Image Formats
The following image formats can be loaded (e.g., as a texture in a material) or exported (e.g., as a rendered image):
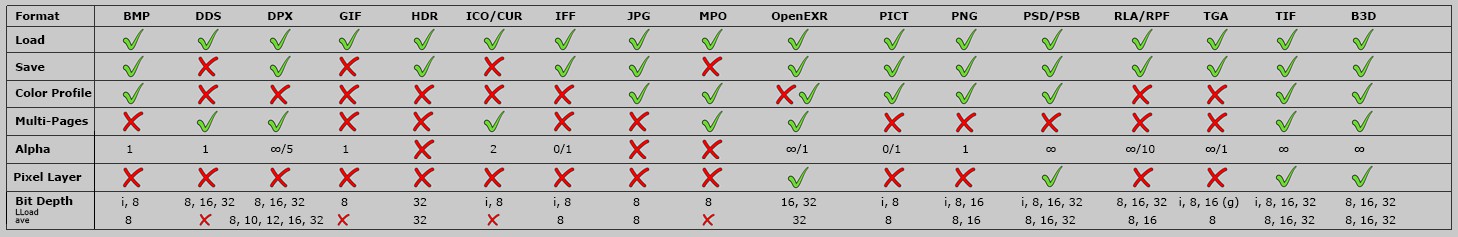 The various image formats and their properties. Multi-Pages is only for import; if multiple entries exist, these are for loading or saving; "i" for bit depth represents indexed colors.
The various image formats and their properties. Multi-Pages is only for import; if multiple entries exist, these are for loading or saving; "i" for bit depth represents indexed colors.
As the table shows, the TIFF format offers the greatest flexibility, which is why this is the most widely used image format in production pipelines (also because it can be compressed loss-free).
Image formats and maximum resolutions
Cinema 4D can render images with a maximum resolution of 128,000 x 128,000 pixels. However, not all image or video formats can handle this large resolution.
The following formats are affected:
- BMP, IFF, TGA, AVI: 32000 x 32000 pixels
- PSD: 30000 x 30000 pixels
- JPG: 65000 x 65000
- PICT: 4095 x 4095
- RLA, RPF: 16000 x 16000
- TIFF unrestricted, but TIFF with layers (PSD) are restricted to 30,000 x 30,000 pixels.
The following formats are not affected:
- DPX
- PNG
- PSB
- HDR
- EXR
- B3D
Miscellaneous
The following list includes images formats for which a lot of information is supplied or that offer options when saved from Cinema 4D (e.g., for compression), which are then described.
TIFF
Save options
- Byte Order: This is a setting that dates back to the "Middle Ages" of computer graphics. This setting was used to define the platform on which the file was to be opened. These days most programs can handle either setting.
- Compression: If None is selected, no compression will take place. Pack Bits and LZW are loss-free compression processes and JPEG is not loss-free.
IFF
The modes EHB, HAM-6 and HAM-8 are supported.
BMP
Save Options
Bitmap Info Header: You can select from:
- V3: the file contains only RGB info.
- V4: in addition to the RGB info, alpha channels can also be included.
- V5: like V4, only that color profiles are included (which, however, are not evaluated by many programs).
JPEG
Save Options
Quality: Defines the JPEG quality.
B3D
BodyPaint 3D proprietory image format. Saves textures, including all layers, layer masks and alpha channels.
RLA/RPF
The RPF format is a further development of the RLA format. Both formats add numerous channels to the rendered image that can be edited in compositing programs.
Save Options
Depending on which options are enabled, corresponding information will be written into the file (RLA has fewer options than the RPF format; functions of the same name work identically).
- Subpixel Weight: Information about sub-pixel color.
- Z: This channel contains information about the camera's distance from the object and makes it possible to calculate depth of field effects.
- Material ID: Information about effect channels and materials.
- Object Buffer: Information about the G Buffer.
- UV: Information about UV coordinates so subsequently created textures can be mapped correctly.
- Normal: Information about the orientation of objects and textures.
- Subpixel Mask: Information about which sub-pixels belong to which objects
- Abdecdung: Antialiasing information regarding object edges.
- Object ID: Lets objects be assigned explicitly.
- Color: The object's actual color only. No transparencies, no reflections.
- Transparency: Transparency information for the object.
OpenEXR
A HDR image for mat that can be saved with either 16 (float comma) or 32-bit (float comma/integer) per color channel. OpenEXR is the more current format compared to other commonly used HDR formats (Radiance (HDR)). Furthermore, OpenEXR can contain any number of channels.
HDR formats are well-suited for compositing or as Image-Based Lighting (lighting via Global Illumination). See also Color Depth.
Save Options
Comperssion Method: You can select from a range of loss-free or lossy compression methods.
16-bit Float Comma: Saves in a special, less precise float comma format that can be edited faster.
Layer Numbering: Disable this option of you don't want to use the Cinema 4D OpenEXR layer numbering system (_0001, _0002, etc.).
Radiance (HDR)
This is the normal HDR image format. Even though this is labeled as 32-bit in the table above, this is not quite correct. HDR tricks a little and uses 8 bits per color channel plus a common exponent. When saving, use one of the other real 32-bit formats.
PNG
A commonly used graphics format with loss-free compression, i.e., the image size can, depending on the scene, be about half or one-third the size of a TIFF image (PNG does not support CMYK as TIFF does).
Save Options
The Interlaced option can be enabled, which produces a result similar to JPEG: these images will be displayed in their entirety much faster in the browser.
DPX
An image format commonly used in movie production and used in post-production (i.e., for the processing from camera to projector).
The following are not supported when loaded:
- YcbCr files
- RLE images
Save Options
The Planar option can be enabled if required by the software in which the image will subsequently be edited. Internally, the color channels will be saved as a single block.
The Bit Depth setting lets you set a color depth of 10 or 12 bits.
DDS
DDS (Direct Draw Surface) is a Microsoft container image format developed in the course of their DirectX development. It is used in the field of gaming. All DDS formats, including alpha channels, can be read.
The following DDS formats can be loaded into Cinema 4D as described:

Save Options
Compression
Several compression formats are available for DDS images:
- No Compression will generate no compression loss at all.
- DTX1: Maximum compression; should not contain alpha channels.
- DTX3: Medium compression; well-suited for alpha channels that clearly define regions.
- DTX5: Low compression; saves alpha channels that define regions that define regions using grayscale gradients (= best quality).
MipMaps: MipMap technology, which is often used in the gaming industry, that projects textures onto objects in different resolutions depending on the objects’ distance from the camera. Additional lower resolution versions of the original texture are saved, which naturally increases the image file size.
Note that the output resolution has to be higher in multiples of 4 if one of the compression modes is used. Otherwise a warning prompt will appear and the resolution will be set to the next best size.