Materials define the way objects look in Forger. The material editor allows the creation of new materials, modify existing ones and assign materials to objects.
Covered topics:

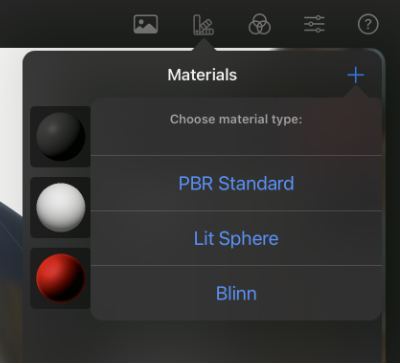
New materials can be created by pressing the add (+) button in the top right corner of the Materials view. The new material is automatically selected, which activates the display of its parameters. After setting the material, the arrow in the header of the dialog can be used to switch back to the Materials view of all materials. There, a context menu can be opened by holding down a click on a material, which can be used, for example, to set the name of the material or to delete a material that is no longer needed. You can edit the settings of a material at any time by clicking on it in the Materials view or by clicking on the arrow icon next to the material in the settings of a mesh (see also left side of the next image).
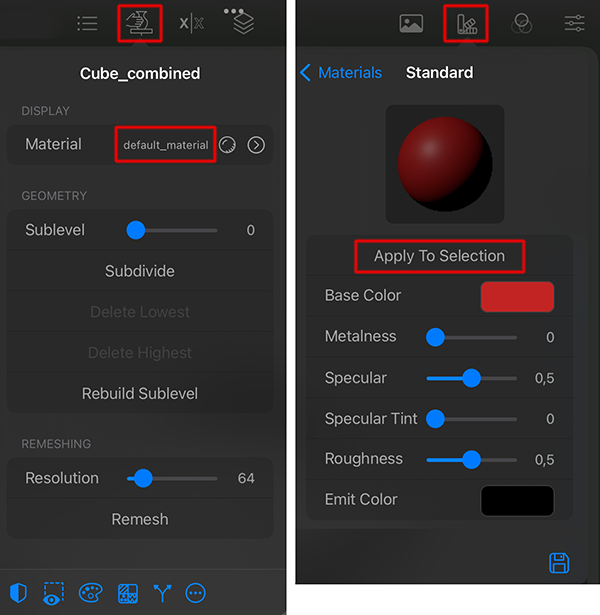
Materials can be applied to selected objects by pressing the Apply to Selection button that can be seen whilst editing materials (see right side of the image) or by dragging and dropping onto meshes from the Materials manager.
Already existing materials can also be asigned directly from the settings of the object (see left side of the image) by clicking on the name of the material (the default material is applied to all new or imported meshes).
By using the Save icon at the lower right of the Materials manager you can save the current material settings as default.
Note:
Any Forger scene will already contain a material named "default_material". This material is automatically applied to all new objects and cannot be deleted, but can be modified.
Material behaviors in Forger are controlled by their parameters, each material type has different parameters that can be one of the following:
Constant: A color, decimal or boolean number. Its value does not vary across the surfaces it is applied to.
Texturable - Color: A color image, that can vary across the surfaces that it is applied to based on the UVs and the values located near the texels of those coordinates.
Texturable - Scalar: A scalar image (in linear space, black and white), that can vary across the surfaces that it is applied to based on the UVs and the values located near the texels of those coordinates.
This is the default material type. It's a physically-based, gamma-correct material that can represent many kinds of surfaces. It also has texturable parameters that you can use to have further control over the shading of the surfaces using it.
This material factors in Environment Lighting if you have set any from the "IBLs" section in the objects menu.
Base Color: (texturable - color). The diffuse base color of the surface. The applied Vertex Colors of the object will get multiplied by this color.
Metalness: (texturable - scalar). Represents how "metallic" the material is, with a value of 1.0 it will be fully metallic, values closer to 0.0 will make the material appear non-metallic. Note that although the metallic model has no diffuse component, it has a tinted incident specular.
Specular: Incident (maximum) specular amount. This is in lieu of an explicit index of refraction.
Specular Tint: A concession for artistic control, this parameter tints incident specular toward the base color. Note: grazing specular is still achromatic (i.e. in the specularTint parameter doesn't tint incoming light at grazing angles).
Roughness: (texturable - scalar). Controls the glossiness of specular reflections, the lower the value, the sharper the reflection. A value of 0.0 will result in a mirror-like reflection while a value of 1.0 will create reflections closer to a rubber-like diffuse reflection, any value in-between will result in blurred reflections.
Emit Color: Emission energy, non-black values give the appearance that the material is emitting incandescence.
LIT Sphere materials offer some presets to choose from, displaying dull and shiny surfaces as a basis. After choosing one of these presets, you can tweak the materials settings further:

|
|
Ignore Light Direction: This option makes the LitSpheres ignore the light direction and look exactly as they do in the image itself, when this option is enabled, the image is "projected" from the default directional light "default_light".
Note:
The LitSphere material type is not influenced by Image Based Lighting.
This is the legacy material type, it has been kept in Forger because it's useful for sculpting as gamma correct materials present harsher light-to-shadow transitions. That although more correct, can be hard to sculpt with given that it may hide forms.
Diffuse: Defines the object’s color when a light is emitted onto its surface.
Specular: Defines the effect the material has on the reflected light.
Shininess: Controls the size and brightness of the specular reflection.
Note:
The Blinn material type is not influenced by Image Based Lighting.