Table Of Contents
The Redshift Light is an all-purpose light which can be used to model point, spot, IES and directional lights as well as area lights of various shapes.

Specifies the light type.
|
|
|
|
|
| Light Type: Area | Point | Spot | Infinite |
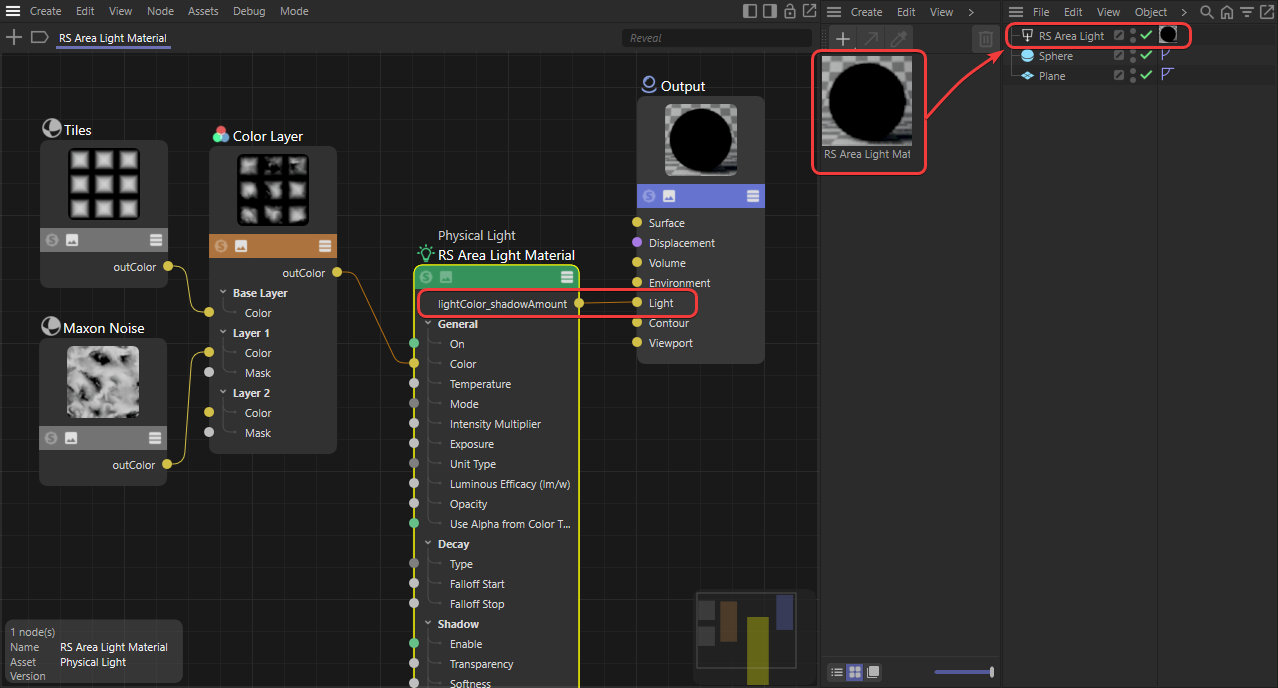
Many settings of the Redshift light object can also be set through the material node system. Using this button will create a new Redshift Light material and connect it to this light. Light parameters controllable by a light shader include the lights Color settings, Decay, Shadow options and Attenuation.
With this, you can create procedural shading setups for light color and other compatible inputs, eliminating the need to load an external texture. When manually setting up a light material, the "lightColor_shadowAmount" output from a light node should be connected to the Light input of the Material Output node, and that light material should be assigned directly to the light in the Object Manager.
|
| Creating a procedural light color |
If a Shader Graph material has been assigned to the light, you can open the connected Redshift Light graph by using this button and edit the shader.
You can find these commands in a menu to the right of the Type menu. You can use them to add a Target expression tag to the light. By linking an object to that tag you can aim the z axis of the light to that object. Using the Add Target Tag and Null command creates an additional Null object and uses that as the Target Object with the Target expression tag.
Certain light types can be previewed in the Cinema 4D editor viewport. For these lights the following options will become available in the Object tab.
In the Basic tab of the Redshift light object you can find an option to choose an individual Display Color. Activate this option to use that color also for the Wireframe preview of the light.

On the left side you can see how the light object has been assigned a red color. Without the "Blend Object Color" option enabled, only the spot's star icon in the viewport will be colored. If the option is enabled, the wireframe cone of the spot will also be colored, as you can see on the right side of the image above. However, this option does not change the color of the light for rendering.
Displays a wireframe representation of the light decay or light direction in the viewport. When this option is checked, some light types allow manipulation of certain parameters directly in the viewport.
Provides an approximation of the illumination of the light in the viewport.
Adjusts the viewport illumination scale.
These options only affect the Cinema 4D viewport and have no effect in the IPR or when rendering.
Specifies the intensity of the light or the number of physical units (see below).
Specifies an f-stop value that allows you to intuitively increase/decrease the light's intensity when matching to a plate, or rendering large/tiny scenes without using hugh/miniscule Intensity Multiplier numbers. A value of 0.0 means the intensity does not change.
For example, an Exposure value of 1.0 means the light doubles in intensity and a value by 2.0 means the light quadruples in intensity, etc.
Specifies the physical units to use for the light intensity.
Specifies how many lumens are emitted per Watt. Only relevant when using Radiant Power or Radiance unit types.
Specifies the decay of the light;
For physical correctness you must use the 'Quadratic' decay option.
In the example below the light source in the bottom right has its decay type switched between the 3 different types. Quadratic is physically accurate based on the light's size and intensity. Linear demonstrates how you can specify the start and stop falloff to control exactly where the light starts to be visible and then decays to nothing. None turns off decay entirely.
|
|
|
|
| Decay Type: Quadratic | Linear | None |
Specifies the distance from the light at which Linear fall-off occurs.
Specifies the distance from the light at which Linear fall-off ends.
Specifies the color mode.
Specifies the color of the light by using the standard color chooser options.
Specifies the color of the light using a color temperature value (in Kelvin). Redshift supports color temperatures between 1667K and 25000K. Lower values are 'warmer' or more red, while higher values are 'cooler' or more blue.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature
Temperature mode demonstration ranging from low values resulting in warm tones on the left to high values resulting in cool tones on the right.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Color
Color mode demonstration ranging from reddish tones on the left to bluish tones on the right.
You can load a bitmap image here to color the light and to use it like a projector.
Specifies the physical shape of the area light;
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Area Shape: Rectangle | Disc | Sphere | Cylinder | Mesh |
Here you can link to your geometry, that is then used to emit light. See Mesh Lights for info on how to use them.
It depends on you Area Shape choice if and how many of these settings you can access. Use them to scale the chosen shape.
Enables directionality control for Rectangle and Disc Area lights, similar to a barn door effect or spot light. The lower the Spread, the more the light is concentrated in the direction of the light normal. A Spread value of 1.0 is the default, physically correct lighting behavior, while a value of 0.0 makes the light a parallel light.
Note that a Spread of 0.0 is close to a fully directional light, but the light rays will not be perfectly parallel. This is due to a mathematical sampling limitation.
|
|
|
| Spread: 1.0 | 0.3 |
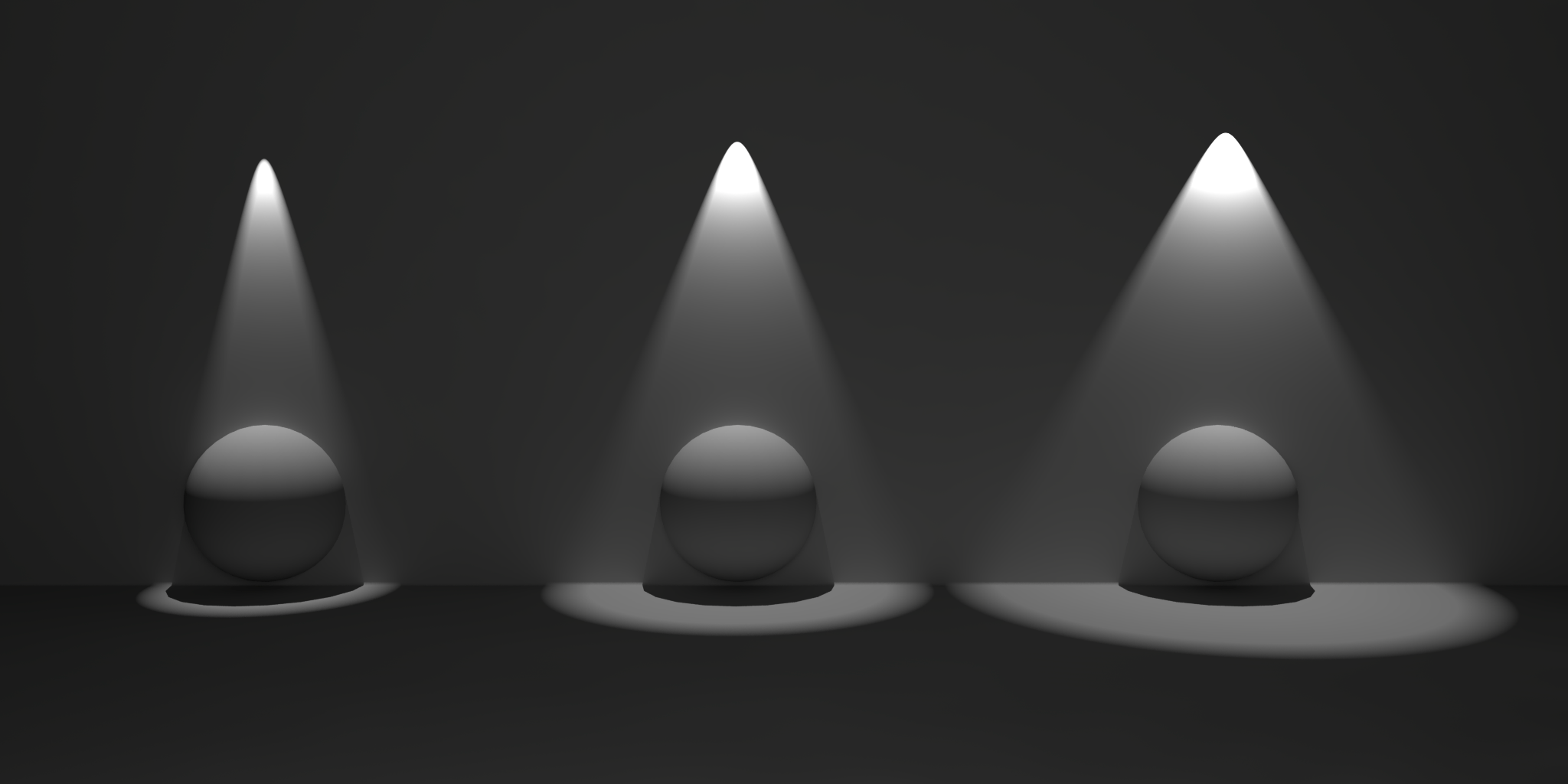
This is only accessable for a Spot light and specifies the angle of the spot light cone.
Below shows three physical lights set to 'spot' with cone angle values smallest on the left to largest on the right:
This is only available for a Spot and specifies the angle over which light falls off at the edge of the spot light cone. Smaller values will produce a sharper edge.
Below shows three Spot lights with Falloff Angle values smallest on the left to largest on the right:
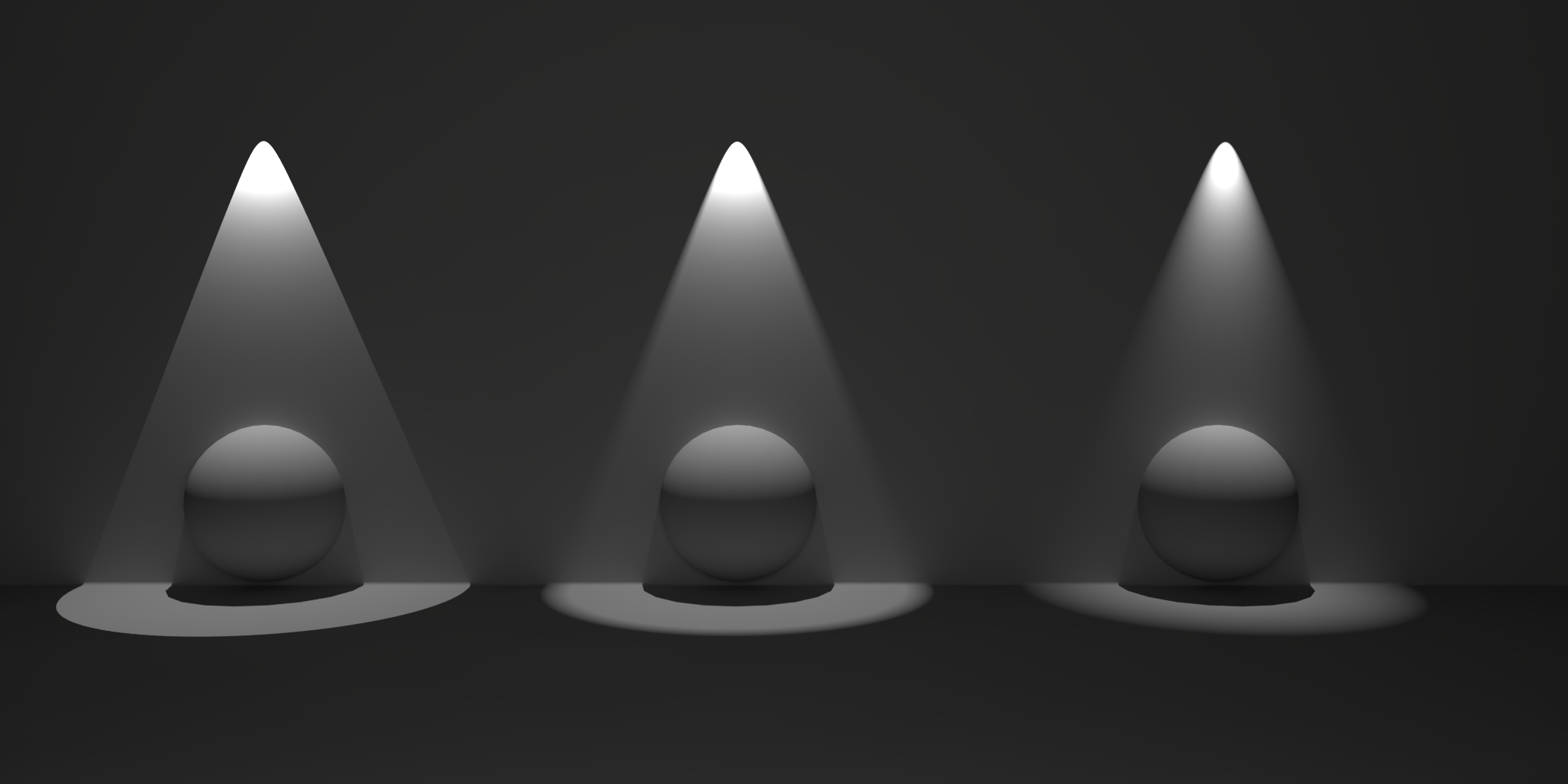
This is only available for a Spot and changes the light intensity distribution within the light cone. With increasing values the light intensity will decrease faster between the center and the outer border of the spot cone. The images below show a spot aiming straight at a wall. The only difference between the images is the value for the Falloff Curve.
|
|
|
| Falloff Curve: 0.0 | 50.0 |
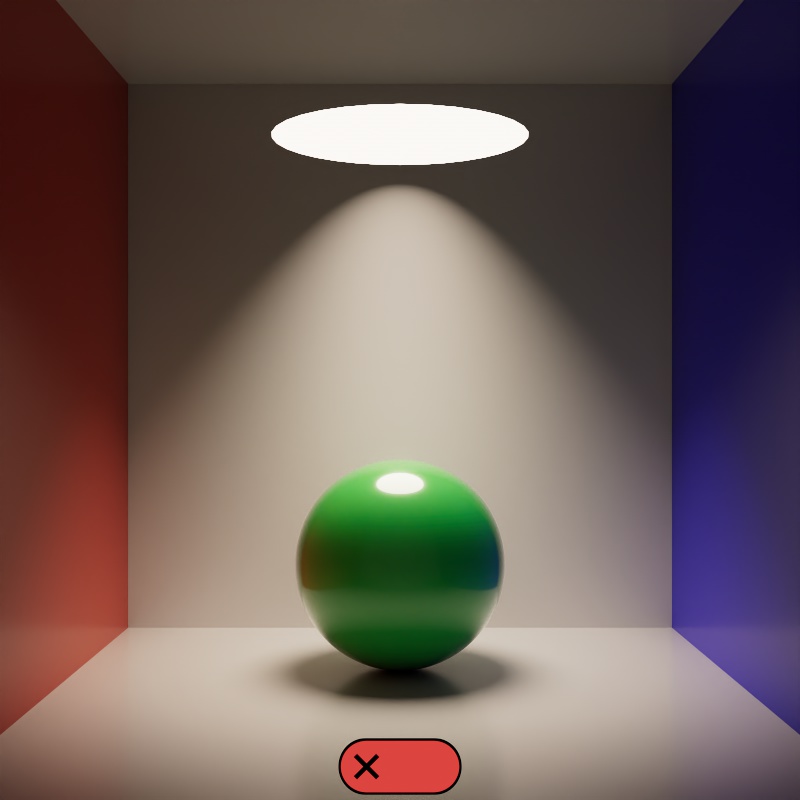
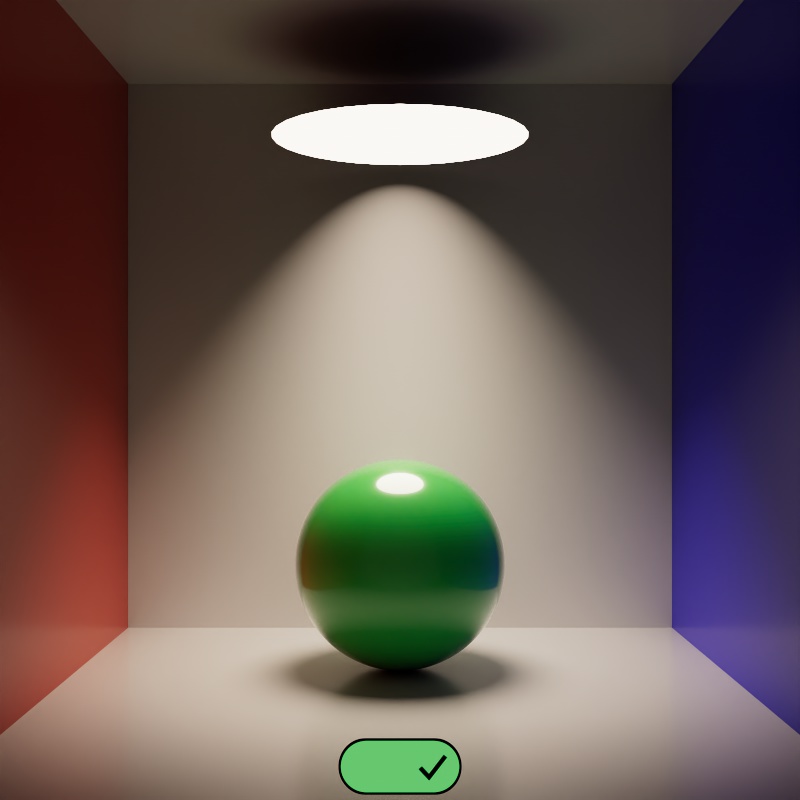
When enabled, a light blocks rays in the same way as a physical object — allowing a light to cast shadows based off of its size and shape. When disabled, by default, a light does not block rays.
Note, this option has no bearing on a lights direct visibility to the camera — visibility is controlled by the Camera slider in the ray contribution section.
In the example below, notice how the light casts a shadow on the ceiling when Block Rays is enabled — this is from global illumination rays being occluded by the light. When disabled, no rays are blocked so the global illumination rays fill this area with light.

|

|
| Blocks Rays: Disabled (default) | Enabled |
Enables bi-directional lighting such that light is emitted on both sides of the shape. Only valid for Rectangle and Disc area shapes.
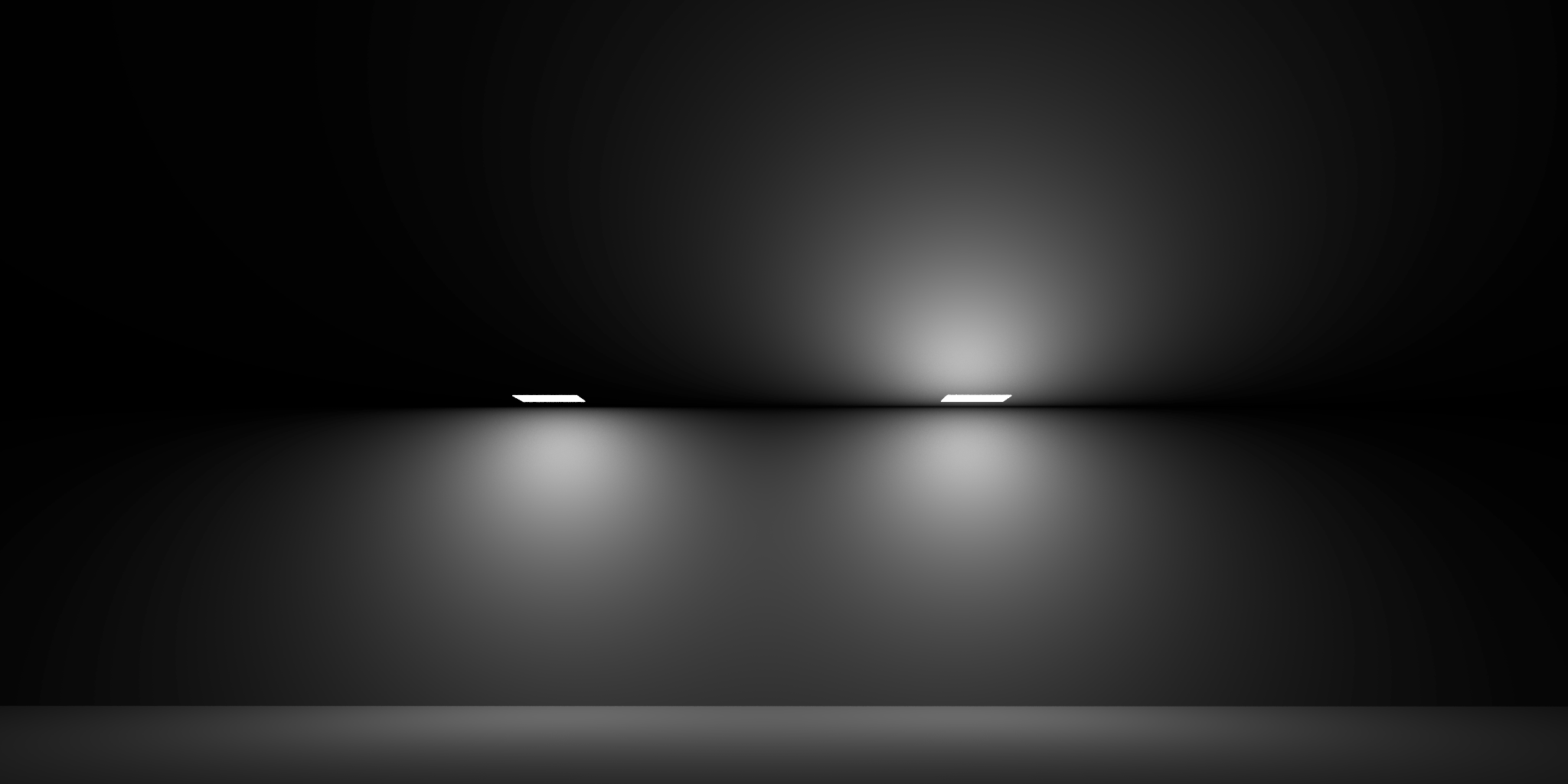

The image shows a rectangular light with Bi-directional disabled on the left and enabled on the right.Note how the light comes out of both sides with bi-directional enabled.
Removes the area of the light from the lighting calculation. Enabling this option prevents the light intensity from changing when the size of the light changes.
Only applicable for Area Lights
Controls the base opacity of the area light.
The total light opacity is the result of the opacity value, opacity texture, and an alpha channel (if present and enabled) from the light's color texture multiplied together.
Only applicable for Area Lights
Controls the opacity of an area light from a grey scale texture. Dark colors reduce the opacity while bright colors increase the opacity.
Only applicable for Area Lights
If texture used to control the light's color has an alpha channel, enabling this option will use the alpha channel to control opacity in addition to the opacity options above.
Enable or disable shadow casting.
Specifies the transparency of the shadows cast by the light. Smaller values yield darker shadows. The default value of 0 will produce a completely black shadow. A value of 1 will produce no shadow at all.
The example below shows how a completely opaque sphere's shadow transparency can be controlled by this light setting.
|
|
| Transparency 0 to 1 |
Specifies edge softness for non-area light shadows. A value of 0 means no softness and will yield sharp shadows. Values above 0 will produce softer shadow edges.
Softness is only available for Redshift Physical and Redshift IES lights.
|
|
| Softness 0 to higher values |
Enables soft gobo texture projection, to match the softness of the shadows, giving the same appearance as if the light was an area light.
Softness Affects Gobo is only available for Point, Spot, Infinite and Photometric IES lights.
This is the name of the AOV light group this light is associated with.
For more information on Light Groups and how to set them up and use them please see here.
Specifies whether the light can illuminate 'Matte Shadow' surfaces (see Matte Shadow Catcher shader).
Matte Shadow Illuminator is not available for Dome, Portal and Physical Sun lights.
This option allows you to control how specular reflections are affected by rough/refractive objects that block the light and whether or not the light rays bend as they pass through. Prior to 2.6.10 this option was not available and the light rays would never bend. Specular ray bending is an important effect for rendering realistic-looking glass and lenses.
This effect is available only for area lights and dome lights. Spot and IES lights can not be seen through bent rays because their source is infinitesimally small.
Care must be taken when using 'Always', as this can disable Multiple Importance Sampling, which is a crucial technique for getting clean renders for rough surfaces.
Light/Shadow linking is not available for specular rays that have been bent.
This option lets you override the maximum trace depth for GI rays on a per-light basis.

|
The contribution parameters covered below control how much a light is able to affect each shading component. The ability to control the intensity of each component offers creative flexibility, each can be raised or lowered and even completely disabled.
For physically correct results all contribution values should be left at 1 so the contribution of each shading component is equal and it matches a light's overall intensity. A value of 1 is indicated by a blue pole at the center of the bar in the examples below, when the bar is to the left of the pole then the output is lower than physically accurate and when the bar is to the right the output is greater than physically accurate.
The example scene in this section features a Cornell Box with a bust from Three D Scans that is separated into pieces with different materials to illustrate the impact a light has on each shading component. The components and materials used in the scene are:
Camera: An additional light used to demonstrate camera visibility and transmissive effects where relevant.
This light uses an HDRI texture from AmbientCG.com.
Diffuse: A green Standard material with reflections.
Reflection: A fully metallic Standard material with diamond plate bump mapping and no diffuse component.
Transmission: A fully transmissive Standard material with reflections.
Single Scattering: A pink transmissive Standard material with single scattering and reflections.
Multiple Scattering: A teal sub surface scattering Standard material with reflections and a very subtle diffuse component.
Volume: A blue Standard Volume material with no emission.
Global Illumination: The Cornell box demonstrates bounce lighting in shadow regions where no direct lighting is cast.
Toon Diffuse, Toon Reflection, Toon Rim: A toon material with a green diffuse component and a sine wave pattern, a white reflection component with a half tone dot pattern, and a light blue rim component.
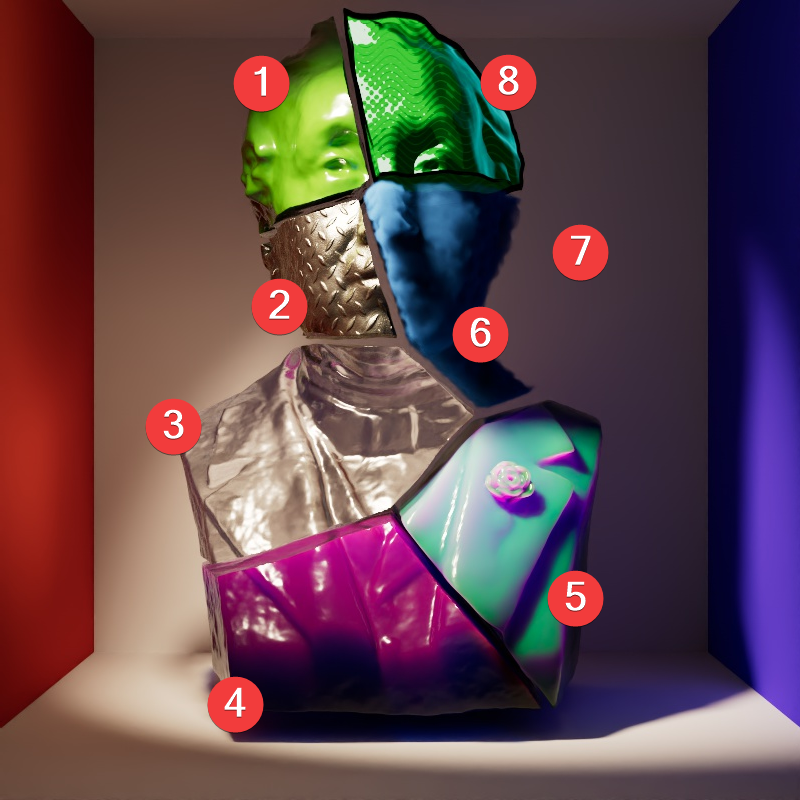

|
| Contribution Sections |
Only available for area lights and dome lights.
Scales the visibility of the light to camera rays. Lower values dim the visible appearance of the light to the camera while higher values make the light appear brighter. A value of 0 makes the light appear invisible to the camera.
Note that this does not affect the contribution of a light on any materials or objects in the scene, it only affects the direct visibility to the camera.
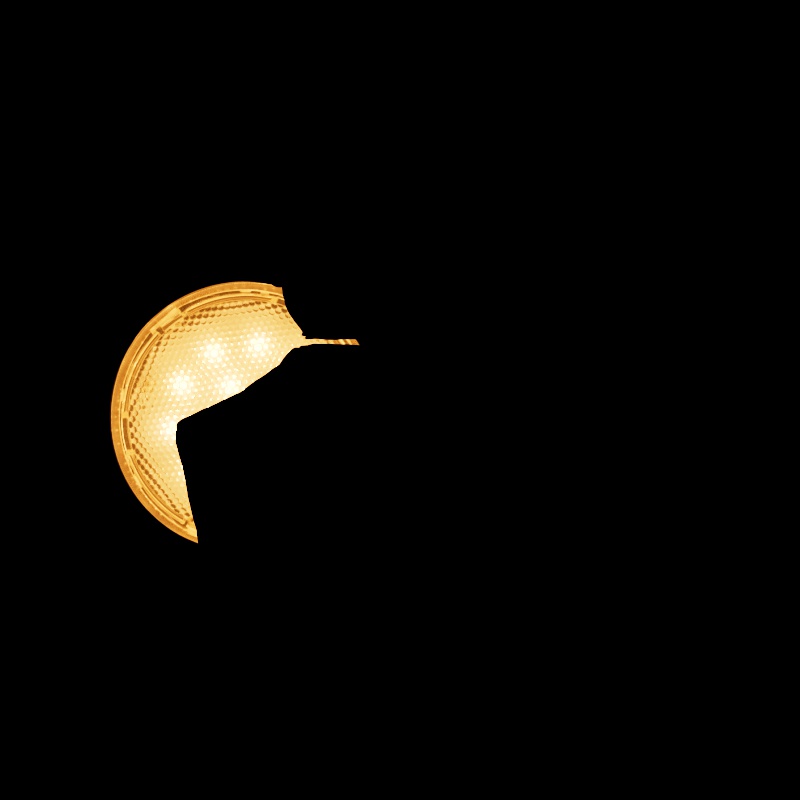

|
||
| Camera: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 Blocked Rays: Enabled |
Camera: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 Blocked Rays: Disabled |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of light for diffuse shading. Diffuse shading is generally responsible for the base color shading of most materials.
Note that this affects global illumination intensity as well.
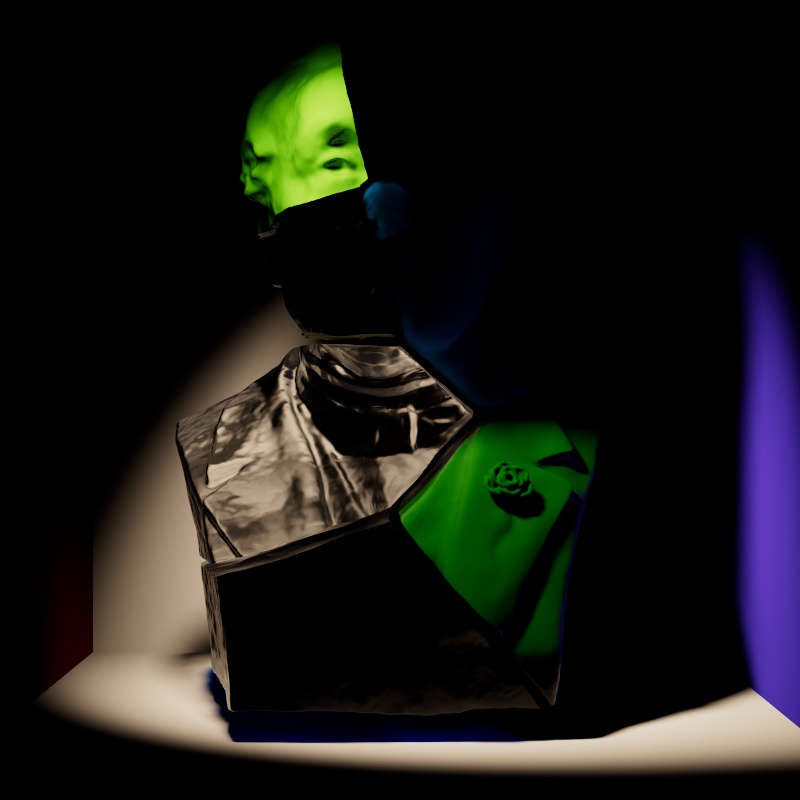

|
|
| Diffuse: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference with GI disabled) |
Scales the intensity of light for specular reflections, the direct reflections of a light source.
Note that reflections of other objects are still seen in reflective materials even with a reflection contribution value of 0. In the example below, the metallic material with diamond plating is mostly heavily affected because it has no other shading component besides reflection, however, the specular highlights on the diffuse material, transmissive material, single scattering material, and multiple subsurface scattering material are affected as well.
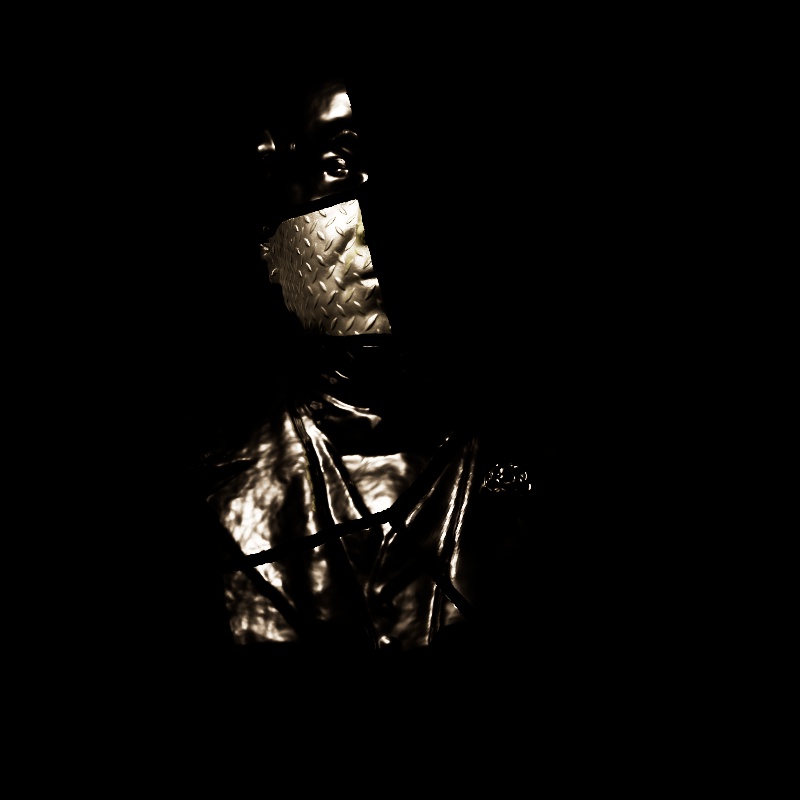

|
|
| Reflection: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of a light as seen through a transmissive / refractive material. This can be thought of as the visibility of a light in a transmissive material.
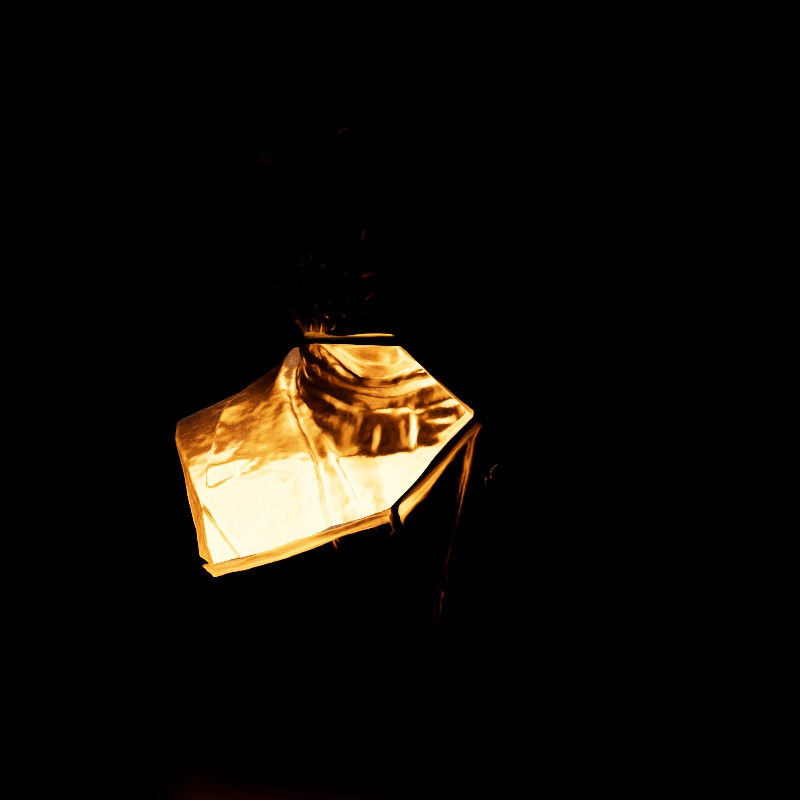

|
||
| Transmission: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 Block Rays: Enabled |
0 - 2 1 Disabled |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Note that a light can be visible in transmissive materials even when the Camera contribution is set to 0 — making the light appear invisible to the camera but still visible in transmissive materials. In this example the light has Block Rays enabled so the light casts shadows even when Camera is set to 0.
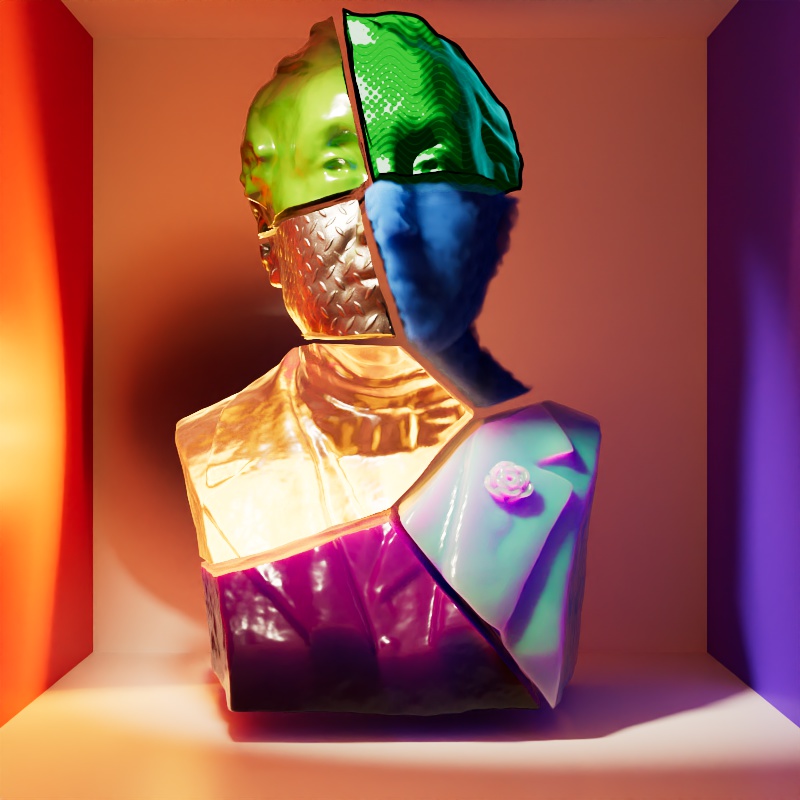

|
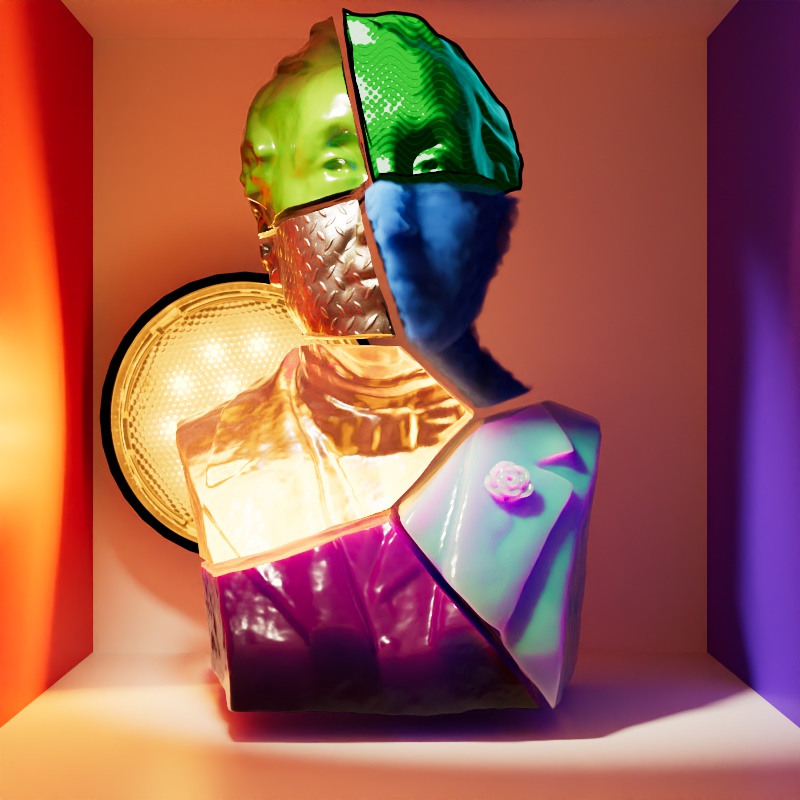

|
| Transmission: 1 Camera: 0 |
1 1 |
Scales the intensity of light for single scattering. Single scattering simulates microscopic particulate suspended in a medium and is part of the Transmission controls of a Standard Material — this is similar to multiple subsurface scattering but is better suited to thinner volumes.
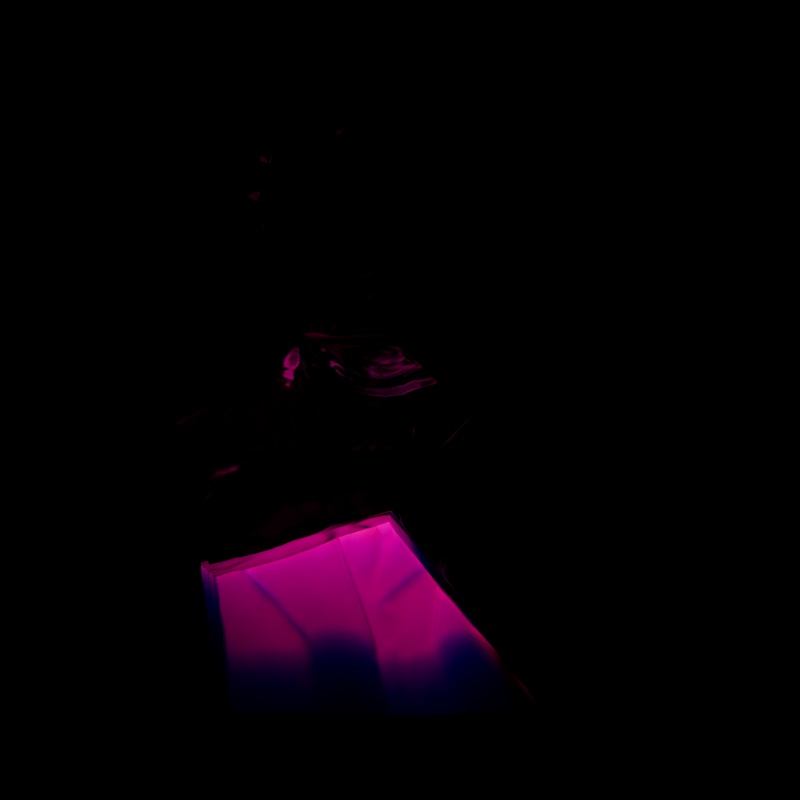

|
|
| Single Scattering: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of the light when seen through sub-surface multiple scattered materials.

|
|
| Multiple Scattering: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of a light's global illumination contribution.
Global Illumination requires Diffuse contribution, this is because global illumination simulates the secondary bounces that only occur after the first bounce of light which is what diffuse contribution represents.
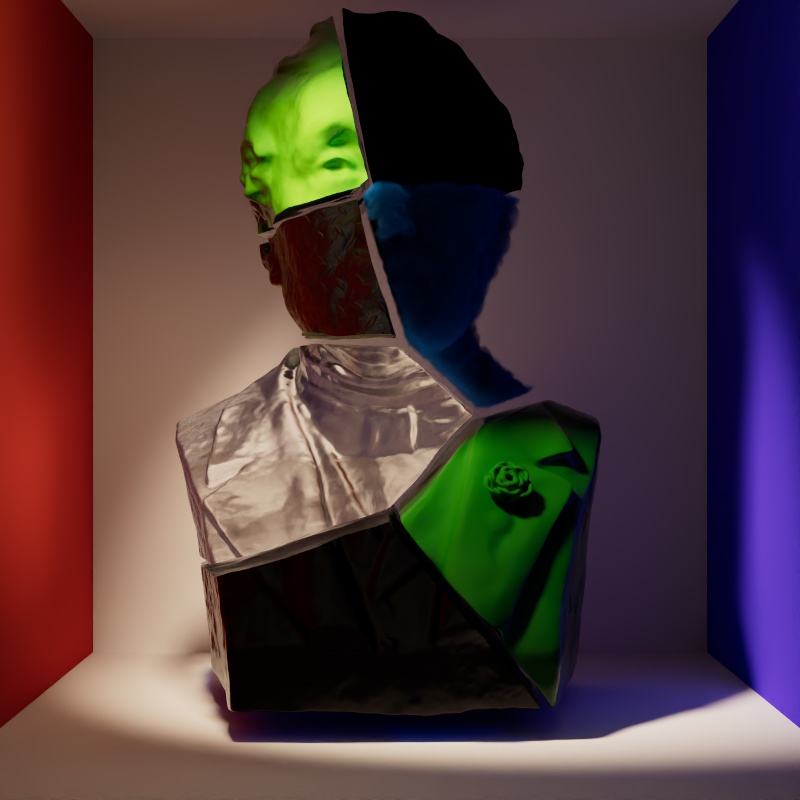

|
|
| Global Illumination: 0 - 2 Diffuse: 1 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of a light's volume contribution, this affects the scattering component of a volume material and environmental fog. A value of 0 disables volume contribution.
In the example below, a blue volume is illuminated by the light and the scene is demoed with and without environment fog.
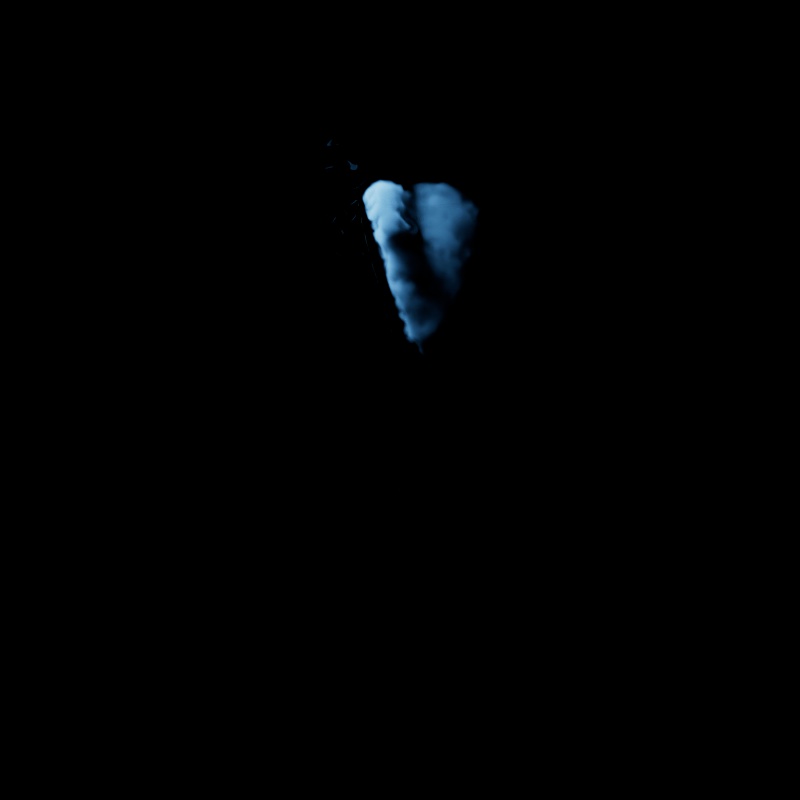
|
||
| Volume: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 Without Environment Fog |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
0 - 2 1 With Environment Fog |
Scales the intensity of a light's Toon Diffuse contribution. A value of 0 disables the effect.
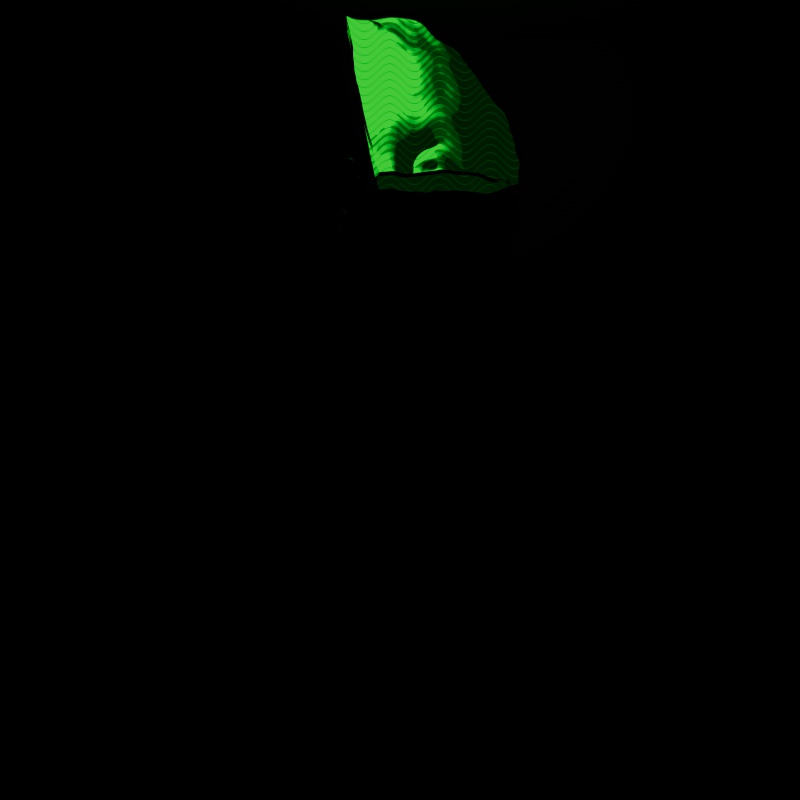

|
|
| Toon Diffuse: 0 - 2 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Scales the intensity of a light's Toon Reflection contribution. A value of 0 disables the effect.
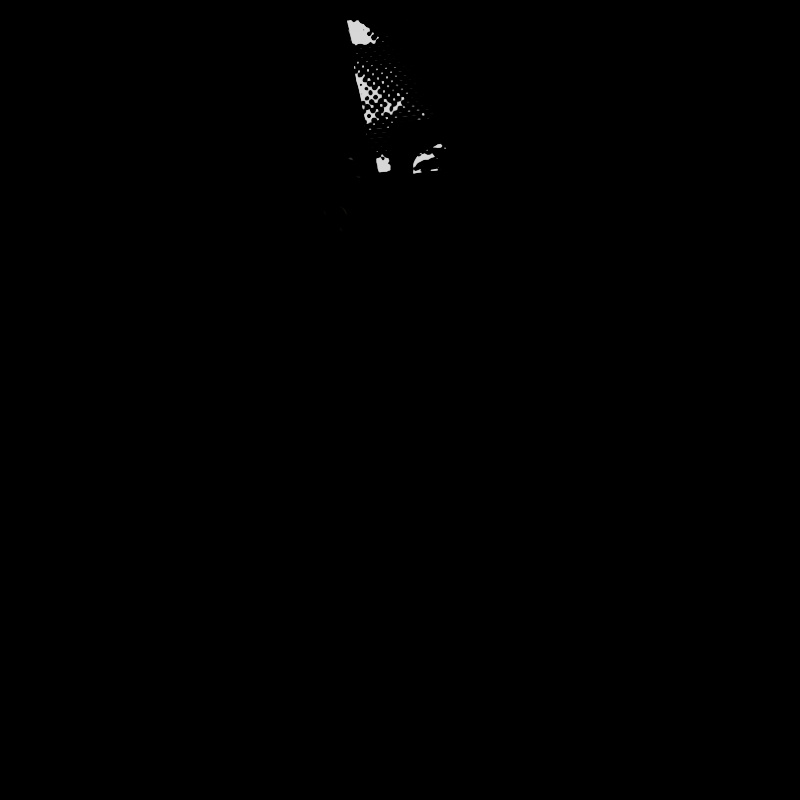

|
|
| Toon Reflection: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
Only available for point, spot, and infinite lights.
Scales the intensity of a light's Toon Rim contribution. A value of 0 disables the effect.
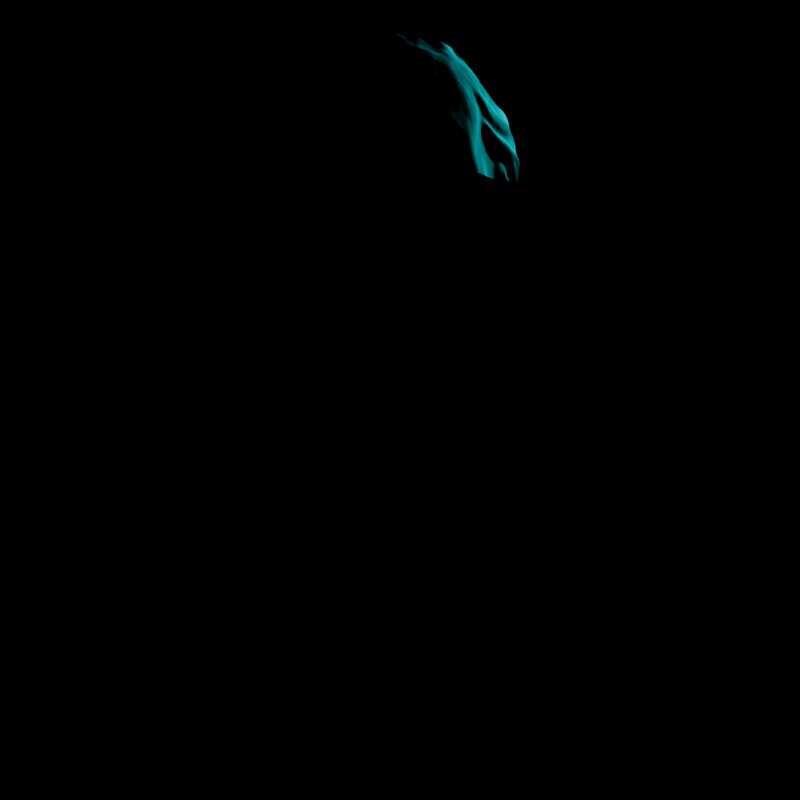

|
|
| Toon Rim: 0 - 2 Other Contribution Types: 1 |
1 0 (Isolated for Reference) |
By default, all Redshift lights start in a Casts Caustics mode called "Render Settings". In this mode, a light's caustic capabilities are controlled by the "Light Casts Caustics" parameter found in the Caustics tab of the Render Settings. This allows you to easily control all lights in a scene from the Render Settings, making caustics much more simple to set up and control.
When Casts Caustics is set to "Render Settings" the default behavior of lights is:
When Casts Caustics is set to "On":
When Casts Caustics is set to "Off":
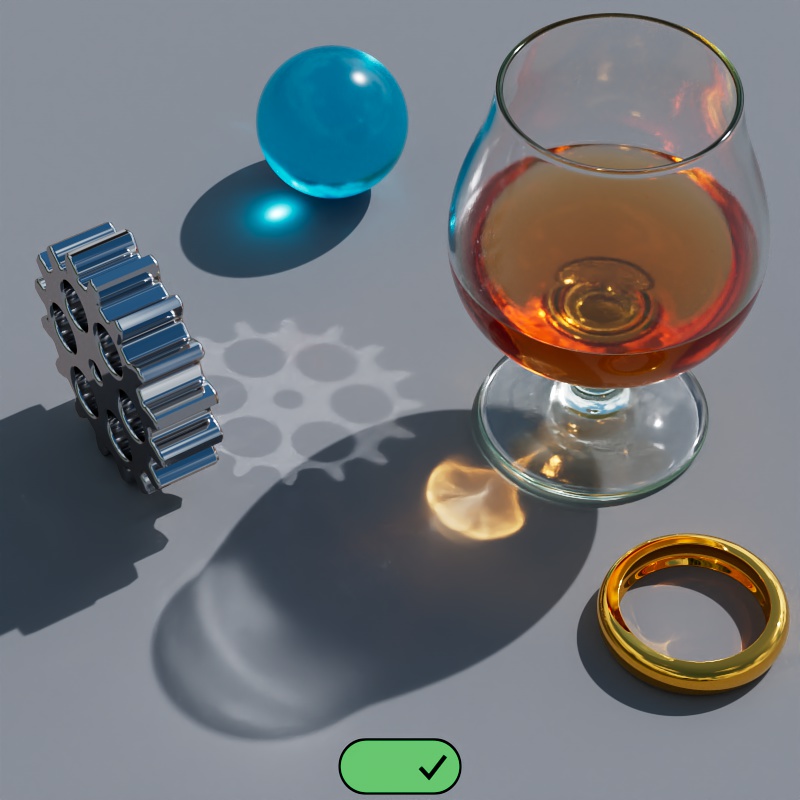

|
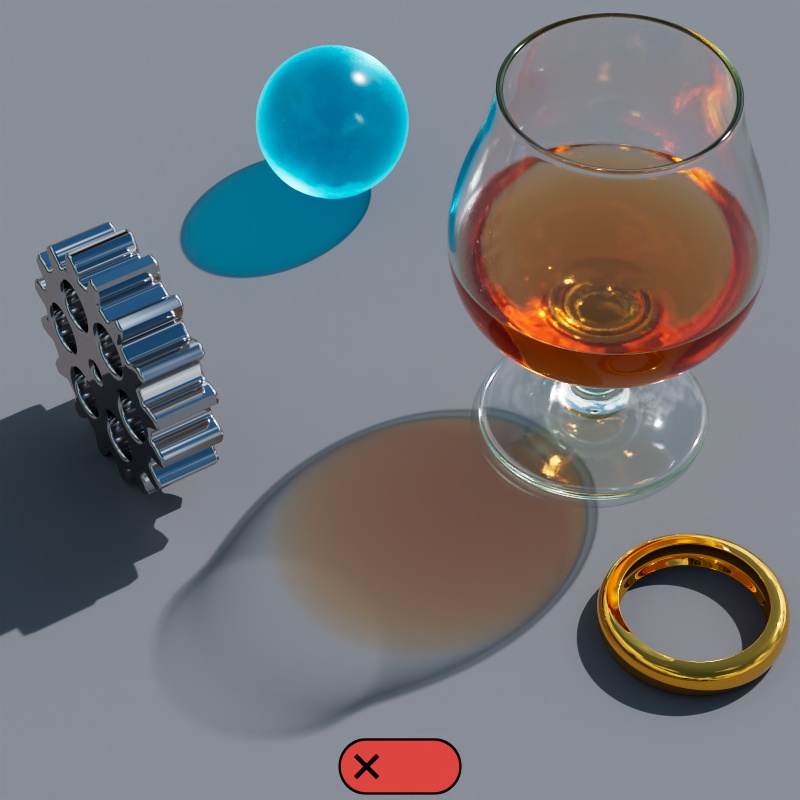

|
| Casts Caustics: On | Off |
Only editable when Casts Caustic is set to "On."
Casts Refraction Caustics must be enabled on an object for this option to have any effect.
When enabled, Transmission Shadow Opacity is set to 1 for Standard Materials that are lit by any light with this option enabled. This ensures that a transmissive object's shadow is appropriately dark so that it can be lit up by the more realistic caustics.
Controls the brightness of the caustics as a multiplier relative to the intensity of the light. For the most realistic look use a value of 1 for caustics that match the intensity of the light. Increasing this value results in brighter caustics. A value of 0 can be used to effectively disable caustics for the light but Override Refraction Shadows will remain in effect, resulting in opaque shadows for transmissive materials.
Controls the number of photons cast for the light. This is determined by multiplying the Photon Multiplier value by the "Num Photons" value found in the Photon Caustics Render Settings.
For example, if Num Photons is 10,000 and the Photon Multiplier is set to 1.5 then the light will cast 15,000 photons. If the Photon Multiplier were set to 3 then it would cast 30,000 photons.
In this tab, objects-specific lighting behavior can be specified.
You can find more specific examples about using these settings for Light Linking and Shadow Linking on this page.
Specifies whether the objects in the list should be excluding or included with respect to the light settings.
The list of objects that should be affected (in Include Mode) or not affected (in Exclude mode). For each object in the list the light behavior can modified to receive light, receive shadows, and to affect the object's children.