The Simulation System
General
Maxon lays the foundation for a new Dynamics System in Cinema 4D with a new simulation technique. It is a system that can calculate all possible types of physical behavior, such as Rigid/Soft Body, clothing and spline ("rope") simulation. This category also includes the Particle and Pyro system, which can be used to simulate liquids, particle flows, smoke, fire and explosions.
Currently, all tags that can be found in the tag menu Simulation Tags work with the new simulation system:
-
Rigid Bodies are non-deformable, solid objects that follow the laws of gravity and collision. They can be assigned to polygonal objects and polygon generating generators.
-
Cloth, Soft Body, Balloon: can be assigned to polygonal objects and polygon generating generators. Soft Body and Balloon also use the Cloth tag - only with different presets.
-
Rope (the previous Spline Dynamics tag): Can be assigned to splines.
-
Connector: Is assigned to rope or clothing tag-wearing objects and Rigid Bodies and attaches them to each other.
-
Cloth Belt (the previous Belt tag): Is assigned to objects to which the Cloth tag is assigned and connects these objects to other polygonal, non-simulated objects.
-
Rope Belt (the previous Hair Constraint tag): Is assigned to objects to which the Rope tag is assigned and connects these objects with other polygonal, non-simulated objects.
-
Collision: is assigned to non-simulated polygonal objects and polygon-generating Generators that serve as obstacles for the simulation system, i.e., objects can collide with them and do not penetrate them.
-
Pyro: assign polygon or spline objects to serve as Emitters for smoke and fire or as exit areas for explosions. The presets of the parameters provide a generation of smoke and flames.
-
Pyro Fuel: is identical to the Pyro tag, except that here the presets have already been adjusted to create explosions.
Basic information on the Particle simulation system can be found here. This can be used to simulate motion graphics effects, but also, for example, liquids or the flying sparks of a campfire. Particles can also interact with other dynamically simulated elements of the scene.
Hair or fur can also be simulated. The Hair Object is required to create hair on an object. Various Hair Tools are available for cutting and styling hair. Specialized materials are available for rendering hair, for example here as Redshift Nodes.
The new Cloth/Spline simulation system works different than the old system internally. It differs as follows:
-
Old system: The old system is based on impulses and forces that resulted in increases in acceleration and velocity. Masses and springs played large roles.
-
New simulation system: Object points are connected with specific rules (called constraints) depending on the application area. For example, for clothing there are 2 main types of constraints: distance constraints for points connected by mesh edges and bending constraints for adjacent mesh polygons. The former try to keep the point distance constant, the latter the angle between the polygons. Then there are, for example, contact constraints that gently move points (or edges, triangles) that come too close to each other apart in order to avoid penetrations. For each animation image, a Solver has to reconcile all this and position the points accordingly.
This all sounds complicated but in the end it boils down to the following advantages: The new simulation system is faster (can also be calculated on the GPU, for example), more precise, more realistic, more stable and easier to use. Furthermore, the following can be done using the new system:
-
Most Simulation Force objects work.
-
The Tearing function does not require a Cloth Surface object.
-
The object to which the Cloth tag is assigned no longer has to be polygonal and can even be a Generator.
-
For cloning Generators such as array or Cloner object, the Simulate tags belong to this Generator, each clone is then assigned these properties. In ordinary hierarchies, each Child object must be provided with a Simulate tag to participate in the simulation - so here the hierarchy regarding Parent object movements is removed (does not apply to the inheritance of Pyro Emitters to Child objects).
The new simulation system also has - as is generally the case with simulation systems - basic solver settings, which you can find under in the Simulation category. Since these settings naturally have an effect on the simulation's behavior, you can apply different settings to different simulations by using multiple Simulation Scene objects that have the same parameters as the Simulation Scene Settings. The Simulation Scene objects can then be assigned different tags, forces, cloth belts or collision objects. The tags assigned to a Simulation Scene object interact with one another but not with those of another Simulation Scene object.
Tips and tricks for Cloth, Balloon and Soft Body simulations
-
At the beginning of a simulation, there should be no contacts, taking into account the Thickness setting. Otherwise, at the start of the simulation and within a single animation frame, everything that can lead to wrinkling or trembling will be moved out of the contact zone.
-
If movement or deformation changes are too rapid or abrupt, penetrations may occur during collision. Generally speaking, it helps to increase the Substeps setting.
-
With simulation elements that are far away from the world origin, mathematical rounding errors can occur (GPUs calculate with 32 bits - instead of 64 bits with the CPU), which can manifest itself in strange simulation behavior (e.g., different clothing behavior with the same settings, e.g., 2 flags that are far away from each other flutter totally differently). There are a number of options here that provide relief:
- Vary the scene scaling ( Scale Scene...).
Scale Scene...).
- Move the objects involved in the simulation closer to the world origin.
- Especially in connection with the Force object: increase the mass of the simulated elements or the acting forces. It can also help to deactivate Respect Mass in the Force object. -
For example, it is not easy to control physical textile behavior. Textiles are mainly characterized by their stiffness - or lack thereof. Even though the new Simulation System has a Bendiness setting, it is dependent on a series of factors that affect the stiffness. These are e.g., Substeps, Iterations (both simulation project settings), Bendiness, Stretchiness (Cloth or Rope tag) and also the mesh density. Therefore, blanket statements such as "Bendiness = 1 and the object behaves like leather" cannot be made.
-
The mesh density and distribution just mentioned also has a major influence on the behavior of a simulation.
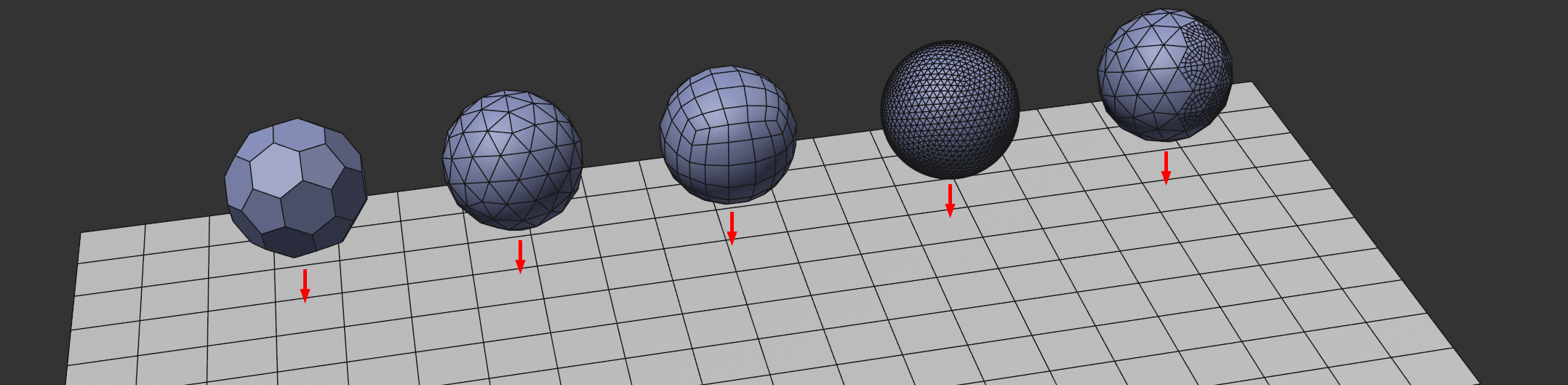
You can see in this image 5 spheres with the same diameter, exactly the same Cloth tag settings, but different meshes. When falling and colliding with the layer, these objects will behave completely differently. The second to last sphere with the dense mesh will deform much more than the others; the sphere on the right side has a much higher mesh density, which causes the mass to be concentrated there. This will make it rotate downwardly and to the right when it hits the floor.
-
You can save calculation time if the simulation works with a low-resolution surrogate (proxy) object, while e.g., the
 Mesh Deformer ensures that the deformation is transferred to a high-resolution "beauty" object. Note also the Simulate Before Generators in the Preferences menu.
Mesh Deformer ensures that the deformation is transferred to a high-resolution "beauty" object. Note also the Simulate Before Generators in the Preferences menu. -
In rare cases, too many collisions may occur at the same time and the simulation will stop with a corresponding error message. In such cases, you should use a lower resolution for objects involved in the collision (or let lower-resolution proxy objects collide). Alternatively you can increase the Passes value in the Project Settings - the number of simultaneous collisions will decrease (see also Velocity Clamp).
Limitations)
-
The advantage in speed for the calculation for the graphics card (GPU) is only noticeable if the simulation is complex enough. For smaller scenes in which only a few hundred polygons are used, the CPU can be faster
-
When calculating using the GPU, the start of the simulation may be delayed slightly. During this time, a large amount of data is compiled or loaded into the graphics card memory. This only happens the first time it's started.
-
Simulations will produce different results on different computers. You will also get different results if you calculate the simulation on the CPU or GPU (selected here:Device). Therefore you should always bake/cache the simulations if you require identical results (e.g., when using a render farm). This can be done for the Cloth tag, for example, in the Cache tab.
-
Simulations do not like strong, opposing forces or constraints. This can result in paradoxical forces and movements. A possible solution would be, for example, to reduce acting forces. For example, you can increase strechiness in the connectors. And/or avoid very large masses (and thus too large weight forces).
-
When leaving the scene, the simulation result will be deleted from the memory. The simulation must be calculated again. However, you can bake the simulation to always have it on hand.
-
Note that simulations are deleted from memory when loading or switching to another scene. Have the scene recalculated, if necessary.
- Vary the scene scaling (
 Scale Scene...).
Scale Scene...). - Move the objects involved in the simulation closer to the world origin.
- Especially in connection with the Force object: increase the mass of the simulated elements or the acting forces. It can also help to deactivate Respect Massin the Force object.
.