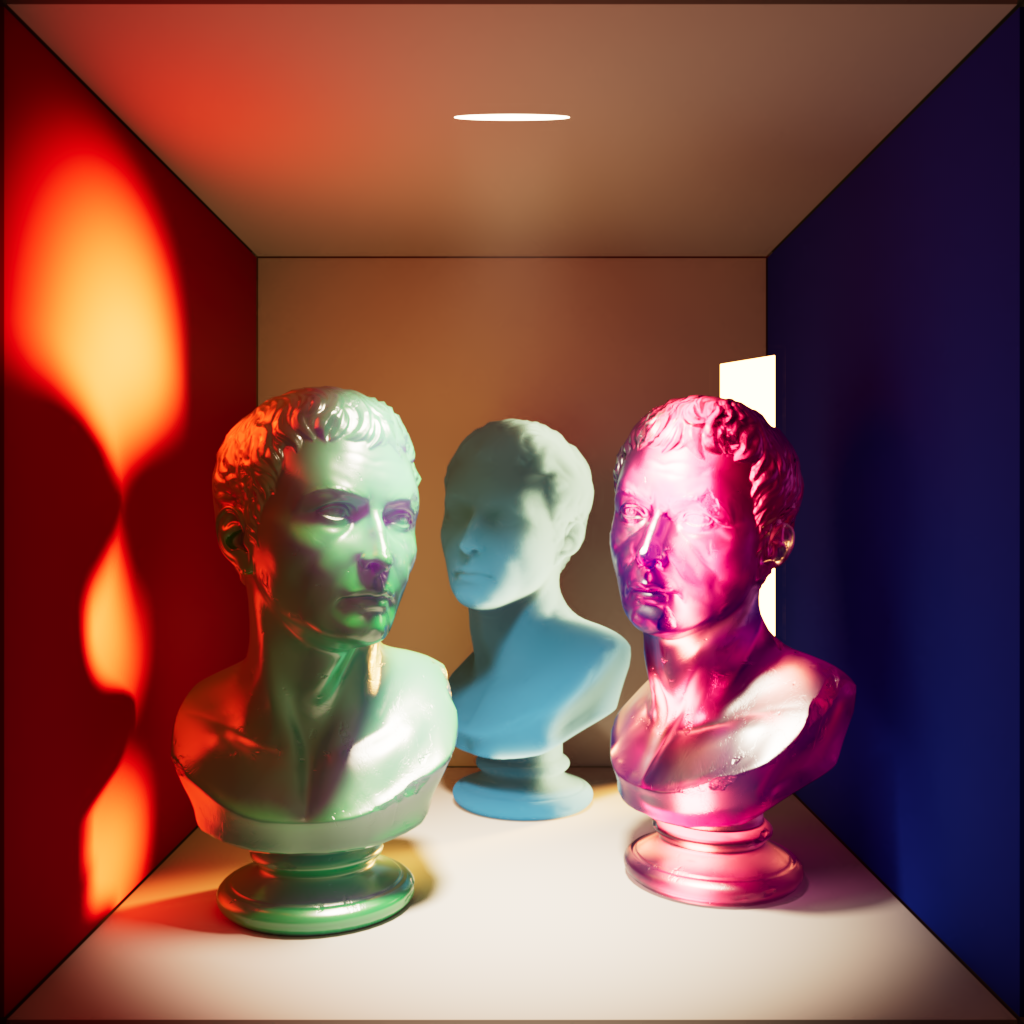
Reflection
Scales the intensity a light has on specular reflections.

|

|

|
| Reflection: 0 | 1 | 10 |
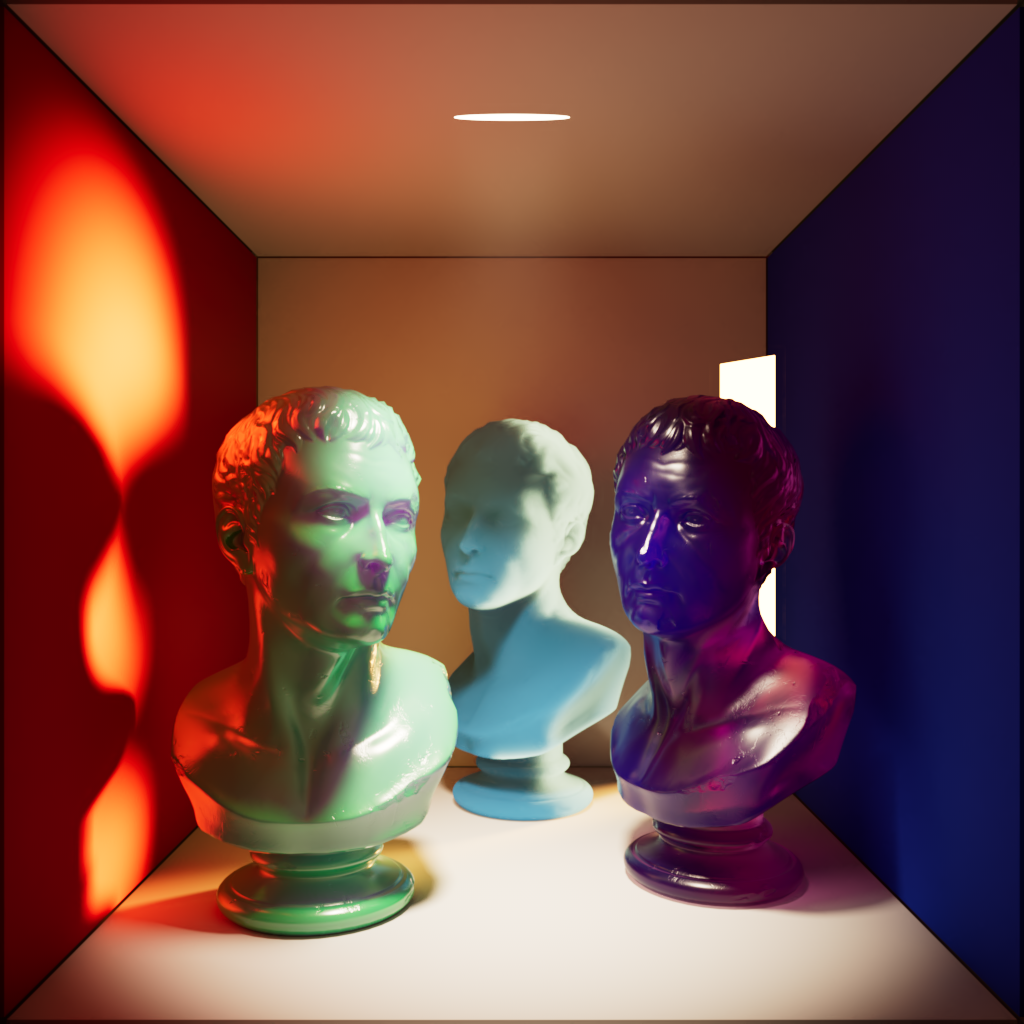
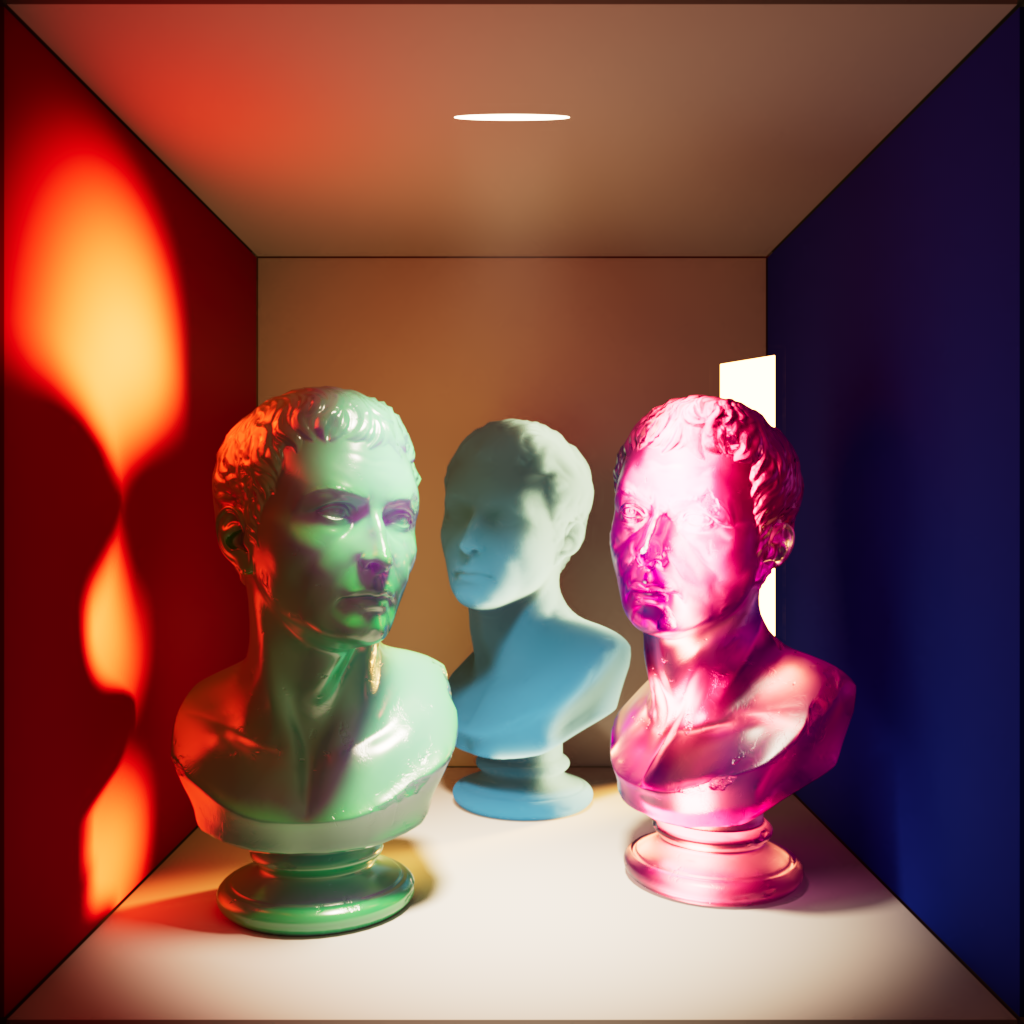
Transmission
Scales the intensity of a light when seen through a transmissive / refractive object.
A light must be visible in order for transmission scale to have any effect.
When a light is visible a transmission scale of 0 results in the same effect as disabling a light's visibility.

|

|

|
| Transmission: 0 | 1 | 10 |
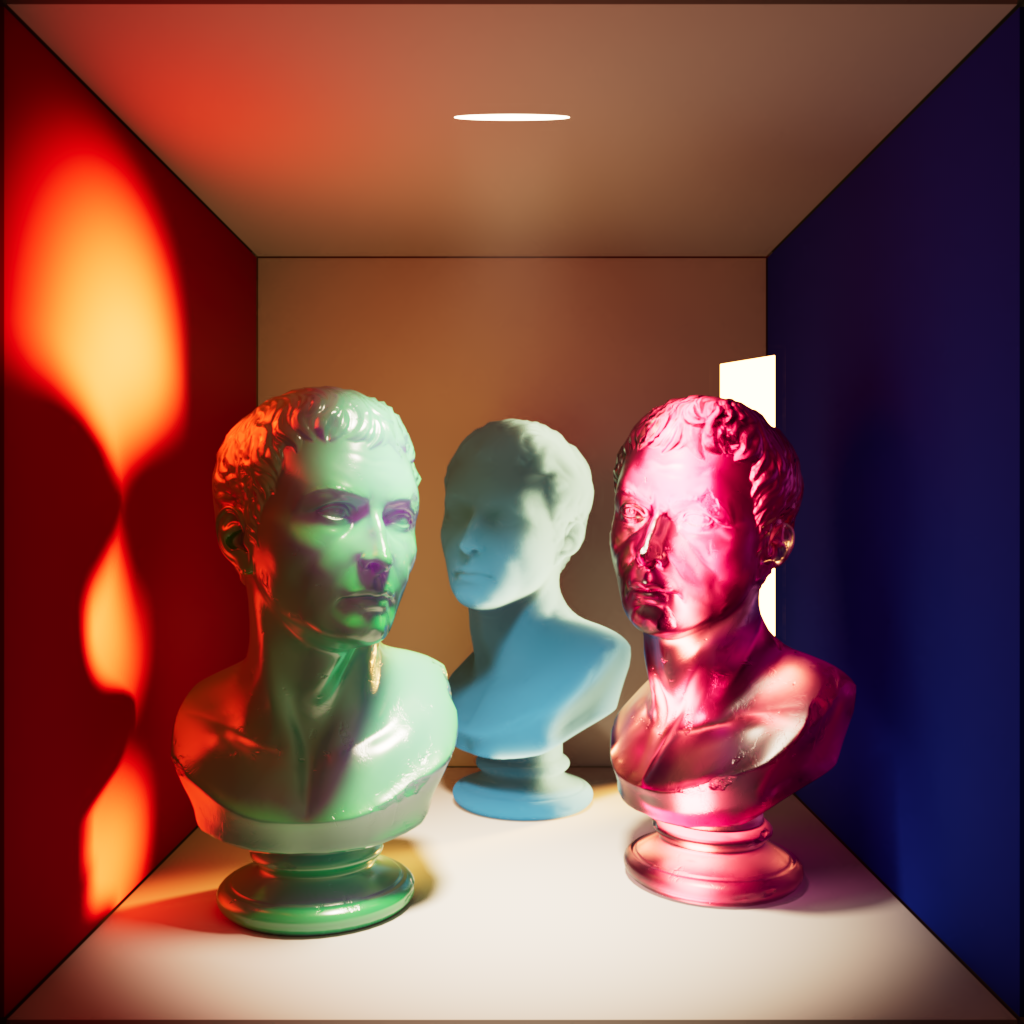
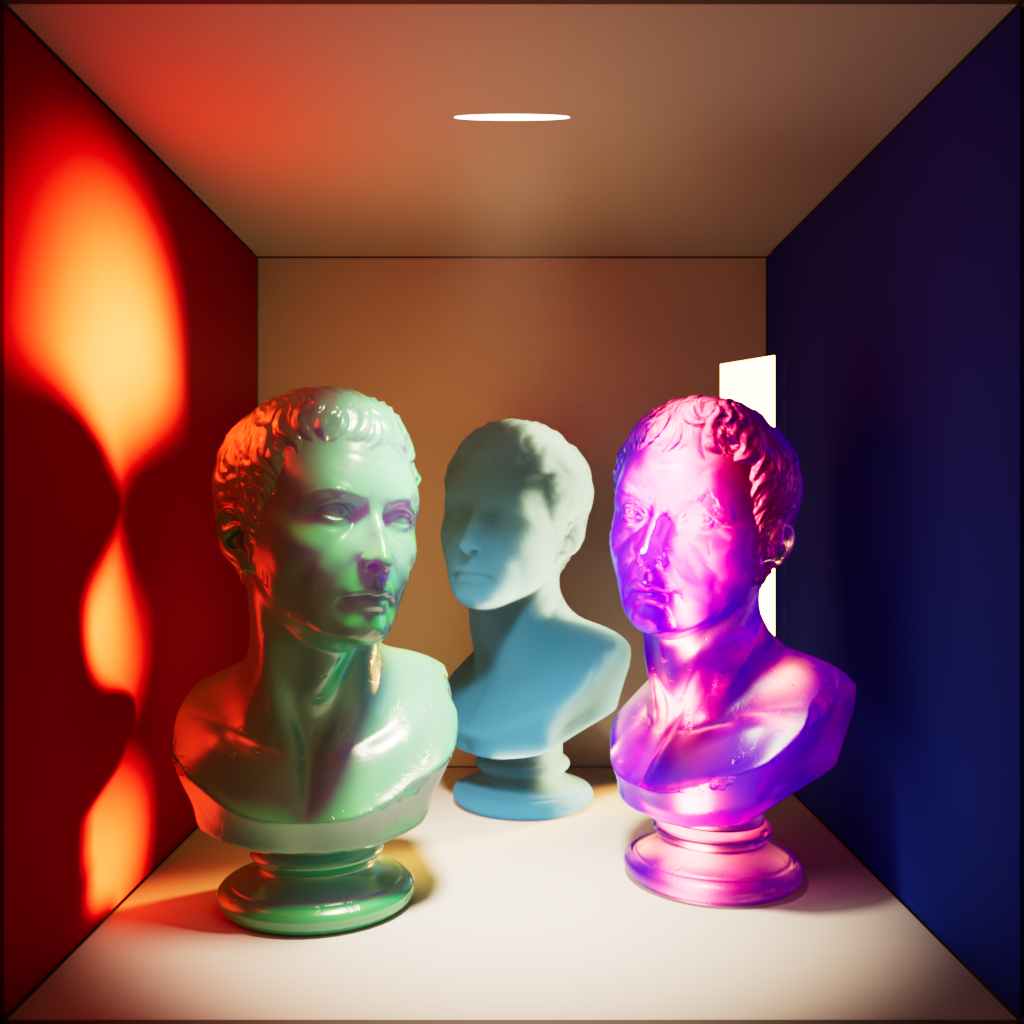
Single Scattering
Scales the intensity a light has on single scattering.

|

|

|
| Single Scattering: 0 | 1 | 10 |
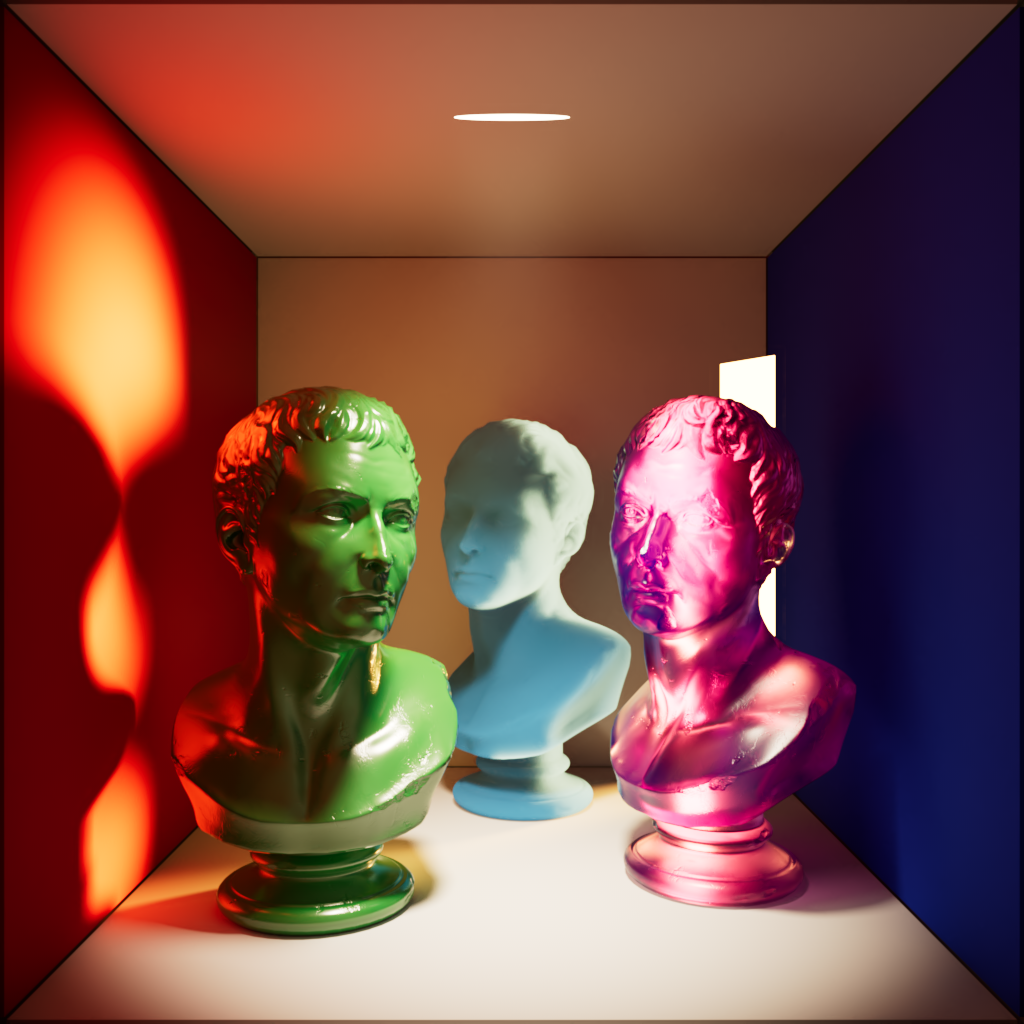
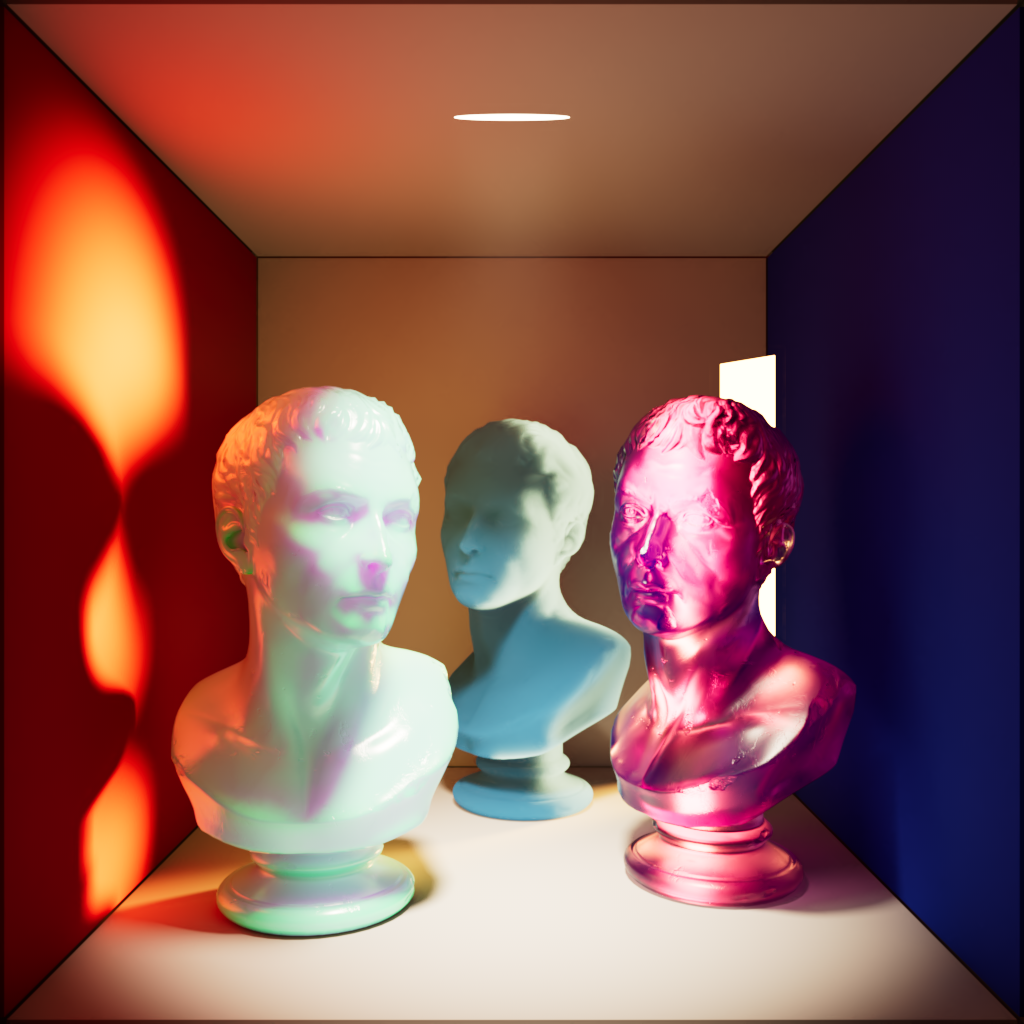
Multiple Scattering
Scales the intensity of the light when seen through sub-surface multiple scattered materials.

|

|

|
| Multiple Scattering: 0 | 1 | 10 |
Global Illumination
Scales the intensity of a light's global illumination contribution.
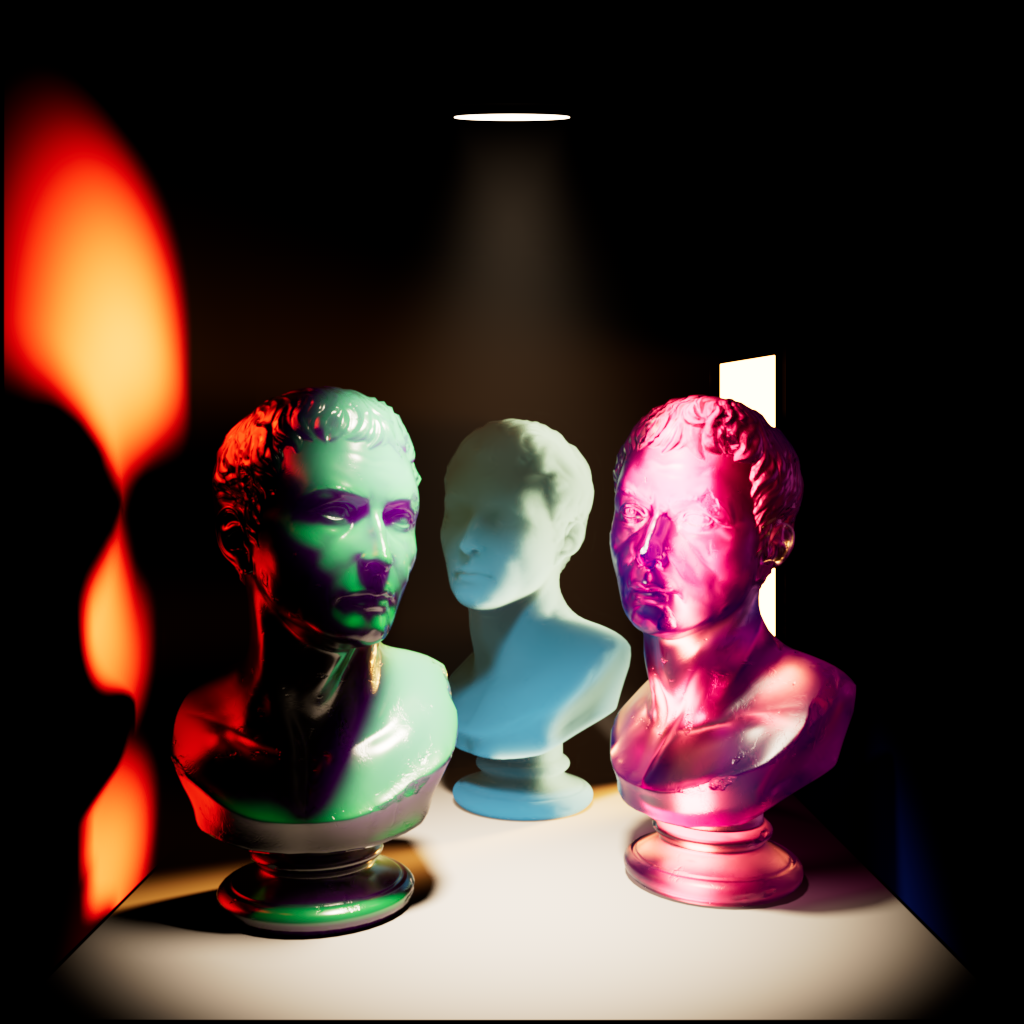

|

|
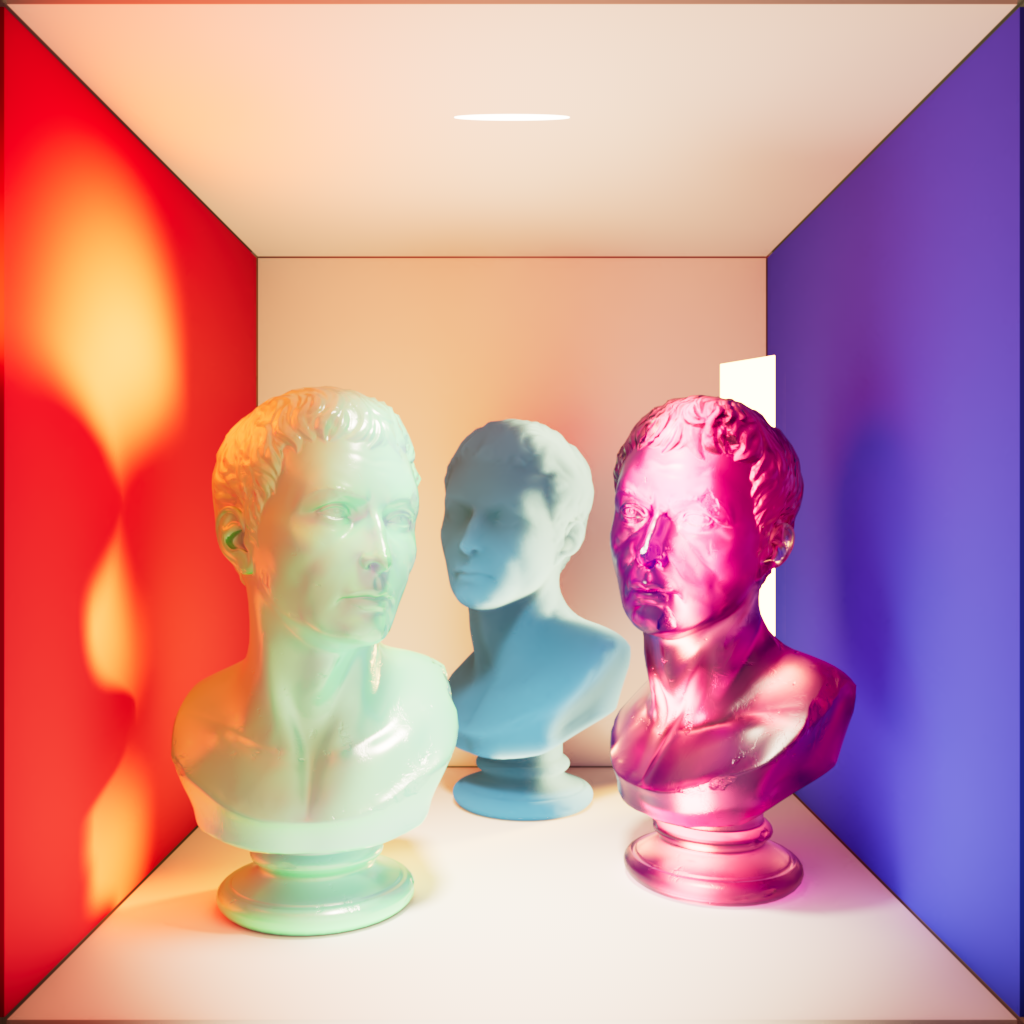

|
| Global Illumination: 0 | 1 | 10 |
Volume
Scales the intensity of a light's volume scatter contribution. A value of 0 disables volume scattering for the light.
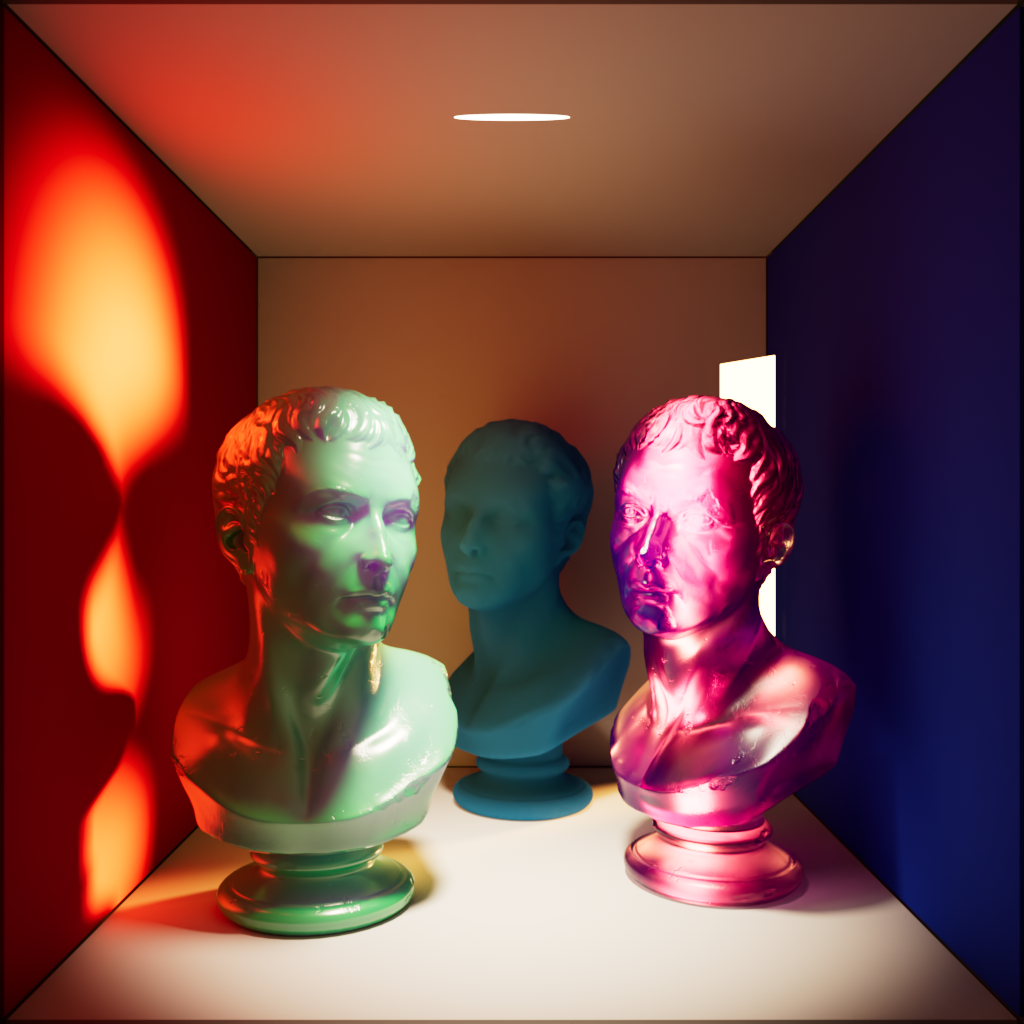

|

|
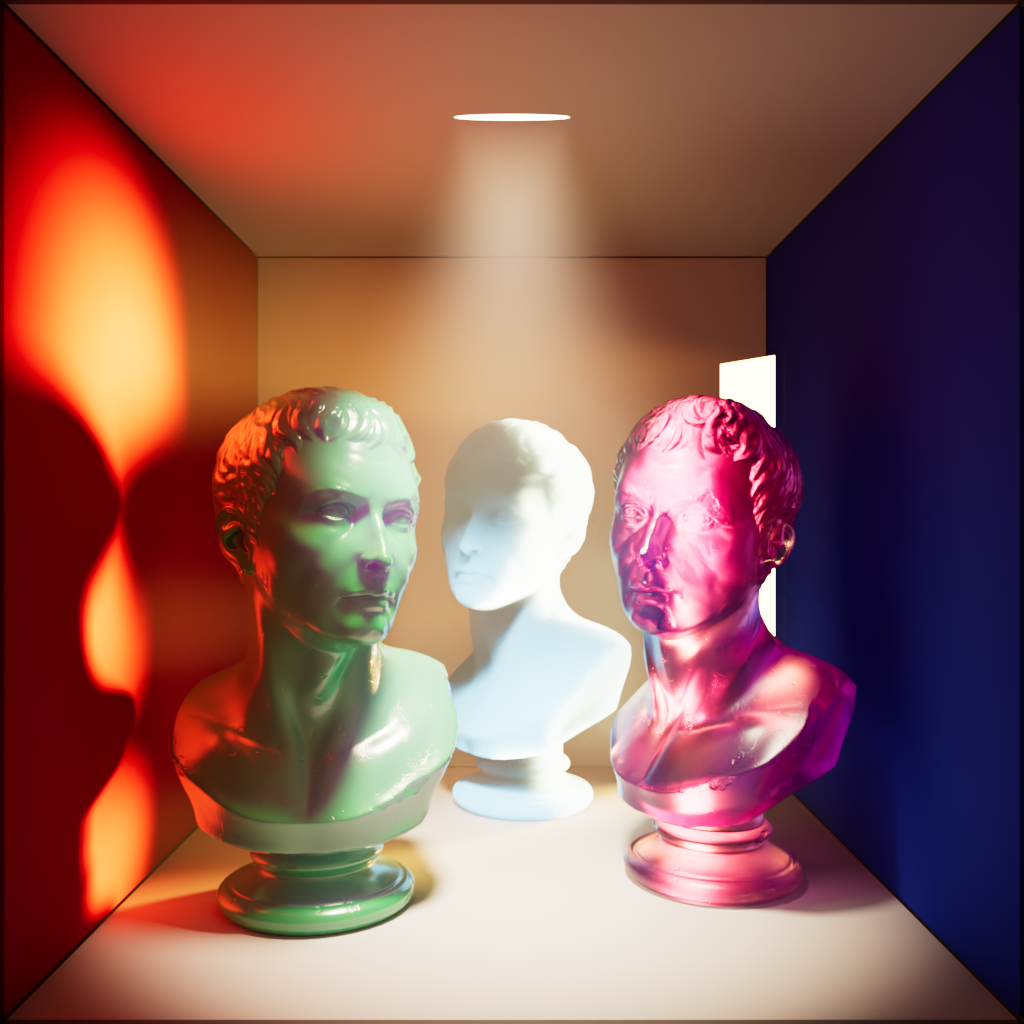

|
| Volume: 0 | 1 | 10 |
| Observe in the first image the volume object in the middle is still illuminated by global illumination even though all lights have volume contribution set to 0. | ||