Motor
![]()
A motor is a simulation element that acts on Rigid Bodies in the Simulate system - or on Soft Bodies in the case of Bullet dynamics - and applies a permanent force or torque.
A motor can therefore be used to drive the wheels of a vehicle, a roller conveyor belt, etc.
In contrast to its angle, the position of a motor is irrelevant. The angle determines the direction of force or torque axis. Both are displayed in the Viewport by a motor visualization.
If necessary, assign the motor to an object so that it aligns itself accordingly (in the case of a car model, for example, to the chassis), as in the following example (see also Connector position) is shown.
Example 1
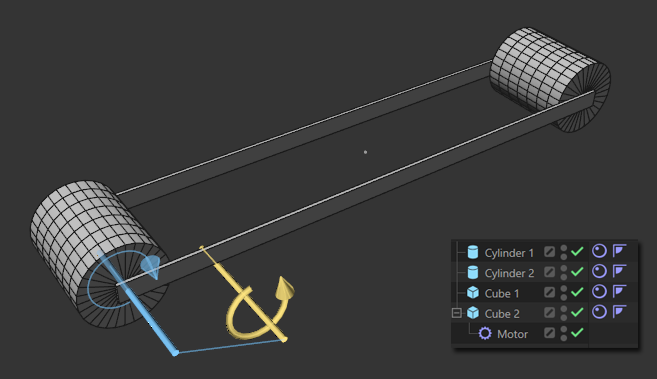 The position of the motor does not matter, but the motor rotation axis should be parallel to the wheel rotation axis. Not shown here are the necessary Connectors.
The position of the motor does not matter, but the motor rotation axis should be parallel to the wheel rotation axis. Not shown here are the necessary Connectors.
When using motors, make sure that driven objects are attached to the rest of the geometry with a Connector(Hinge mode) so that any forces generated can be transferred to them. In the example file above, the vehicle drives autonomously over a Landscape object.
Example 2
In this scene, the balls roll down a track and enter the field of action of a cube field, which in turn regulates a linear motor to lift the balls upwards. An XPresso Falloff Node checks whether the balls are in the field.
